Monolithic slab on coarse soil
Monolithic slab on coarse soil: what is its feature? What are the advantages and disadvantages? How to lay a monolithic slab? Find out the answers to these questions in this article.
A monolithic slab is a concrete casting with reinforcement that fills the construction pit. On a monolithic slab, there are no restrictions for building a garage or a frame bath, a factory workshop or a residential building. It differs from the tape base in the thickness of the casting and the number of reinforcement.
Positive features include:
- ease of installation;
- the possibility of erecting multi-storey structures;
- strength and resistance to deformation;
- resistance to erosion (during heavy rains or thaw);
- the possibility of building a basement floor, protected from melt water;
- stability of the shape of the structure (does not change properties due to temperature changes);
- the ability to resist the forces of frost heaving (when the moisture-containing soil freezes, its volume increases and tends to raise the foundation).
There are no disadvantages of a solid slab, except for its high cost.
Coarse clastic soils
Coarse clastic soils (unconsolidated soils) are rock fragments containing more than 50% of particles with a size of 2 mm or more.
Types of coarse-grained soils: crushed stone, block, gruss, pebbles, gravel.
Coarse clastic soils with voids differ in the content of the filler, which is characterized by the presence of clay, sand or clastic fraction (larger than 2 mm) in the form of rock minerals. When the content of sand or clay is 30-40%, the bearing capacity of the soil decreases.
Coarse-clastic soil can be heaving if the fine component is silty sand or clay.
Coarse-clastic soil with voids includes: mountain clay-carbonate marl, chalk limestone flask, clay mudstone, sedimentary siltstone, shale, etc.
Coarse-grained soil as a solid foundation for the foundation
An important criterion for the long service life of the foundation is the location of slates in a dense layer. They do not change their properties under pressure, but are washed away by surface currents of water after rain and snow melt, filled with moisture, freeze and increase in volume.
During installation, it is necessary to deepen the foundation by 0.5 m, even if the soil freezes to a great depth.
Clastic rock is frost-foamy if it consists of sand particles or clay soil.
Coarse clastic rocks with fine sand filler, gravel, large calcareous fractions are non-rocky soils, regardless of the degree of moisture content and the level of soil freezing.
Deepening the foundation on non-rocky soils
Foundations transmit the external impact of the load on the foundation, so the choice of foundation depends on the type and properties of the soil. With hydrophobic soil (absorbing and retaining moisture), it will be useful to build on a solid monolithic slab. A solid foundation involves a shallow and deep structure. For the construction of a monolithic foundation on coarse soil, a shallow monolithic foundation is suitable.
A shallow solid foundation allows you to lay a layer of insulation between the soil and the slab. To do this, use rigid polystyrene foam, the height of its plate is 15 cm. Due to the preservation of a constant temperature regime, a shallow solid foundation will increase the level of thermal insulation of the 1st floor, eliminate settlement and deformation. The insulation is laid on top of the drainage mixture, the thickness of the pillow is 30-40 cm.
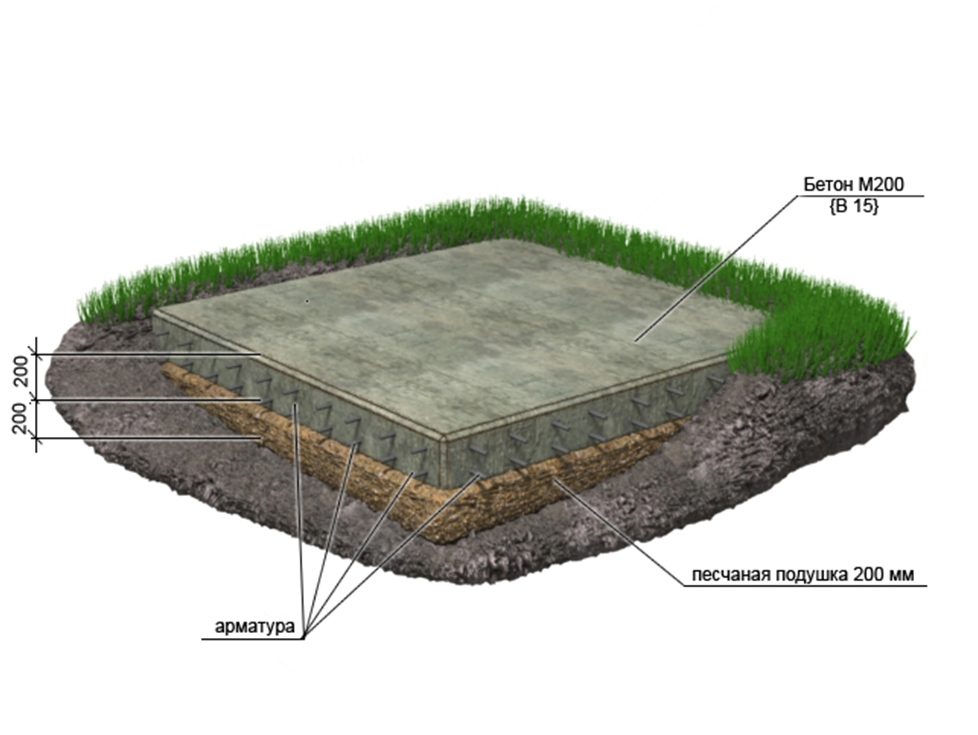
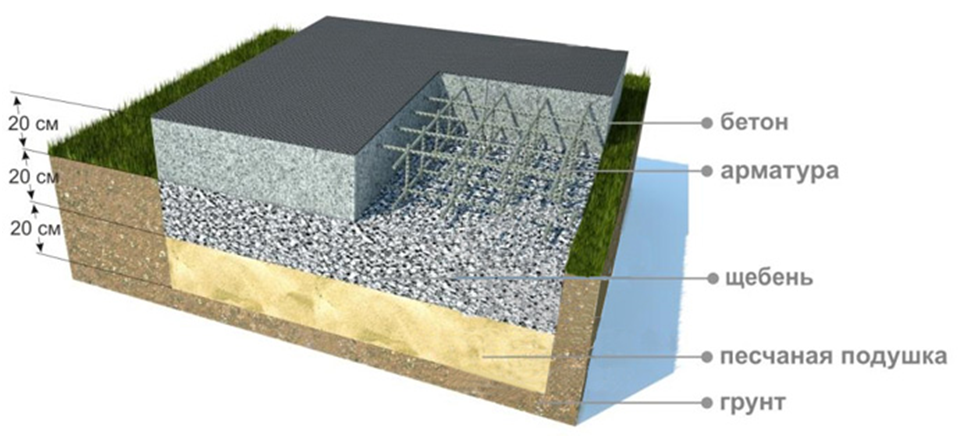
Slab foundation: construction technology
- Preparation of the area for the foundation. It is necessary to completely remove the top layer of soil to the depth established by the calculation. In this case, it is better to remove and level the last layer manually in order to avoid bumps and holes. The pit should exceed the dimensions of the foundation by 1-2 meters on all sides for the convenience of performing work.
- Preparation of a pillow of sand and gravel. It is necessary to compensate for the forces of soil deformation, as well as to drain groundwater and exclude their capillary rise to the base of the foundation. The thickness of the pillow depends on the characteristics of the soil: on sandy soils it can be 15 cm, on clay soils prone to severe heaving - at least 30 cm.
- Formwork device. Removable formwork is made of planed boards with a thickness of at least 20 mm, fastening them at the corners with self-tapping screws. From the outside, the formwork must be reinforced with struts.
- Waterproofing is carried out using a thick polyethylene film, geotextile or roofing material, laying it overlapping on the bottom of the pit with an approach to the formwork.
Calculation of the thickness of the foundation monolithic slab
When calculating the thickness of a monolithic slab, the following should be taken into account:
- soil indicators;
- land surveying;
- foundation loads;
- house design features.
Based on these data, the calculation of the monolithic foundation slab, its thickness and area is carried out. For example, if you carry out the calculation of shallow foundations, then the minimum thickness value is 150 mm. But such a plate is suitable only for light buildings and ideal non-porous soil. The thickness of the slab foundation is 200-300 mm, most often - 250 mm. More than 300 mm is already irrational. A foundation thickness of 250 mm is sufficient for the construction of a low-rise building, regardless of what materials it is built from.
Installation of a monolithic slab
- Formwork is erected from dry boards at the bottom of the pit (necessary to give strength to the structure). It consists in knocking down boards at a distance of 0.5-1 m and pouring the trench monolithic.
- Between the tiled structure and the angle of inclination of the pit, you need to leave a place for shedding the soil (about a meter).
- Concrete gives a large load, so it is important to secure the formwork boards well on both sides.
- After pouring a mixture of sand and gravel. On non-rocky rocks with a high content of sand or gravel, a pad is not needed.
- A dense film is covered on the sole of the pit for tiled installation.
- Along the length of the building, a stainless steel mesh or reinforcement is laid, laid crosswise.
- Then vertical supports are driven in, corresponding to the height of the monolithic slab.
- The next layer of mesh is strung on the supports and fixed in increments of 20 cm.
- The last mesh cover is installed 3-5 cm below the level of pouring concrete.
- Monolithic structures are poured with a concrete pump.
- Laying of concrete mass is carried out by an electric vibrator.
When erecting a monolithic solid foundation, the height of the slab corresponds to the massiveness of the building. Typically, the thickness of the structure for country cottages varies from 15 to 35 cm. For brick and block buildings, the thickness of the foundation is 20 cm.
Foundation waterproofing
To protect structures from rain and melt water, a blind area is installed along the perimeter of the outer walls (its width is 20 cm more than the roof overhang) with a slope of 5-10% from the building. If there is a sidewalk, additional waterproofing is not required.
Such a monolithic shallow foundation may involve laying a layer of insulation between the soil and the slab. To do this, you can use rigid polystyrene foam. The thickness of its slab should be equal to 15 cm. This solution will reduce heat losses occurring through the floor of the 1st floor, and virtually eliminate soil failure, which occurs due to the balancing of the temperature field under the building and around it. The insulation should be laid on a layer of coarse sand, the thickness of the pillow should be 30-40 cm.
For coarse soil, a shallow monolithic foundation is most suitable. At a price, a monolithic slab will be comparable to other buried foundations, since penetration in such soils, as a rule, presents certain difficulties. Therefore, it is worth giving preference to this option if there is no strict need to have a basement or basement floor under the house.
 Masonry mortars for brick kilns
Masonry mortars for brick kilns Why do the windows fog up in the apartment
Why do the windows fog up in the apartment Construction and schemes of brick ovens
Construction and schemes of brick ovens How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks
How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks How to drill bathroom tiles
How to drill bathroom tiles Monolithic slab on coarse soil
Monolithic slab on coarse soil Which electric heater is economical
Which electric heater is economical