Gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m²
The nominal gas consumption for heating a house is 100 m², for a month or for the entire heating period, if the system has already been installed and has been in operation for a long time, it is quite simple to calculate - it will be enough to take meter readings at the beginning and at the end of the month during the year, sum them up, and then calculate arithmetic mean parameter. Another thing is if you need to know this data at the stage of drawing up a house project in order to make a choice of an economical and efficient energy source and appropriate heating equipment.
Therefore, the question of how to correctly determine the weighted average gas consumption for heating a building of a given area is so important. There are several options for such calculations.
The procedure for carrying out calculations for heating with network gas supply
Natural gas supplied to consumers through engineering networks is by far the most optimal energy carrier for organizing a heating system for private housing. This is due to the low price of fuel, the absence of the need to create its reserves, and the rather high efficiency of modern gas equipment.
Naturally, when choosing a gas boiler for heating a house, it is necessary to focus on its power, since not only the efficiency of the entire heating system, but also the energy consumption will depend on it. However, gas consumption is affected not only, and not so much by the power of the boiler, but by many other factors that should also be taken into account. These include the climatic conditions of the region of residence, the design features of the building itself, the area and height of the ceilings of heated rooms, the quality of insulation of building structures, the number and type of windows, and other important parameters.
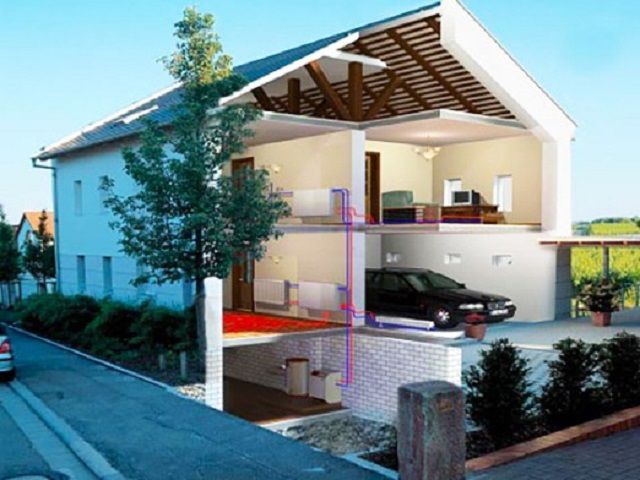

It should be understood that the nameplate power of the boiler shows its maximum capabilities, which, of course, must be higher than the required characteristics. So, for example, after making calculations in the required heat output for heating a house, the optimal model of the heater is always selected with higher rates. For example, if as a result of calculations it is obtained that the heating system requires 12-13 kW, then the owner will most likely select a boiler with a power of about 15-16 kW.
All this is being said now in order to make it clear: it would be erroneous in the preliminary calculation of gas consumption for heating and planned costs to rely only on the characteristics indicated in the technical documentation of the boiler. The list of product parameters usually contains gas consumption (m³ / h), but this, again, is to achieve the power declared by the manufacturer. If we take these indicators as a basis, then the total results may seem daunting!
But it is necessary to correctly calculate at least an approximate gas consumption not only in order to make sure that it is the most economical fuel, but also to determine what measures can be taken to reduce consumption, and hence reduce regular payments for it.
The main indicator from which you need to start the calculations is, rather, not the declared power of the heating device, which is still unlikely to be used "to its fullest", but the necessary thermal power for high-quality heating of the house and replenishing its heat losses.
Very often, the ratio of 1 kW of thermal energy per 10 m² of heated space is taken as the basis for such heat engineering calculations. This approach, of course, is very convenient for calculations, but still does not fully reflect the real conditions of a particular house and region of residence.
It is better to make a more thorough calculation, taking into account the main factors affecting the required thermal power. It is quite easy to do this if you use the method proposed on our portal.
How to independently calculate the required thermal power?
An accessible methodology for conducting independent calculations is given in the publication of the portal dedicated to.
The value obtained as a result of the calculations will become the “starting point” for determining the average gas consumption for heating.
Further calculations will require a formula that takes into account the energy potential embedded in the "blue fuel", that is, the amount of heat that is released during the combustion of one cubic meter of gas.
V = Q / (Ni × ηi)
Let's decipher the notation:
- V- the desired value, that is, the gas flow to obtain a certain amount of thermal energy, m³ / h.
- Q- the required thermal power, W / h, to ensure comfortable conditions in the premises.
How to calculate it - already decided. But again, an important remark needs to be made. As can be seen from the calculation conditions, the obtained value will be the maximum calculated for the most unfavorable conditions of the coldest decade of the year. In reality, there will not be so many such periods during the entire heating season, and even a boiler with a well-planned heating system never works constantly. And since our goal is to determine exactly the average, and not the peak gas consumption, it will not be a big mistake to take the average value of the generated power as 50% of the calculated one. Again, not to be confused with the nameplate capacity of the heating boiler.
- Hi- specific lower calorific value of gas combustion. This is a calculated tabular value that complies with existing standards. So, for network gas, it is taken equal to:
Pay attention to the type of gas. Most often, G20 is used in household networks. But the gas of the same second group can also be used, but already of the G25 type, which is characterized by a high nitrogen content. Naturally, its energy potential is less. If you do not know what type is used in your network, it is easy to check with the regional gas supply organization.
One more nuance. There is one more value in the table - hs. This is the so-called higher value of the calorific value of gas. The point is that the water vapor formed during the combustion of gas also has latent thermal energy, and if it is used, then the overall return on fuel naturally increases. It is this principle that is applied in a new generation of boilers - condensing, in which, due to the transfer of steam to a liquid state of aggregation, another 10% of heat is taken. That is, the indicated indicator can be taken as a basis for calculations for heating systems with boilers of this type.
The specific heat of combustion is indicated in joules, but for the correct calculation it must be converted to watts. The ratio is as follows:
1 kW = 3.6 MJ
In our case it turns out:
- ηi- the efficiency of the boiler, that is, a value showing how efficiently in a particular model the thermal energy obtained from gas combustion is spent precisely on heating the coolant.
This is the passport value of the product. In modern models of boilers, it can also be indicated by two values \u200b\u200b- according to the highest and lowest calorific value of gas, through a fraction sign: Hs / Hi, for example, 92.3 / 84%. Naturally, you can choose a value corresponding to the actual operating modes of the boiler. But, as a rule, for a reliable calculation, “without embellishing” the capabilities of the equipment, the value for the Hi mode should be taken.
So, all the data for the calculation are known - and you can proceed to practical calculations. Let's look at an example:
Suppose it was calculated that 9.4 kW of thermal energy is needed to effectively heat a particular house of 100 m². Network gas - G20. Boiler efficiency - 0.88. It is required to determine the average gas consumption for heating.
As already mentioned, to determine the average flow rate, the required thermal power can be divided by two, that is, we take for calculations 9.4 / 2 = 4.7 kW
V = 4.7 / (9.45 × 0.88) = 0.565 m³/h
- For a day, on average, it is spent - 0.565 × 24 = 13.56 m³;
- Monthly average - 13.56 × 30.5 = 413.71 m³;
- The heating period in different regions may differ in its duration. But, for example, take 7 months:
413.71 × 7 = 2896 m³
Knowing the price of one cubic meter of gas, you can roughly plan your "accounting" for the upcoming heating season.
Once again, it should be emphasized that the resulting value of consumption per hour is a very average. Of course, at the peak of winter frosts it will be higher, but then it will “recoup” in the autumn or spring months, during thaws or during periods of stable weather normal for the region.
To simplify the task for the reader, we will place a calculator that will help determine the average hourly, daily and monthly consumption of natural gas. The total costs will then be easy to calculate, given the approximate duration of the heating season in the region and the level of prices for "blue fuel".
 Masonry mortars for brick kilns
Masonry mortars for brick kilns Why do the windows fog up in the apartment
Why do the windows fog up in the apartment Construction and schemes of brick ovens
Construction and schemes of brick ovens How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks
How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks How to drill bathroom tiles
How to drill bathroom tiles Monolithic slab on coarse soil
Monolithic slab on coarse soil Which electric heater is economical
Which electric heater is economical