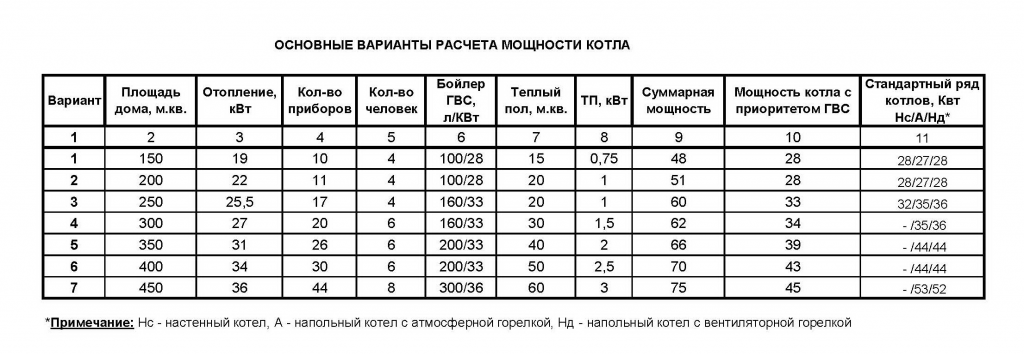
How to calculate the power of a heating boiler
The heating system of the house should be such that in its premises, regardless of the weather outside the window, the same temperature is always maintained. The heating network can perform such a task only when a sufficiently powerful boiler has been chosen. Therefore, before creating any heating system, it is necessary to calculate the power of the heating boiler.
Most used methods
They provide for the use of one standard indicator - the number of watts per unit area or volume of a room.
So, the heat output of a boiler with a strong efficiency can be determined using the method:
- By area.
- By volume.
The first one is very often used by sellers, because it is simple. According to him, in order to calculate the thermal power of the device, you need to multiply the area of a private house by 100 watts.
For example, a private house has an area of 150 sq. m. According to the area method, in order to heat it, you need to create 150 * 100 \u003d 15,000 W or 15 kW of heat. Accordingly, sellers recommend choosing such models of long-burning boilers or classic devices that have this heat output. However, they often advise increasing it by 20%.
As for the method by volume, it uses the following standard indicator: 41 W per 1 cu. m. To calculate the power of a long-burning boiler or gas appliance using this method, you need:
- Determine the volume of the internal space of a private house. If the above house has walls with a height of 3 m and is one-story, then the volume is 450 cubic meters. m.
- Multiply 41 by the volume of the building. The result will be the demanded power of a steam device or a home-made long-burning boiler. For the example used, the boiler power is 41x450 = 18450 W or 18.45 kW.
Both methods are not entirely accurate because they do not take into account the design features of a private house and the level of its thermal insulation.
Algorithm of the method that takes into account heat loss at home
The heat losses of a private house, which any long-burning gas or solid fuel boilers must compensate for, depend both on the design of the building and on the air temperature outside the window. It is clear that the greatest heat loss will be at the lowest temperature. It is this amount of heat that should be equal to or slightly less than the heat output of any long-burning boiler selected with high efficiency.
The algorithm of the method by which these losses can be calculated, that is, the demanded power of the boiler, provides for:
- Measurement of thickness and calculation of the surface area of all structural elements of a private house (walls, windows, doors, ceiling, floor).
- Determine the amount of heat that can pass through them in 1 hour.
- Calculation of the amount of heat required to heat the ventilation air.
- Summation of all obtained indicators.
Getting initial data
- Engage in determining the surface area of all structural elements of the house. The easiest way to do this is if there is a housing project. If it is not there, then you need to take a tape measure and measure the width and length of walls, windows, doors. The data is recorded in a notepad. Immediately it is necessary to calculate the surface area of the measured parts. The surface area of the walls is adjusted for the area of windows and doors.
- Measure the thickness of the walls (at the same time, find out the thickness of brickwork, plaster, thermal insulation), doors and other elements. The data is recorded in a notebook. At the same time, they indicate what materials the measured fence is made of.
- Determine the minimum air temperature on the coldest winter days.
- Choose the temperature to which the air inside the house should be heated.
- Take a reference book and write out the thermal conductivity coefficients for all the materials from which the house is made.
Calculation of heat that escapes through the walls
This stage of such a process as calculating the power of a steam or water heating boiler involves the use of two formulas.
First: 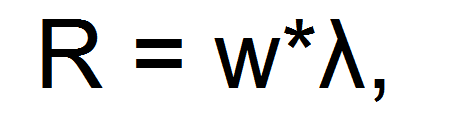
where R is the thermal resistance of the structural element(for example, brickwork). Determined in m²*°С/W,
w is the thickness of the structural element(should be taken in meters)
λ is the thermal conductivity of the material, from which a separate element of the house is made (unit W / m * ° C).
where Q is the amount of heat that passes through the structural element(defined in W),
Rzag - total thermal resistance of the wall,
tv is the temperature to which the air must be heated using steam or hot water boilers of high power,
tn - the lowest air temperature outside the window,
S - defined in sq. m surface area constructive element.
When determining the amount of heat that goes through the wall, you need to calculate several R, namely for brickwork, plaster, thermal insulation. Then these R's are summed up and the result is substituted into the second formula.
In a similar way, heat losses are determined through windows, doors, and the ceiling of the highest floor.
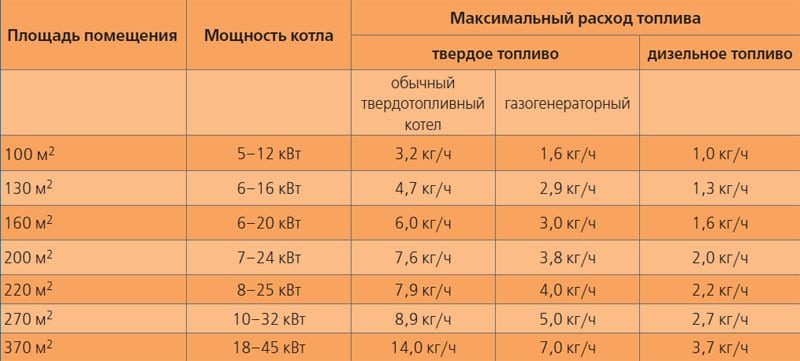
Calculation of floor heat losses
It is carried out only for the floor, under the surface of which soil or a basement is placed. For the floor of the second and other floors, this process is not necessary.
The amount of heat that leaves through the floor with a beautiful surface and which must be compensated by hot water or high power, is determined in the following sequence:
- Draw a plan of the building. Be sure to keep the scale.
- On the plan in the middle of the house draw 3 figures. Each must be inside the other. They should follow the outer contours of the building. If the house is a rectangle, then these figures must be rectangles. The distance from the outer walls to the sides of the largest figure should be 2 m. The same distance is maintained between the parallel sides of other figures. The space between the figures forms zones. In general, it turns out 4 zones. The first is the area near the outer walls, the fourth is the space inside the innermost figure.
- Determine the area of each such zone and calculate what should be the heating (Q) to compensate for heat loss through each of them. To do this, use the above formula.
The R values for zones are standard:
for the 1st zone R = 2.1;
for the 2nd - R = 4.3;
for the 3rd - R = 8.6;
for the 4th - R = 14.2.
- Calculate the sum from Q of all floor zones.
After that, the amount of heat loss through walls, windows, doors, ceiling and floor is calculated.
Calculation of heat costs for supply air heating
The formula is used for it:
where Qvent is the amount of heat required to heat the air to a temperature tw(unit W),
c is the specific heat capacity of air(always equals 0.28 W/(kg*°C)),
m is the mass of air to be heated.
All quantities except the mass of air are known. Mass is defined as the product of the density of air and its volume. The density depends on the temperature outside. This indicator does not need to be calculated, because its values \u200b\u200bfor different temperatures are recorded in reference books. The owner of a home-made steam device can only take a reference book and make a selection of an indicator that corresponds to the coldest weather in his region.
As for the volume of air, this indicator must be calculated for different rooms of the house separately and then the sum of all the results should be determined. If this is not a kitchen and a bathroom, then this indicator is equal to the volume of the room. At the same time, it is taken into account that air volume should change every hour. Supply air rate for a kitchen with a gas stove is 100 m³ / h, for a bathroom - 25 m³ / h. Standards for other rooms can be found in the relevant documents.
When the calculation of the amount of heat required for heating is completed, the result is added to the heat loss through the structural elements of a private house. The final figure is the power of a steam or hot water solid fuel boiler.
 Masonry mortars for brick kilns
Masonry mortars for brick kilns Why do the windows fog up in the apartment
Why do the windows fog up in the apartment Construction and schemes of brick ovens
Construction and schemes of brick ovens How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks
How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks How to drill bathroom tiles
How to drill bathroom tiles Monolithic slab on coarse soil
Monolithic slab on coarse soil Which electric heater is economical
Which electric heater is economical