Installing a gas pipe in the house. Installation of gas pipes in a private house. Connection price and benefits
Approved and put into effect by Decree of the Moscow Government No. 758-PP
1. General Provisions
1.1. The requirements of this standard are aimed at ensuring the safe and efficient functioning of internal gas pipelines and gas equipment of residential buildings.
1.2. This standard applies to the design and construction of new, operation and repair of existing in-house gas supply systems for residential buildings built according to standard and individual designs.
1.3. The requirements of this standard are mandatory for fulfillment by: owners and other legal owners of residential buildings; management and (or) organizations servicing residential buildings; organizations - customers/contractors for construction, reconstruction, maintenance and repair.
1.4. This standard was developed by the State Housing Inspectorate of the city of Moscow. 2. Basic concepts.
For the purposes of this standard, the following basic concepts are used:
2.1. Internal gas pipeline (also known as intra-house gas pipeline) is a gas pipeline laid inside a building from the place of its primary intersection of building structures to the point of connection of gas appliances and devices that use gas as fuel for cooking, hot water supply, and decentralized heating.
2.2. In-house gas equipment - technical products of full factory readiness: gas meters; pipeline shut-off valves; gas appliances and apparatus.
2.3. Gas appliances and appliances are household gas appliances that use gas as fuel for cooking, hot water supply and decentralized heating.
2.4. An in-house gas supply system is a unified system consisting of an internal gas pipeline and in-house gas equipment installed on it.
2.5. A chimney is a structural element of a building designed to remove gas combustion products to the external environment from household gas appliances used for hot water supply and heating.
2.6. Cleaner organizations are enterprises that carry out maintenance and major repairs of chimneys.
3. Requirements for intra-house gas supply systems of residential buildings.
3.1. The design, construction, reconstruction and repair of gas supply systems are carried out by specialized organizations in accordance with the requirements of building codes and standards.
3.2. The need for repairs of internal gas pipelines, gas equipment of residential buildings and chimneys is determined in the prescribed manner based on the results of an inspection of their technical condition and taking into account the standard service life.
3.3. Gas pipeline entries into residential buildings must be provided in non-residential premises accessible for inspection and repair of gas pipelines. It is not allowed to enter gas pipelines into basements, elevator rooms, ventilation chambers and shafts, waste disposal rooms, warehouses, rooms classified as explosion and fire hazard categories "A" and "B", as well as into rooms removed from the housing stock. All basement gas pipelines located in residential buildings in the city must be placed on the facades of buildings.
3.4. Gas pipelines where they pass through the external walls of residential buildings are enclosed in cases. The space between the gas pipeline and the casing is sealed to the full thickness of the wall being crossed. The end of the case is sealed with elastic material.
3.5. Shut-off devices are installed for gas risers, as a rule, on wall-mounted gas pipelines of residential buildings, at a distance of at least 0.5 meters from door and window openings, as well as in front of each gas appliance.
3.6. Intra-house gas pipelines are laid through non-residential premises of apartments.
3.7. Laying gas pipelines is not allowed: in basements; through ventilation shafts and chimneys, elevator shafts and staircases, waste disposal rooms; through rooms where the gas pipeline may be subject to corrosion; in places where gas pipelines may be washed by combustion products or come into contact with heated metal; in premises removed from the housing stock; by crossing ventilation grilles, window and door openings.
3.8. Installation of gas pipelines is carried out in accordance with the project after arrangement of interfloor ceilings, walls, floor coverings and plastering of walls in kitchens, inspection and cleaning of chimneys and ventilation ducts.
3.9. Gas pipelines inside a residential building are laid openly. It is not allowed to cover the gas pipeline with a false wall. When installing gas pipelines, measures are taken to prevent clogging of the pipe cavity. At the intersections of the electrical wire and cable with the gas pipeline, the clear distance between them must be at least 100 mm, and for parallel installation - at least 400 mm.
3.10. The distance from gas pipelines and pipelines for other purposes should be taken from the condition of ensuring the possibility of installation, inspection, and repair of gas pipelines and the fittings installed on them. The distance from the gas pipeline to the sink must be at least 300 mm.
3.11. Deviation of risers and straight sections from the design position is allowed no more than 2 mm per 1 m of gas pipeline length, unless other standards are justified by the design. All branches must be made at an angle of 90 degrees.
3.12. It is prohibited to weld branch pipes at the locations of circumferential welds. When inserting branches with a diameter of up to 50 mm, the distance from the seams of the welded gas pipelines to the circumferential seams of the main gas pipeline must be at least 50 mm. Assembly for welding of pipes is carried out with offset seams at the joining points: - for gas pipelines with a diameter of up to 50 mm - 15 mm; - for gas pipelines with a diameter from 50 to 100 mm - 50 mm.
3.13. The distance from the weld to the end of the gas pipeline thread must be at least 100 mm. Sealing welded and threaded connections of gas pipelines and fittings into walls, ceilings and cases is prohibited. Hidden work (laying a gas pipeline through walls, in a case, through a ceiling) is carried out step by step. The distance from the weld to the case must be at least 50 mm. The welded joint of a gas pipeline with a diameter of up to 200 mm must be located at least 200 mm from the edge of the support.
3.14. When welding shaped parts, assemblies, and fittings into a gas pipeline, the integrity of the welded elements with the gas pipeline is ensured. Distortions in vertical and horizontal planes are prohibited. It is prohibited to install pipes and bent parts made from pipes that have dents, folds (wrinkles), cracks, slag inclusions in the seams, or burrs. Ovality of bent parts is allowed within no more than 10% of the gas pipeline diameter. It is prohibited to construct a straight section of the outlet, the length of which is less than the diameter of the pipe.
3.15. The laying of gas pipelines in places where people pass is carried out at a height of at least 2.2 m from the floor to the bottom of the gas pipeline.
3.16. The gas pipeline is secured to the walls using brackets, clamps, and hooks in accordance with the requirements of the project. Fastening the gas pipeline riser in houses with gas stoves is carried out on the 1st, 4th, 8th floors, in houses with gas water heaters on the 1st, 4th, 5th floors and in all cases on the top floor. Attaching the gas pipeline lower to the device is carried out in front of each gas device. The distances between the support fastenings of gas pipelines are determined in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.12-86.
3.17. Vertical gas pipelines at intersections of building structures are laid in cases. The space between the gas pipeline and the case is sealed with tarred tow, rubber bushings or other elastic material. The protrusion of the end of the casing above the floor must be at least 3 cm, and its diameter is taken from the condition that the annular gap between the gas pipeline and the casing is at least 5 mm for gas pipelines with a diameter of no more than 32 mm and at least 10 mm for gas pipelines of larger diameter.
3.18. Internal gas pipelines, including sections laid in casings, are painted. Waterproof paints and varnishes are used for painting.
3.19. When installing a gas pipeline inside a residential building, pipes are used that are specially designed for laying a gas pipeline, have a metal design and a certificate of conformity. Pipe connections should be made by welding. Threaded connections are allowed only in places where shut-off valves and gas appliances are installed.
3.20. To seal threaded connections, flax strands are used in accordance with GOST 10330-76, impregnated with red lead in accordance with GOST 19151-73, mixed with drying oil in accordance with GOST 7931-76, as well as fluoroplastic and other sealing materials if they have a passport or certificate from the manufacturer. When installing disconnecting devices, a surge is installed after them. The taps must be installed so that the axis of the tap plug is parallel to the wall; it is prohibited to install the thrust nut towards the wall. When installing gas appliances and connecting them to gas networks, you must comply with the requirements of the project and factory instructions.
3.21. The gas pipeline to the stove can be laid at the level of the connecting fitting. In this case, the shut-off valve is installed at a distance of at least 20 cm to the side of the stove. For overhead wiring, the shut-off valve should be installed on the descent to the slab at a height of 1.5 - 1.6 m from the floor. It is allowed to connect gas appliances to the gas pipeline through a flexible hose that does not have butt joints and has a heat resistance of at least 120 degrees. The service life is established by the passport for the flexible hose, after which the flexible hose must be replaced.
3.22. Sections of gas pipelines that are disconnected during dismantling of gas appliances are cut off, freed from gas and welded tightly. When the gas pipeline is removed from the basement, the inactive basement gas pipeline and sections of the gas pipeline through the ceilings to the switching point are dismantled, and the holes in the floor are sealed. When installing gas pipelines, it is prohibited to use previously installed gas pipes and casings that are subject to dismantling as a casing.
3.23. At all stages of construction, in order to verify the effectiveness of previously performed production controls, inspection controls should be carried out selectively. Based on the results of production and inspection quality control of construction and installation works, measures must be developed to eliminate identified defects, while the requirements of designer supervision of design organizations and state supervision and control bodies operating on the basis of special provisions must also be taken into account.
3.24. Gas stoves in residential buildings are installed in kitchens with a height of at least 2.2 m, which have a window with a window (transom), an exhaust ventilation duct and natural lighting. Gas stoves are installed in kitchens with an internal volume of at least 8 cubic meters. m with a gas stove with 2 burners; 12 cu. m with a gas stove with 3 burners; 15 cu. m with a gas stove with 4 burners.
3.25. In existing residential buildings, the installation of gas stoves is allowed: in kitchens with a height of at least 2.2 m and a volume of at least specified in clause 3.24 in the absence of a ventilation duct and it is impossible to use chimneys as such a duct, but if there is a window with a window or transom at the top of the window; in private corridors, if there is a window in the corridor with a window or transom in the upper part of the window, the passage between the slab and the opposite wall must be at least 1 m wide, the walls and ceilings of the corridors made of flammable materials must be plastered, and the living quarters must be separated from the corridor by dense partitions with a door; in kitchens with sloping ceilings with a height in the middle part of at least 2 m, gas equipment is installed in that part of the kitchen where the height is at least 2.2 m.
3.26. In existing residential buildings, it is allowed to install gas stoves in premises that meet the requirements of paragraphs. 3.24 or 3.25, but having a height of less than 2.2 m up to 2 m inclusive, if these premises have a volume of at least 1.25 times the standard. Moreover, in houses that do not have a dedicated kitchen, the volume of the room where the gas stove is installed must be 2 times larger than that specified in clause 3.24.
3.27. The possibility of installing gas stoves, heating and other devices in buildings located outside a residential building is decided by the design organization and the operational organization of the gas industry. At the same time, the premises in which the installation of gas appliances is planned must comply with the requirements for the premises of residential buildings where the placement of such appliances is allowed.
3.28. Wooden unplastered walls and walls made of other combustible materials in the places where the slabs are installed are insulated with non-combustible materials: plaster, roofing steel on an asbestos sheet with a thickness of at least 3 mm, etc. The insulation must protrude beyond the dimensions of the slab by 10 cm on each side and at least 80 cm on top . The distance from the stove to the walls of the room insulated with non-combustible materials must be at least 7 cm; the distance between the slab and the opposite wall must be at least 1 m.
3.29. For hot water supply, instantaneous and capacitive gas water heaters are used, and for heating - capacitive gas water heaters, small heating boilers or other heating devices designed to operate on gas fuel.
3.30. The number of floors of residential buildings in which the specified gas appliances and apparatus are installed should be provided in accordance with SNiP 31-01-2003 “Residential multi-apartment buildings”.
3.31. It is allowed to convert small-sized (small-sized) factory-made heating boilers intended for solid or liquid fuels to gas fuel. Heating installations converted to gas fuel are equipped with gas burners with automatic safety systems.
3.32. In one room it is not allowed to install more than two capacitive water heaters or two small heating boilers, or two other heating devices.
3.33. The installation of chimneys must comply with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.05-91* “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning” as for heating stoves.
3.34. Water heaters, heating boilers and heating devices are installed in kitchens and non-residential premises intended for their placement and meeting the requirements of paragraphs. 3.40. 3.41.
3.35. Installation of these devices in bathrooms is not permitted. The possibility of moving gas water heaters from bathrooms, in which they were placed in accordance with previously applicable standards, into kitchens or other non-residential premises of a residential building during the reconstruction of a house or gas supply system is decided on a case-by-case basis by the design organization in agreement with gas industry organizations carrying out operation intra-house gas pipeline.
3.36. In existing residential buildings, it is allowed to install gas heating appliances and heating appliances for individual use in the corridors that meet the requirements of paragraphs. 3.40. 3.41. The distance from the protruding parts of gas burners or fittings to the opposite wall must be at least 1 m.
3.37. Gas instantaneous water heaters are installed on walls made of non-combustible materials at a distance of at least 2 cm from the wall, incl. from the side wall. If there are no walls made of non-combustible materials in the room, it is allowed to install the instantaneous water heater on plastered, as well as on walls lined with non-combustible or low-combustible materials at a distance of at least 3 cm from the wall. The surface of fire-resistant walls is insulated with roofing steel over an asbestos sheet with a thickness of at least 3 mm. The insulation should protrude 10 cm beyond the dimensions of the water heater body.
3.38. Gas heating boilers, heating devices and capacitive gas water heaters are installed near walls made of non-combustible materials at a distance of at least 10 cm from the wall. If there are no walls made of non-combustible materials in the room, it is allowed to install the above-mentioned heating devices near the walls, protected in accordance with the instructions of clause 3.28, at a distance of at least 10 cm from the wall.
3.39. The horizontal clear distance between the protruding parts of the instantaneous water heater and the gas stove must be at least 10 cm. When installing in the kitchen a gas stove and a cylinder water heater, a gas stove and a heating boiler or heating device, as well as a gas stove with built-in devices for heating water ( heating, hot water supply) the volume of the kitchen should be 6 cubic meters more than the volume provided for in clause 3.24.
3.40. The room intended to accommodate a gas water heater, as well as a heating boiler or heating apparatus, the combustion products of which are discharged into the chimney, must have a height of at least 2 m. The volume of the room must be at least 7.5 cubic meters. m when installing one device and at least 13.5 cubic meters. m when installing two heating devices.
3.41. The kitchen or room where boilers, appliances and gas water heaters are installed must have a ventilation duct. For air flow, a grille or a gap between the door and the floor with a clear cross-section of at least 0.02 square meters should be provided at the bottom of the door or wall opening into the adjacent room. m.
3.42. It is not allowed to place all gas appliances in the basement floors (basements), and for LPG gas supply - in the basement and ground floors of buildings for any purpose.
3.43. It is allowed to convert heating and heating-cooking furnaces to gas fuel, provided that the furnaces, smoke and ventilation ducts meet the requirements of the standards for the construction of heating furnaces converted to gas fuel, approved in the prescribed manner; gas burners installed in the furnaces of heating and heating-cooking furnaces are equipped with automatic safety systems in accordance with the requirements of GOST 16569-86 "Gas burner devices for heating household furnaces. Technical conditions."
3.44. When installing gasified stoves, their fireboxes must go into non-residential (non-office) premises. In the absence of non-residential (non-office) premises, the fireboxes of gasified stoves may be located on the side of residential (office) premises. In this case, the gas supply to the furnaces should be provided by independent branches, on which, at the point of connection to the gas pipeline, a shut-off device is installed outside the above premises. The premises into which the fireboxes of gasified heating and heating-cooking stoves open must have an exhaust ventilation duct or a window with a window, or a door opening onto a non-residential premises or vestibule. The passage in front of the stove must be at least 1 m.
3.45. For space heating, it is allowed to install gas fireplaces, air heaters and other factory-made appliances with combustion products discharged into the chimney. The gas burners of these devices must be equipped with automatic safety devices. The room in which a gas fireplace or heater is to be installed must have a window with a window and an exhaust ventilation duct. When installing these devices, it is necessary to comply with the requirements provided for in clause 3.38.
3.46. The possibility of using and placement conditions for household gas appliances not specified in this section should be determined taking into account the purpose of the appliances, their thermal load, the need to remove combustion products and other parameters established by this section.
3.47. Foreign-made gas appliances must have warranty cards indicating the addresses and telephone numbers of service centers that carry out their installation, repair and maintenance.
3.48. When transferring residential premises with gas pipelines to non-residential use, the issue of their removal must be resolved at the same time. The location of gas pipelines in non-residential residential buildings is not permitted.
4. Requirements mandatory for persons using gas equipment in residential buildings.
4.1. Persons using household gas appliances and apparatus are obliged to:
4.1.1. When carrying out annual maintenance of gas equipment by specialists of a gas utility company, receive instructions from them on the rules for using gas in everyday life, and observe safety measures when gas appliances are working and not working.
4.1.2. Maintain and keep gas equipment clean. Monitor the operation of gas appliances, chimneys, ventilation, check for the presence of draft before turning on and at the end of operation of gas appliances with the discharge of combustion products into the chimney. Clean the chimney pockets.
4.1.3. When finished using gas, close the taps in front of gas appliances.
4.1.4. If gas equipment malfunctions, call gas company workers.
4.1.5. If you smell gas, immediately stop using gas appliances, turn off the taps at the outlet to the appliances and on the appliances, ventilate the room and call emergency services. Before this, do not light a fire, do not smoke, do not turn on electrical equipment and other electrical appliances.
4.1.6. If you detect the smell of gas in the basement, entrance, or on the street, you must: - inform the gas service and take measures to remove people from the gas-polluted environment, prevent turning on and off electric lighting, the appearance of open flames and sparks; - before the gas service workers arrive, organize ventilation of the room.
4.2. Persons using gas equipment in residential buildings are prohibited from:
4.2.1. Carry out unauthorized gasification in the house, rearrangement, replacement and repair of gas equipment.
4.2.2. Carry out redevelopment of the premises with the presence of gas equipment without coordinating this issue with the relevant organizations.
4.2.3. Use gas appliances when there is no draft in chimneys and ventilation ducts.
4.2.4. Make changes to the design of gas appliances, smoke and ventilation systems, and to the laying of gas pipelines.
4.2.5. Leave operating gas appliances unattended, except for appliances with appropriate automation, allow children and persons who do not control their actions and do not know the rules for using these appliances to use gas appliances.
4.2.6. Use gas equipment and the room where gas appliances are installed for purposes other than their intended purpose. Use gas stoves to heat the room.
4.2.7. Use open fire to detect gas leaks (use soap emulsion for these purposes).
4.2.8. Store flammable, toxic and explosive substances in rooms with gas equipment.
4.2.9. Build up the gas pipeline with walls, panels, wall them up in the walls and seal them with tiles. The gas pipeline must be accessible for inspection and maintenance.
4.2.10. Store empty and filled cylinders with liquefied gases in rooms and basements.
4.2.11. Close the tap on the gas riser.
5. Requirements for the safe operation of chimneys of residential buildings.
5.1. Maintenance and repair of smoke ducts is carried out by specialized organizations of cleaners under contracts with the organization that manages the residential building.
5.2. Chimneys must be dense, separate, vertical, without ledges. It is allowed to slope chimneys from the vertical at an angle of 30 degrees with a horizontal distance of no more than 1 m, while the cross-section of the channel must be maintained along its entire length. The cross-sectional area of the chimney should not be less than the area of the gas appliance pipe connected to the chimney. In existing buildings, it is allowed to connect no more than two water heaters to one chimney, provided that combustion products are introduced into the chimney at different levels, no closer than 75 cm from each other or at the same level with the device for cutting in the chimney to a height of at least 75 cm. The calculation of the chimney should be carried out when two water heaters are operating simultaneously. The intersection of smoke and ventilation ducts with gas pipelines, water pipes, and electrical cables is prohibited.
5.3. Quality control of the repairs made to smoke ducts is the responsibility of housing maintenance organizations.
5.4. Chimney repair work is carried out according to schedules agreed with the contractor.
5.5. Smoke ducts are checked within the following periods: brick - 1 time in 3 months; asbestos-cement, pottery and heat-resistant concrete blocks - once every 12 months. A primary check (for density and isolation, for the absence of blockages and for the presence of draft) is carried out annually in the third quarter during the preparation of houses for winter. In new-built houses, the initial inspection is carried out at the time the house is accepted for use.
5.6. In the period from November to April, it is necessary to inspect the chimney heads in order to prevent them from freezing and blocking, noting the inspection results in a special journal. Control over the implementation of inspections is carried out by the heads of the housing maintenance organization.
5.7. If faulty chimneys are detected, the devices connected to them must be immediately disconnected from the gas supply, and residents are warned against signature of the dangers of using gas water heaters.
5.8. Before starting scheduled chimney repair work, gas appliances connected to them must be turned off by employees of the gas supply company in accordance with the notification received from the contractor.
5.9. Connection of gas appliances after repair of chimneys should be made only after receipt of a report on the technical condition of the chimney by employees of the gas supply company.
5.10. Based on the results of regular, extraordinary and post-repair inspections and cleaning of smoke ducts, acts of the established form are drawn up.
5.11. When performing maintenance:
5.11.1. The technical condition of iron connecting pipes (hereinafter referred to as iron pipes) is checked according to the following parameters: - total length of no more than 3 m in new buildings and no more than 6 m in existing ones; - number of turns - no more than three, with a radius of curvature not less than the diameter of the pipe; - the links must fit tightly into one another along the flow of exhaust gases by at least 0.5 of the pipe diameter; - when connecting to a chimney, the reinforced steel structure should not cross the channel cross-section and have a limiting washer or corrugation; - the height of the vertical section is at least 50 cm, in rooms with a height of 2.7 m - at least 25 cm is allowed; a slope of at least 0.01 (1 cm per linear meter) towards the gas appliance; painting - fire-resistant varnish; - the presence of fire-resistant cutting at the intersection of difficult-to-burn partitions; - distance from reinforced concrete to the ceiling and walls: non-combustible materials - at least 5 cm; from hard-to-burn materials - at least 25 cm.
5.11.2. The presence and compliance with the standards of a “pocket” for collecting garbage in the chimney with a hatch for cleaning is established - at least 25 cm from the bottom edge of the reinforced concrete.
5.11.3. The technical condition of smoke ducts within the attic is monitored: - presence of grout, whitewash and numbering; - the presence of a fire-prevention cutting equal to 50 cm to the building structure made of combustible materials and 38 cm for structures made of non-combustible materials.
5.12. When carrying out repair work and maintenance of chimneys, it is necessary to comply with fire safety requirements.
5.13. When monitoring the technical condition of smoke ducts above the roof, the following are checked: - the condition of the plaster, whitewashing, and ironing of the caps; - the presence of umbrellas and deflectors on chimneys, numbering of smoke channels; - the correct location of the head relative to the roof ridge and nearby structures, trees - the absence of a wind support zone: - 0.5 above the roof ridge when they are located (counting horizontally) no more than 1.5 m from the roof ridge; - level with the roof ridge, if they are 1.5 - 3 m from the roof ridge; - below the ridge of the roof, but not below a straight line drawn from the ridge down at an angle of 10 degrees to the horizon, when located more than 3 m from the ridge. In all cases, the height of the pipe above the adjacent part of the roof must be at least 0.5 m, for houses with a combined roof (flat roof) of at least 2 m.
5.14. The roofs of gasified houses must be equipped with ladders, scaffolding and parapet gratings.
6. The procedure for pre-commissioning tests and acceptance into operation of internal gas pipelines and gas equipment of residential buildings after completion of construction, reconstruction, repair and overhaul of gas supply systems.
6.1. After completion of construction and installation work, control of the work performed is carried out, which includes:
6.1.1. Checking compliance of the laying of gas pipelines and gas equipment with the project and the requirements of regulatory documents. In the event of a forced deviation from the design solution, appropriate changes must be made, agreed upon with the author of the project and the gas supply company.
6.1.2. Testing gas pipelines and gas equipment for strength and tightness. The tests must be carried out by the construction and installation organization in the presence of a representative of the operating organization. The test results should be recorded in the construction passport. Gas equipment, including foreign-made equipment, must be certified and have permission for use from the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia. The presence of a certificate of conformity and permission must be reflected in the equipment passports (forms).
6.2. Acceptance into operation of gas pipelines and gas equipment after completion of construction, reconstruction, repair, overhaul is carried out in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents. The order of organization and sequence of work on switching gas pipelines and starting gas are determined by the instructions of the gas supply company.
6.3. Gas-hazardous work on in-house gas equipment is carried out in the presence of a work order for hazardous gas work, drawn up taking into account safety requirements; technological instructions, orders and instructions issued by the management of the gas supply enterprise for each type of work.
6.4. Completion of work on pre-launch testing and acceptance of internal gas pipelines, gas equipment of residential buildings and chimneys after construction, reconstruction, repair and overhaul of gas supply systems, as well as activities and work of the next cycle of maintenance of gas pipelines, gas equipment and chimneys must be documented for each residential building by the organization who performed the specified work.
7. Composition and frequency of maintenance and repair of in-house gas equipment.
7.1. The composition and timing of maintenance are determined by the type of gas equipment and its operating conditions. Maintenance work on gas pipelines and gas appliances in residential buildings is carried out in accordance with the instructions developed by the gas supply company.
7.2. During the operation of gas equipment, maintenance of gas equipment is performed; replacement of components and parts; connecting and disconnecting gas equipment; emergency restoration work.
7.3. The task of maintenance is to ensure the operation of in-house gas supply systems and provide instructions to the population. Types of maintenance: - periodic maintenance (hereinafter referred to as PTO); - unscheduled repairs upon request (hereinafter referred to as RRP). Technical maintenance is carried out according to the annual and monthly schedules of the gas service company under contracts with the owner of the building, unscheduled repairs are carried out at the request of the population.
7.4. Unscheduled work at the request of the population is carried out within the following time frames: - elimination of gas leaks immediately; - troubleshooting gas equipment within 24 hours. When performing repair work, the malfunction specified in the application is eliminated and the entire scope of work provided for during the technical maintenance is performed.
7.5. The service life of gas equipment is established in accordance with the manufacturer's passports (instructions). For internal gas pipelines this period is 30 years. Upon expiration of the standard service life, the technical condition of gas pipelines and equipment should be diagnosed in order to determine the residual resource with the development of measures to ensure safe operation for the entire period of extension of the operational cycle, or to justify the need for replacement.
7.6. The given composition of activities and works are mandatory for implementation in the mode of repeatable annual maintenance cycles of gasified residential buildings.
Download Gas pipelines and gas equipment for residential buildings
Do you want to connect your house to a centralized gas supply? But this desired event can take a lot of time, effort and money, right? Do you want the gasification of your household to take place without unnecessary stress and fines, but don’t know how to proceed correctly?
We will help you understand the procedure to connect gas to a private home in the shortest possible time and without problems. The article discusses all stages, starting with documentation and ending with putting the installed system into operation. Visual photographs and informative videos have been selected.
Understanding the features of this process will allow you to use your resources more profitably - after all, excavation work can be done on your own. But for the insertion, the participation of a gas service employee with a special permit will be required. Knowing the specifics of installing gas communications won’t hurt either.
With the help of gas, you can successfully organize heating, hot water heating, and cooking in your home. Gas equipment is reliable and diverse, and the cost of blue fuel is usually lower than using electricity, solid or liquid fuel for the same purposes.
In addition, gas lines rarely fail, but power outages are a common occurrence. The reserves of firewood, coal, diesel fuel and other similar energy carriers have to be constantly replenished.
The main problem with natural gas is its danger to human health and its ability to explode. Even a small leak can lead to poisoning or an explosion. That is why the requirements for the installation of gas communications are very high; you should not even think about doing all the work yourself.
To properly introduce gas into a private home, use a special unit called a reducer to reduce gas pressure
Gas pipes almost always need to be laid open (except for underground sections of the pipeline). They cannot be hidden under any decorative elements to improve the interior.

It is recommended to avoid installing detachable connections whenever possible. All places where pipes are connected must be located in such a way that the contact point can be inspected at any time and repaired if necessary.
Gas pipes must not be laid inside walls or deep into the foundation. This rule also applies to other elements, such as platbands, door frames, window frames, partitions, etc.
In some cases, it is permissible to lay a gas pipe in a wall niche, but this point must be clearly reflected and justified in the project. Special requirements are also imposed on the slope of the pipes. Horizontal deviation of the line position is allowed by only 3 mm towards gas appliances.
Vertically, no deviations are allowed, but the riser may have a slight slope: no more than 2 mm per meter. It should not pass through living areas, toilets or bathrooms. The gas riser should be located on the staircase; it is often routed through the kitchen.
You will also have to pay close attention to the installation of shut-off valves. Thus, the position of the central axis of the plug should be strictly parallel to the wall along which the pipe runs. When choosing the position of the tap, you should make sure that the position of the shut-off device is not blocked by the wall. The gas pipe should be located at a distance of 100 mm from the ceiling and from the walls.

Gas pipes are fixed along the wall not closely, but at a short distance, so that communications remain accessible for preventive inspection and repair
The gap between the wall and the pipe can vary from the radius of the pipe to a maximum value of 100 mm. This clearance is necessary so that the structure can be easily examined. A distance of 2.2 m should be maintained from the floor. Gas pipes are placed on special strong supports; sagging of the structure is unacceptable.
Therefore, you need to make sure that there are no gaps between the bracket and the pipe. All these important points are taken into account in, which must first be compiled by specialist engineers.
Gas pipes should be laid no less than 30 cm from the electrical panel, and no less than 25 cm from open wiring. You should step back at least five centimeters from the hidden cable.
Gasification of households step by step
When figuring out how to connect natural gas to a private home, you should take into account the lengthy procedure for completing various documentation.
Stage #1 - documentation of gasification
First, the owner will have to submit an application with a request for gasification of the house, to which must be attached documents on ownership of both the house and the plot, as well as all available technical documentation in relation to these objects.

Before starting the installation of a gas pipeline, specialists draw up technical conditions and a detailed design of the gas system, which indicates all elements, dimensions, distances, etc.
After this, specialists must examine the site and the house to draw up a document called a . At the same stage, it should be clarified whether it will be necessary to lay part of the highway through the neighbors’ plots.
It is better to immediately discuss this issue with them, obtain permission and agree on the specifics of the work. This way you can avoid many problems and delays.

Gas pipes are passed through walls and ceilings using a protective sleeve and seal, while only a solid piece of pipe can be located inside the sleeve
Based on the technical conditions, a package of design documentation for the site will be drawn up and agreed upon. Only after this will it be possible to hire a contractor to carry out a complex of installation work.
The installation of the external and internal parts of the gas pipeline, connecting it to the common pipeline, connecting gas equipment and other important stages will be carried out.
In the process, you will have to draw up a number of important agreements, such as:
- for carrying out research work and drawing up technical specifications for designers;
- for the preparation of project documentation;
- to carry out installation work on laying internal and external water supply systems;
- for the supply of natural gas, etc.
In addition, it is necessary to obtain a number of permits. For example, you will need permission to gasify the site from the local architectural department.
You should also invite specialists who will inspect the existing chimney in the house (or one specially built for a gas boiler and other gas appliances). The satisfactory condition of the structure is confirmed by the relevant act.
With the cost of connecting a suburban area with a house to a centralized gas supply, completely devoted to this issue.
Stage #2 - supplying the pipeline to the house
Almost all elements, devices and materials that will be used in the gasification process should have quality certificates. It is usually recommended to use pipes made of low-alloy or low-carbon steel. The diameter of the structure should be 150 mm with a wall thickness of 5 mm.
The use of non-galvanized seamless steel alloy pipes is allowed. The pipeline is assembled by welding, the quality of which must be impeccable for individual sections of the pipeline. Threaded connections are used at installation points of shut-off valves.
In addition to steel pipes, plastic structures have been increasingly used for the installation of gas pipeline systems in recent years. They are lighter in weight, easier to install, well resistant to cold, heat, aggressive chemicals, do not conduct electricity, etc.
When laying plastic pipes in the ground, you can do without additional protective measures, as is done for steel structures. However, plastic is used only for the installation of external gas pipelines; the entrance to the house and the internal system must be metal. Plastic is also not applicable in areas with very harsh winters and increased seismic hazard.

Laying an underground gas pipeline is approximately 60% more expensive than installing an above-ground gas network, but this installation method is considered safer
Laying a gas pipeline underground is, for obvious reasons, more expensive, but if it is done correctly, then such a pipe will be reliably protected from outside influences and accidental damage.
If the pipe needs to be laid across the road, the contractor will have to block the road and draw up a detour traffic pattern. The scheme is approved by the local traffic police department, on the basis of which the executor receives a warrant.
It is recommended to give preference to the above-ground laying of a gas pipeline in areas where the soil has increased corrosion characteristics, but if power lines are located nearby, then it is better to give preference to underground communications.
On one site, you can combine both types of laying, for example, lay a gas pipeline underground across the road, above ground through the neighbors’ property, etc.

It is not always possible to lay a gas pipe underground; when laying a gas pipeline externally, special safety measures must be taken, taking into account the influence of external factors
Once the project is ready, you can proceed directly to the installation work. Of course, they will be carried out by specialists who have the necessary training and equipment.
Stage #3 - arrangement of the boiler room
Both the boiler room and the kitchen should have a window that can be opened at any time for ventilation. The opening area must be at least half a square meter. The ceiling height should be at least 220 cm. Door leaves should be made to open outward rather than inward.

Gas boilers with a power of less than 30 kW can be installed directly in the house, having allocated a separate room for these purposes, but for more powerful devices you will need a separate boiler room
It should be taken into account that the number of burners on a gas stove depends on the size of the kitchen. Thus, in a room with an area of less than eight square meters, it is allowed to install only stoves with two burners; for a stove with three burners, at least 12 square meters are required. m, for a four-burner device - at least 15 sq. m, etc.
If the boiler power exceeds 30 kW, you will need to build a boiler room for it, located at some distance from the house. Good forced ventilation should be provided here, the walls, floor and ceiling should be finished with fire-resistant materials.
You should not use the boiler room as a storage room; the presence of foreign objects and materials can cause an accident.

There are serious requirements for the location of the chimney of a gas boiler, which take into account the characteristics of the material for finishing the walls of the boiler room and its roof. Legend: d – diameter of the chimney pipe near the boiler, D – diameter of the chimney outside
The boiler room, which is located in the house, must be supplied with water, as well as a sensor to determine the level of carbon monoxide in the air. It is recommended to install an alarm system that will shut off the gas supply in the event of a leak. You should not install more than two low-power boilers in one boiler room.
For a 30 kW device, a room with a volume of at least three cubic meters is required; for high-power boilers, more than 60 kW, at least 11.5 cubic meters are needed. m of space. People should not be in the boiler room for more than four hours a day.
The covering of the floor, walls and ceiling in the boiler room must not only be resistant to fire, but also not produce dust. Dirt often causes breakdowns of gas equipment.
A prerequisite for connecting to the main gas supply is installation. Our recommended article will familiarize you with the rules for choosing a gas flow meter and the specifics of its installation.
Stage #4 - entering communications into the house
In order to correctly introduce gas into the house during the installation of your own gas supply system, make a hole in the lower part of one of the external walls, but not in the thickness of the foundation.
An insert in the form of a steel sleeve is first inserted into the hole, and then a pipe is inserted into the house through it. The main riser and internal gas pipeline are then connected to it.

The insertion of the gas pipe into the main pipeline is carried out by a special service. This is followed by the first start of gas, checking for leaks, setting up gas equipment, etc.
The riser is usually placed vertically, 15 cm away from the wall and secured with special hooks to secure the vertical position. The pipe is installed at a slight slope towards it.
All places where gas pipes pass through walls deserve special attention. The holes need to be made large enough, since they also need to include protective sleeves through which the pipes are passed.
Previously, all areas of communications that will be located in the wall should be covered with several layers of oil paint. The gap between the surface of the pipe and the sleeve should be filled with a layer of tow impregnated with resin, and also filled with a layer of bitumen.
In this case, you need to make sure that there are no places in the wall that are connected by welding or threading. Only a solid pipe can be located in the thickness of the wall.

Only metal gas pipes can be laid inside the house. High demands are placed on the vertical and horizontal position of structures
The fewer connections there are in the gas pipeline, the larger the sections of solid pipes, the better for the safety of the structure. In order not to cut the structure when it needs to be bent and changed direction, it is allowed to heat the area with a gas burner, but this method should not be abused.
The individual parts of the gas pipeline are connected on the ground, then the pipes are installed along the walls, connected, and secured with special brackets. Narrow pipes, less than 40 mm in diameter, can be fixed to the wall using clamps or special brackets.
Thicker structures are suspended on brackets, as mentioned above. In any case, you need to firmly fix such fasteners in the wall using concrete mortar and wooden plugs.

Narrow gas pipes can be fixed to the wall using special fittings. It is important that these elements are securely reinforced in the thickness of the wall
Welding gas pipes is a special art. In order for the seam to be truly smooth and durable, it is necessary to carefully prepare the surfaces to be joined. The edges of communications should be trimmed, leveled and cleaned to one centimeter. Only after this can you begin welding work. It is recommended to use high quality electrodes.

For the installation of gas pipelines, in addition to pipes, many auxiliary elements are used. All of them must be of high quality, confirmed by a certificate
Threaded connections should be made as few as possible. They must be carefully sealed to eliminate any risk of gas leakage. First, the thread is treated with whitewash, then a sealant is wound around it (linen thread, FUM tape, etc.), only after that the connection is screwed in.
Stage #5 - trial run and final activities
After assembling the system and introducing gas into a private house, you will have to go through a number of final steps. Before starting up and setting up the equipment, home owners must undergo safety training. To lay the internal and external gas pipelines, you can, if desired, invite either one contractor or two different ones.
These can be either specialists from a local gas organization or third-party organizations that have the appropriate licenses. But direct connection to the main gas pipeline must be carried out by a separate tie-in service.
After this, the first gas is released into the system and performed. This service is paid separately. By this time, a service agreement for existing gas equipment should already be concluded.
After the first start-up of gas, a specialist from the service company must set up such equipment; this is an important point on which the validity of the warranty obligations depends.
If for some compelling reason connecting to the main gas system is not yet possible, pay attention to option c. It is possible that at the moment this method of organizing gas supply to the house will be more attractive to you personally.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Detailed information about the procedure for gasifying a private house is presented in this video:
Carrying out work on gasification of any facility is a job for professionals with the appropriate skills and licenses. The owner of the site is responsible for completing the necessary documents, choosing a contractor, etc.
The whole procedure is usually expensive, but the result is worth the money and effort.
Please write comments, ask questions, post photos on the topic in the block below. Tell us about how you connected your site to the centralized gas supply. It is possible that your experience will be useful to site visitors who will have to go through a similar path.
Installation of a gas pipeline is the most responsible and important stage of any construction; even the slightest mistakes are fraught with it. Therefore, only highly qualified specialists from the relevant service can carry out such work. And we will look at the features of the process so that we know what to be prepared for.
Why gasify housing?
Today, natural gas is the most convenient and, importantly, profitable type of fuel. Sooner or later, every owner of a private house will want to gasify their property. Of course, there is an alternative - electricity. However, its cost is too high and it is very expensive to heat large areas in winter in this way. Plus, you will always depend on weather conditions - any hurricane can cause a break in the cables and then you will have to be left for some time without food, hot water and heating. But damaging a gas line is much more difficult.
There is, of course, another “grandmother’s” way to heat your home - a stove or fireplace. But ash, coal, firewood, all this will lead to excess dirt. Lighting a stove takes a lot of time and labor, so it's best left as an apocalypse alternative. So, whatever one may say, blue fuel occupies a leading position today.
What kind of gas pipeline should a private house have?
We all know about the explosive properties of gas, so there can be no talk of any amateur activity in this matter. However, you will have to collect all the necessary documents, make a project, submit applications to the relevant authorities, etc. Which means, get ready to visit various services and queues. Let's consider all the requirements that cannot be violated.

All materials, from pipes to welding electrodes, must be of high quality and have certificates. The location of all pipeline elements is also very important. Dismountable joints should only be located in open areas. Be sure to provide free access to them. This will allow you to assess their condition at any time and, if necessary, carry out repair work. It is prohibited to wall up pipes and other components of the gas network into the walls or foundation of a building. It is also unacceptable to run the gas pipeline through platbands, plywood walls, transoms, door and window frames and temporary partitions. True, sometimes it is possible to run a gas pipeline through a specially made channel in the wall, but only in special cases and after approval of the project.
Distortions are also not allowed, all pipes must run strictly vertically, horizontal sections have a slope of 0.002–0.005 m towards the devices. If we are talking about a riser, then in this case a distortion of a maximum of 2 mm per meter is allowed. They are located mainly in stairwells or in the kitchen, but this is prohibited in bathrooms and living rooms. The taps also require special attention; they must be installed so that the axis of the plug is parallel to the wall. The thrust nut must not be placed on the wall side.

It is very important to maintain distances. There must be at least 2.2 meters from the bottom of the pipe to the floor, and 10 cm of free space must be left between the top of the gas pipe and the ceiling. Also, pipes should not be placed close to walls, as this will complicate visual inspection. If this distance is not specified in the project, then you need to leave a gap, the minimum value of which will be equal to the radius of the pipe, but not exceeding 10 cm. The gas pipeline must be located on the supports tightly enough, gaps are not allowed.
Paperwork and equipment selection
But before you face the installation, you will need to run around to different authorities and collect a package of documents. Prepare a passport, title documentation for the land plot and the building located on it. You also need to write and submit an application to the gas service in which you express your desire. After this, you will receive a technical specifications form, which is filled out by the developers. And only then can you start drawing up a project.

You will need to enter into the following agreements:
- on carrying out work and drawing up technical documentation;
- on gasification and installation of relevant equipment;
- act of putting gas equipment into operation;
- for the supply and payment of natural gas.
In some cases, if you do not dare, you will have to stretch pipes through your neighbors’ plots, and then you will need written permission from them. It is necessary for specialists to come to you and inspect the chimney in the house, and at the end they are required to issue a certificate. You will also have to visit the local architectural and planning department. The head of this organization is also required to issue a permit for gasification of the site.
It has already been said that absolutely all materials, especially pipes, taps, hoses, must have the appropriate certificates. Without such documentation, all these elements cannot be put into operation. Blue fuel flows through pipes with a diameter of 150 mm and a wall thickness of 5 mm. Basically, elements made of low-carbon or low-alloy steel are selected. In principle, both seamless and welded structures can be used. Naturally, the gas main is assembled from a fairly large number of pipes. They are connected by gas welding. There are also very serious requirements for the quality of electrodes and they cannot be neglected.

But the list of necessary materials does not end there; you will also need a number of small parts - tees, crosses, couplings, adapters, angles and plugs. They are usually made from cast iron or steel. To properly fix all threaded elements, you should choose the right tool. For example, maximum grip on the part is provided by wrenches with notches and parallel jaws. Is it worth mentioning the boiler, water heater, stove and other equipment?
There is no need to delay installing the meter, because as practice shows, it will significantly reduce your costs.
Procedure for laying gas supply
Having familiarized yourself a little with the theory, you can move directly to the practical part. Despite the fact that the installation of a gas pipeline in a private house or high-rise building should only be carried out by specialists, we are still required to know the procedure for carrying out the work.
How to install a gas supply - step-by-step diagram
Step 1: Drafting
Having collected all the necessary documentation, you can begin preparing the project. It indicates absolutely everything: the dimensions of the pipes and their material, the location of various parts, gas appliances. The types of these devices must be specified. Mounting locations for meters are also indicated. At this stage, the entire system is calculated. But keep in mind that all this is done by a special organization and only if it has the appropriate license. Otherwise, the document will be invalid and you will have to redo everything, which means extra nerve cells and, of course, material costs.
So be very careful when choosing such a service. It would be best to contact a company that has the right to do not only design, but also installation work. This way you can save about 25%. So, to create a project, you need to provide the organization with a package of the following documents: technical specifications and certificates for the installed equipment. If there is an underground gas pipeline, then you may also have to do a topographic survey. They may also ask for executive documentation for the gas pipeline itself.

As a result, the design organization is obliged to come to the site, study the conditions, take all the necessary measurements, and make drawings indicating all gas connection points to heating and other appliances. After which the technical documentation is agreed upon in the department of the gas supply organization and other authorities. Finally, you should have a document in your hands confirming that the project fully complies with the standards.
Step 2: Preparatory work
We have already reviewed the basic requirements for installing a gas pipeline, but we must also properly prepare or build a room in which all the necessary equipment will be located. It must have a window that opens completely. This will allow you to ventilate the room at any time, because the gas is known not only for its explosive characteristics, but is also very toxic. In this regard, you should also worry about a high-quality ventilation system.
The height of the ceilings in the room cannot be less than 220 cm. Area also plays a role; if you have a stove with only 2 burners, then eight squares will be enough. For three-burner units, at least 12 m2, and installation of equipment with 4 burners is only allowed in a room with a volume of at least 15 square meters. When it comes to heating boilers with a power of more than 30 kW, our boiler room should only be a separate building. Naturally, you cannot live in it.

Step 3: Installation of the riser
It is impossible to supply gas to a house without installing an inlet. It is a hole above the foundation. A special case is installed in it. A pipe passes through it, one end of which is connected to the riser, and the other is part of the internal gas pipeline. The riser is mounted strictly vertically at a distance of 15 cm from the wall. For a more secure fixation, you can secure it with hooks. The pipe is brought in at an angle from the riser.
Step 4: Laying Pipes
When installing a pipeline in the walls, its elements are passed only through sleeves. Be sure to cover the sections of pipes that will be walled up in the wall with oil paint. Then the free space between the sleeve and the pipe should be filled with tarred tow, and then filled with bitumen. The pipeline at the intersection with the walls of the house must be solid, without joints. In general, it is advisable to make as few welded and threaded connections as possible; accordingly, the pipes are selected to the maximum length. Monolithic construction is more reliable. In some cases, when it is necessary to perform minor manipulations with the pipe, for example, straighten, bend or slightly unfold, heating with a gas burner is allowed.
All components are prepared at the bottom; only the assembly and fastening of the prepared elements is carried out at the height. Pipes whose diameter does not exceed 40 mm are allowed to be fixed to building structures using hooks or clamps. In this case, fasteners are tightly driven into the surface through wooden plugs or filled with cement. If pipes of larger diameter are used, then hangers or brackets are used to fix them.

Step 5: Welding work
It has already been noted that parts of the pipeline are connected by welding, and very serious requirements are imposed on this type of work. The seam will not be of the required quality if the joint is not prepared in advance. To do this, the ends of the pipes are trimmed, straightened if necessary, and the surface is cleaned by at least 10 mm on each side. Then the elements to be connected are installed coaxially, maintaining the same gap of no more than 2 mm around the entire circumference.
Only specialists in this field have the right to carry out gas pipeline installation work. To provide gas to a private home or to repair gas communications, you need to choose professionals.
Pipe installation is carried out in accordance with SNiP 2.04.08–87 standards. This document regulates all actions, distances and dimensions of installed communications.
The gas pipeline is one of the most important parts of the house. Thanks to it, heating appears in the room; using gas appliances, you can cook food and heat water for hot water. But if used incorrectly, gas can become a serious problem leading to tragedy. To avoid this, standards were invented that were used when installing a gas pipeline. They ensure the safety and correct operation of devices.
Basic Rules:
- The intersection of the gas main and window openings, doors and ventilation is not allowed.
- The distance from the pipe to the electrical panel should be at least half a meter.
- There must be a minimum of 25 cm between the gas system and electrical communications.
- The gas pipeline should be located at a height of 220 mm from the floor; in rooms with a sloping ceiling, this distance is 200 mm.
- A flexible hose with a diameter of 10 mm can be connected to gas equipment.
- Water heaters cannot be installed in the bathroom.
- High humidity creates a reverse draft, due to which the room is filled with carbon monoxide and can cause poisoning.
- The distance between the stove and the pipe must be maintained; it must exceed 80 cm.
- After the metering devices, the pipe slope should begin at 3%.
- The metering device should be located at a height of 1600 mm from the floor.
- The meter should be located at a distance of 80 cm from the heating equipment or stove.
- To install a gas pipeline in the wall, it is necessary to make a hole in the wall separate from the ventilation.
- Access to communications must be ensured. You can place them in a box, but it must be equipped with a lid for access.

Preparatory work
Before installation begins, it is necessary to prepare the site. To do this, you will have to coordinate the work with the relevant organization. Coordination of gas pipeline installation is carried out in the following order:
- Write a statement to the company that monitors the gas industry.
- The specialist will make a verdict on the possibility of carrying out certain works.
- If the work is permitted, the specialist will draw up an estimate for its implementation.
Permits for gas pipeline installation are issued in accordance with SNiP 2.04.08–87 and “Safety Rules in the Gas Industry.” Preparation, coordination and drafting of the project make up a significant part of the costs.
Installation equipment and tools used
To install the gas pipeline, craftsmen use special equipment:
- Long-fiber flax or FUM tape for making threaded connections.
- Lever wrenches with parallel jaws. They should be equipped with notches for better adhesion to the part.
- Apparatus for welding.
- Fittings are parts with fine threads for connecting several elements.




All tools and system elements must have a certificate from the factory that manufactures these parts. All certificates must comply with the requirements of Gosgortekhnadzor. If there are no certificates, then the use of such pipes is impossible.
Procedure

Installation of a gas pipeline begins with measuring all the required dimensions. Based on the data obtained, specialists draw up a project for the future gas network.
After approval, it is necessary to order the production of the parts required for the project, buy consumables and deliver it all to the assembly site.
When all parts of the structure are ready and delivered to the construction site, you can begin work directly. When laying pipes, it will not be possible to use gas equipment, so you will have to worry in advance about an alternative method of heating or cooking at the time of work.
Gas pipeline installation technique

Work begins with introducing the pipe into the building. To do this, a case is placed in the outer wall and an entry is made through it. A riser is already installed inside, located 20 mm from the walls in a vertical position. Connections at this stage are made using a welding machine.
The cases should be located at all intersections of the pipe with interfloor ceilings, walls and staircases.
Gas pipeline fasteners must be installed at a distance of at least 2 m from each other. These rules apply to pipes with a diameter of 25 mm. They must allow repairs and diagnostics of possible damage during operation. The end of each fastener is driven into a special wooden plug located in the wall. After this, the fastening site is filled with cement mortar to give additional strength.
There are a number of rules for performing welding work:

Rules for performing welding work
- Welding can be performed on pipes with a diameter not exceeding 150 mm and with a wall thickness of up to 5 mm.
- Arc welding is used when the pipe thickness exceeds 150 mm or the wall thickness exceeds 5 mm.
- Before installation, it is necessary to prepare the pipes for welding. To do this, they are cleaned of contaminants.
- Each welded joint must be easily accessible. It is not allowed to hide seams in the wall or case.
It is important to note that free access is required for all connections, not just welds.
All connections are made by welding. Threaded connections are allowed only in places where shut-off valves, metering devices (gas meters) are installed, and where a pipe is connected to a hose leading directly to gas equipment.
Gasification of a private home is sometimes a very complex and expensive process. In this article we will talk in detail about connecting gas to a private house and laying a gas pipeline. Also, a lot of material is devoted to the main stage of gasification of a house - this is the preparation of documentation. When you install gas into your home, use this article as a guide or reminder in this complex process. Well, let's now move on to the article itself.
In order to cut into a gas pipeline, you need to find out who owns it. Usually this is GorGaz. Permission from the owner is required to tap into a gas pipeline. If the owner of the gas pipeline has given consent, then the next step is to contact a design organization that will develop a project for gasifying your home and connecting it to the gas pipeline.
Aboveground and underground gas pipelines
Gas pipelines can be divided into aboveground and underground. If the gas pipeline is underground, then we install the inlet part of the gas supply of the house near the stairs, and if the gas pipeline is above ground, then we install the inlets in the kitchen wall.
The underground type of gas pipeline is more expensive, but at the same time, the pipe that runs underground is more protected and the service life of such a pipe is much longer.
In order to lay a gas pipeline underground, you need to make sure that the passage along this section of the road where the installation of the underground gas pipeline is being carried out is blocked, while laying the gas pipeline, with the help of road plans, draws up site plans for the purpose of placing equipment, and also reflects in the plan the geometric data that is adjacent to the houses, which allows you to correctly place road signs in order to restrict traffic in areas where the underground gas pipeline will be installed. This traffic ban scheme must be agreed upon with the local traffic police, as a result of which a warrant is issued for the installation of an underground gas pipeline.
Regarding the above-ground gas pipeline, you need to know that its disadvantage is its susceptibility to corrosion, while the easy form of unauthorized connection is considered a big advantage. Also, this gas pipeline is more convenient for inspection and repair, and the area for its installation is significantly smaller than the area for underground installation. In the event of a gas leak, it is faster and easier to troubleshoot the problem on the surface.

As a result, we found out that gasification at home is:
- project documentation;
- tie-in into a street gas pipeline;
- branching gas networks inside the house;
- installation of gas equipment.
Gasification of a private house from personal experience
At one time I was faced with the problem of how to supply gas to the house and where to apply for permission. Fortunately, I came across an excellent person who was able to give me a number of useful tips. And this is what he advised me in my case; perhaps many will find it useful now.
If you are faced with the problem of gasification of a private home, then you need to follow these steps and obtain a number of documents that I have listed below:
1. Inspection reports of all premises where gas equipment will be installed by the SVDGO foreman.
1.1. Chimney inspection report by the VDPO service.
1.2. Permission from the Heads of the APU for gasification of the house.
1.3. A copy of the BTI technical passport for the house.
1.4. Topographic survey with planting of the house and gasified buildings and premises on the owner’s property.
1.5. Permission to connect to the gas pipeline, if it is laid in neighboring areas, from its owner (usually the owner is GorGaz).
2. Obtain from GorGaz the technical conditions for gasification, and, if necessary, for electrochemical protection of the designed underground gas pipeline.
3. Conclude an agreement for the implementation of design documentation and organize a visit to the site by a design engineer to carry out the necessary measurements.
4. The design and estimate documentation for the gasified facility is calculated.
5. Conclude an agreement for technical supervision.
6. Drawing up a report on the chimney is carried out by the fire service of the VDPO.
7. Conclude an agreement for construction and installation work with a construction organization carrying out gasification.
8. The gas pipeline and equipment are being installed.
9. As-built technical documentation is drawn up.
10. The commission accepts the installed gas pipeline.
11. Conclude an agreement with GorGaz for the supply of gas, for the maintenance of the gas pipeline and in-house gas equipment.
12. Complete safety training when using gas.
13. Agree with GorGaz on the date of the tie-in (gas connection).
14. The tapping is carried out and the initial gas start-up is carried out (the next day after the tapping).
Owners who plan to supply gas to their home have the right to carry out all approvals on their own, otherwise they can always contact a company that directly specializes in the installation of pipelines and gasification of a house or a number of houses.
Gas in a private house or we supply gas to the house (full version)
The first stage of connecting gas to the house
First, find out who owns the gas pipeline running near you, but for the most part it is, of course, Gorgaz. Contact them and resolve the issue of insertion. After permission has been received, go to a design organization that will develop a project just for you.
After which the finished project is handed over to you, and with it you go to the installation organization.
This organization will resolve all issues related to the installation of the gas pipeline, and it is also responsible for the commissioning of a specific section of the gas pipeline. Therefore, when concluding an agreement with an installation organization, make sure that they have the appropriate license for this. After going through all these stages, you have gas in your home, use it, but do not forget about the safety rules.
Let's take a step-by-step look at all the necessary steps to gasify your home.
- 1. The first step to starting gasification is collecting documentation.
Here you will need to collect a lot of documents that can confirm that the house and land are your property, gasification permit acts and many others. The entire design is divided into two stages. First, the documents necessary to begin work on laying a gas pipeline are collected, then documents are drawn up throughout the entire work. Such documents include: a permit issued by the head of the architectural and planning department for the gasification of a specific private house.
You will also need a copy of the technical passport of the technical inventory bureau for your house and the topography of the land plot with the planting of the house and all the structures located on it that will be gasified, on a scale of 1:500, where all communications and the proposed gas pipeline are indicated, which must be certified by the gas service.
They may also request permission from neighbors if the gas pipeline will pass through their territory, although most often such permission is issued by Gorgaz itself, since the gas pipeline is their property.
During the gasification process, you will need documents for all gas equipment that will be installed in the house, as well as a report from the VDPO service on the examination of chimneys.
- 2. Obtaining technical specifications.
You can only get them at Gorgaz, so go visit them. There you will need to present a registration certificate from the BTI for your house, your passport and documents confirming the ownership of a particular house, plot and mandatory permission to conduct gas. After which you will be asked to write the necessary application in order to obtain technical conditions for supplying gas to your home.
A small nuance is that this service is paid, and you will also have to wait 14-30 days for a response.
- 3. The next stage is design.
After solving all the issues in GorGaz, go to the design organization, since there are currently a sufficient number of them. Be sure, once you have decided on the choice of design organization, ask them to provide you with a license that gives them the right to carry out such work.
In addition to the license, it would not be a bad idea to study the cost of providing such services in a design organization; each office has its own and ranges from 10-50 thousand rubles. To avoid further problems, it is best to ask GorGaz which company they can recommend to you. When drawing up an agreement with a design organization, make sure that it includes the service of a designer, engineer or other specialist visiting your home, if you need one.
This is a very important point, since it is the designer who registers and gives approval for the installation of certain gas appliances and the brand of heating equipment, which must be agreed upon personally with you. The finished project is coordinated with the technical department of GorGaz, but this must be done by the person who is responsible for this project. The whole process takes 10-14 days.
When all the above steps have been completed, you can begin calculations and draw up an approximate estimate of the work that is agreed upon in the design documentation. After which you draw up a contract for technical supervision, and attach to it a report on the inspection of the chimneys of your house by the VDPO service.
- 4. We begin the contract with the construction and installation company.
All the necessary documents have already been collected, signed, and all issues with Gorgaz have been settled and with the design organization too. And here you go to the installation organization, which in the future will have to carry out all the required construction and installation work. It is also recommended to ask them for a license to carry out their work, since it is this organization that will hand over the work done to GorGaz.
Note. In many cases, installation and construction companies have a license not only to perform installation work, but also design work. Therefore, if you order design and installation work from one company, this can significantly reduce your costs for gasification at home.
After discussing and approving the timing and cost of these works with the installation company, be sure to conclude an agreement with them, this will still give you at least some guarantees, and in case of which all responsibility will lie with them.
This agreement must spell out certain obligations of them to you and, of course, guarantees on their part.
Be sure to check that the contract contains the following points.
During the laying of internal and external gas pipelines.
- - When performing installation and construction work, this company is obliged to have all the necessary fire extinguishing equipment, including a protective screen, which is needed to prevent the walls from heating up.
- - As-built technical documentation is handed over to you personally by the installation company immediately after all calculations for the work performed.
- - The installation and construction company undertakes to deliver the completed work specified in this contract strictly on time, as well as in compliance with all standards and quality.
- - The installation and construction organization assumes all obligations for the preparation of as-built technical documentation.
You can begin drawing up as-built technical documentation as soon as all work on the installation of the gas pipeline and all gas equipment has been completed. A special commission, which includes the customer himself, the contractor and the responsible person from GorGaz, comes to accept the finished gas pipeline.
This commission must accept all work within 14-30 working days. If everything is in order with the work performed and there are no complaints, the representative from GorGaz, who is part of the commission, must give you a technical supervision receipt, you need to pay for it, and provide a copy to the installation company.
Pay special attention to ensuring that at the time the work is accepted, absolutely all gas equipment included in the list of project documentation has been connected and installed. At the end of the inspection, the installation and construction company is obliged to prepare and submit all documentation related to technical issues to GorGaz, where it should be stored.
By decision of the commission and after GorGaz receives all the necessary documents, your meter will be sealed within 21 days. Now you can enter into an agreement directly with Gorgaz itself, after which gas will be supplied. In the future, according to the agreement, Gorgaz is obliged to carry out maintenance of all gas equipment and the gas pipeline itself.
- 5. Safety training.
Now all the problems with the gas supply are behind you and you must listen to a lecture on the safe use of gas, that is, the so-called safety precautions.
A similar procedure can be carried out without problems in the city gas office itself, which is carried out by a special engineer of this institution. In the journal kept by Gorgaz, you leave your signature, thereby confirming that you have completed this instruction.
But you can also undergo this procedure at home if a certified specialist comes to you and is authorized to provide safety instructions when starting up and setting up gas equipment. As with instructions at GorGaz, you need to confirm with a signature in the appropriate journal that you have completed the instructions.
- 6. Connecting your gas pipeline to the main one.
To tie into the main gas pipeline, you will need to pay the service that will carry out the tie-in. It is recommended to first agree on the time frame within which this work will be carried out. As soon as everything is ready for operation, the gas service supplies gas and conducts a preliminary test run of gas to check the devices, the meter, and to exclude the possibility of a gas leak.
- 7. Work on launching and setting up gas equipment.
The organization from which you purchased this equipment and, accordingly, entered into a service agreement should put the gas equipment into operation and set up. Since this is one of the conditions for guaranteeing gas equipment, the warranty period must be indicated in the coupon issued for it. On average, the warranty is issued for a period of 1 to 3 years.
During commissioning, the work described below must be performed. This is setting the optimal operating mode of the equipment so that gas consumption is rational. At the same time, they must explain to you how to properly use the equipment that you purchased. If for some reason it fails to start, work is suspended until the problems are resolved. After the successful launch of the equipment, the work is formalized by drawing up a bilateral certificate of work done.
Documents that will allow you to perform a thermal engineering calculation will also be useful, which will give you the opportunity to calculate the required boiler power that can provide heat and hot water in your home. To do this, you need to seek help from housing and communal services specialists. These documents include - a floor plan of the premises that are heated, indicating the explication, height and area; what hot water points are there and their quantity (faucet, bath, shower, etc.); description with the possibility of using the boiler for such needs.
You can carry out all these approvals yourself, if you have such experience, but if not, then contact an organization engaged in performing such work.
Laying a gas pipeline
So we have figured out the basic requirements for bringing gas into the house. Now let’s get acquainted with what kind of gas pipeline there is, and which one is best to choose for yourself.
The gas pipeline is primarily divided into underground and above ground. They differ from each other in the way they enter the house. This also applies to the internal wiring of the gas pipeline network, its risers that distribute gas to floors, and devices that consume gas.

Underground gas pipeline and above ground
An underground gas pipeline is much more expensive than an above-ground one. But still, regardless of the fact that the underground gas pipeline is more expensive, the demand for it does not decrease. Since the underground gas pipe is more reliably protected from damage, its service life is therefore much longer. Its demand is also influenced by the fact that the underground gas pipeline is not so dangerous.
There is only one caveat: to lay a gas pipe underground, traffic will have to be partially or completely blocked. In such cases, the installation and construction company is obliged, based on the design documentation that it has in its possession, to draw up a traffic flow diagram for vehicles, pedestrians, and including working equipment. This diagram must also indicate the geometric parameters of the site where the work is being carried out, as well as the entrance to the houses and the location of traffic signs.
The drawn up scheme must be agreed upon and approved by the department of the state road safety inspection itself, that is, by all known traffic police. After which they issue a warrant authorizing work on laying a gas pipeline.
Regarding the gas pipeline running above the ground, there are both disadvantages and advantages. One of the disadvantages is corrosion damage to unprotected sections of the gas pipeline, and you can also connect to such a gas pipeline without permission, which can lead to disastrous consequences. The disadvantage of an underground gas pipeline is that its repair is much more expensive, since just getting to it already costs money.
We will provide comparisons of both types of gas pipeline so that you can decide which one is most suitable for you.
Before laying a gas pipeline underground, do a soil analysis; if it shows that the soil is too corrosive, it is better to abandon this option. But if there are high-voltage wires nearby, then an underground gas pipeline would be the best option. Opt for an overhead gas pipeline if it will have to be laid through your neighbors' land, this way you will not damage the fertile layer of the soil and it is more likely that your neighbors will give their permission. There are exceptions when it is necessary to install a gas pipeline using a combined method. For example, you need to lay gas across the road, then you can lay this section underground, and in your section above the ground.
Another important question. Which pipes are best to choose for a gas pipeline? Maybe polyethylene or steel?
We already know what a gas pipeline can be like, and now let’s see which pipes are best to use for a particular gas pipeline.
Previously, gas pipes were used exclusively from steel. Currently, polyethylene pipes are very popular; they are in many ways superior to steel pipes and have many advantages over them.

Polyethylene pipes are more resistant to the negative effects of chemical compounds and weather conditions. They perfectly combine strength and ductility, which makes it possible to lay a gas pipeline in places with strict climatic conditions. And the whole point is that even at a temperature of -45 degrees these pipes do not lose their impact strength. Also, polyethylene pipes do not conduct electric current, and, therefore, are reliably protected from electrochemical damage. This means that these pipes do not make sense to be additionally protected for laying in the ground. Plastic pipes weigh 7 times less than iron pipes. Transportation and delivery of such pipes also does not create problems, since they are packaged in special compact coils. Very comfortable and easy to install. The service life of plastic pipes is at least 2-3 times longer than steel pipes, in general it is about 50 years.
But all gas distribution throughout the house and its entry into the house is carried out only by steel pipes. Also, polyethylene pipes have certain limitations, which are very important to know about. All restrictions can be viewed in SNiP in paragraphs 2.04.08-87. We will look at some of them:
- It is prohibited to install polyethylene pipes in areas where the air temperature can drop to less than -45 degrees.
- The situation is the same in those areas where seismic activity is above 6 points.
- Laying a gas pipeline with polyethylene pipes is strictly prohibited underground, above ground, inside houses, canals, tunnels and sewers.
- It is prohibited to lay a polyethylene gas pipeline if it passes through natural or artificial barriers.
Let's move on to choosing a gas boiler with which to heat your room.
We have already dealt with the requirements for gasification, types of gas pipelines, now there is another rather important point, such as the choice of a gas boiler, which also relates to gasification of the house.
Today the market is filled with a lot of different modern boilers, but the choice is yours. All of them are divided into wall-mounted and floor-standing boilers.
A distinctive feature of floor-standing boilers is the ability to choose the required power, which is capable of heating a room with an area exceeding 150 m2. If you additionally install a boiler, the gas boiler will provide the entire house with hot water as much as possible.
Wall-mounted boilers are compact. They are also equipped with an automatic safety system, an expansion tank and a water circulating pump. With all this, their cost is not so great. For the most part, these boilers are capable of heating a room with a total area of no more than 150 m2, and supplying hot water to only two taps.
Which heat exchanger is better, steel or cast iron?
Boilers have heat exchangers that can be made of either steel or cast iron. Which one is better to choose, now we’ll figure it out.
A cast iron heat exchanger has a longer service life, about 20-25 years, a steel heat exchanger will last about 10-15 years. A cast iron heat exchanger is more durable due to its high corrosion resistance.
A cast iron heat exchanger, as a rule, consists of sections, which, if the heat exchanger is damaged, can be partially replaced rather than dismantling the entire boiler. However, do not forget that cast iron heat exchangers are very sensitive to mechanical and thermal influences. Therefore, you can add cold water only after it has cooled.
A boiler with a steel heat exchanger is much lighter in weight, and its cost is an order of magnitude lower, in contrast to a cast iron heat exchanger. It is also not subject to mechanical stress, however, it is subject to corrosion.
Volatile and non-volatile gas boilers
Non-volatile boilers have natural circulation, which sometimes causes certain difficulties. Such as a large pipeline diameter, an open expansion tank, the need to install the system in such a way as to ensure its gravity flow. But the biggest drawback is the inability to regulate the air temperature in the room. Moreover, in the room where such a boiler is installed, there must be tidal and exhaust ventilation, as well as a chimney.
Volatile boilers consist of a closed expansion tank and a pump that circulates water. And such a boiler has full automatic control, which is why they are equated to mini-boiler houses. But for its uninterrupted operation, a stable voltage in the network is necessary, which can be achieved using a voltage stabilizer.

Choosing a boiler is not so simple, so it is better to contact a specialist who will help you understand its power, make a wiring diagram and find out about additional automation. Of course, you can make calculations for the power you need yourself. To do this, you need to know that 1 kW of power is consumed per 10 m2, and there should also be a reserve of about 15-20 #, which can absorb unforeseen heat losses.
It is also necessary to provide a method for removing combustion products that are produced in gas boilers during gas combustion. These products can be removed naturally or by force, the so-called turbo. That is, it is an ordinary fan, but it is built directly into the boiler itself. Boilers that have a chimney, then combustion products are naturally drawn through the chimney, due to the draft that is there.
Where a chimney is not provided, it is worth installing boilers with a turbo system. In such cases, specialists will install a coaxial chimney, which is somewhat reminiscent of a pipe in a pipe, then the combustion products are discharged directly through the wall.
The outer pipe supplies air, but the inner pipe removes all gas combustion products. It is also recommended to install such a boiler in rooms where it is highly undesirable to take air from the room.
There are some nuances that you should pay special attention to in order to decide on the choice of a coaxial chimney facing the street. For example, the chimney pipe must be located at least two meters from the ground. When installing a boiler with a coaxial chimney and when designing a gas pipeline, it is necessary to take into account the fact that combustion products, when going outside, do not fall back into the house through the windows. A coaxial chimney is installed at an angle of about two degrees relative to the surface of the earth, since condensation may form in it. A chimney of this type must exhaust combustion products without any obstacles, so it must be installed so that there is at least 1.2-1.5 meters from the chimney to the buildings located nearby.
Home boiler room
One of the conditions for good combustion of gas is its combustion without residue, and this is only possible if there is a sufficient amount of oxygen. In this regard, the room must be of such a size that it is sufficient for the boiler.
The best option for installing a gas boiler in a private house would be a special utility room equipped with a chimney, tidal and exhaust ventilation, and there must also be a window. It is also necessary to ensure air flow into the room. This can be done using a special gap in the door or by making a small hole with a grill. A room for boilers with a power of more than 30 kW can also be used in a simple kitchen.
 Turkish chocolate cake Note to the hostess
Turkish chocolate cake Note to the hostess Recipes for delicious salads with fried potato strips
Recipes for delicious salads with fried potato strips Baked pike with potatoes Pike in the oven with potatoes and tomatoes
Baked pike with potatoes Pike in the oven with potatoes and tomatoes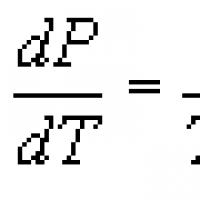 Clapeyron–Clausius equation
Clapeyron–Clausius equation Overpaid wages: actions of the employee and the employer
Overpaid wages: actions of the employee and the employer Green poop in a child: normal or serious danger Green poop for a 6 month old child
Green poop in a child: normal or serious danger Green poop for a 6 month old child Simple and healthy desserts for children
Simple and healthy desserts for children