Gable roof truss system
The truss system of a gable roof, along with mauerlats, is the most important part of the design of a building with a gable roof type.
In gable roofs, both roofing surfaces are inclined towards the outer walls of the building, which ensures a natural runoff of rainwater and melted snow. The slope of such roofs should exceed 5 degrees, and in some areas of the roof it can reach 90 degrees.
The slope of the roof slopes depends on its material, architectural requirements for construction, as well as the climatic conditions of the region. Steep pitched surfaces are installed when using loose roofing material (for example, metal tiles), as well as during construction in areas with high rainfall. A more sloping roof is installed in areas with strong winds in order to reduce their pressure on the roof structure.
The device of Mauerlat and roof truss systems is more labor-intensive and requires significant material and time costs. But this is not the place where you should save money - you need to calculate the optimal angle of inclination of the roof, which will ensure the reliability and strength of the structure in accordance with all building standards and safety regulations.
A gable roof is considered the most optimal roof design option in suburban construction. This type of roof, with its simple shape and uncomplicated design, is built easily and quickly enough, and if the budget is limited, this can be done even without the involvement of outside construction specialists. In other words, you can mount a gable roof with your own hands, having the desire and knowledge base for construction.
The gable roof consists of two rectangular planes - slopes inclined towards the outer walls of the building, as well as triangular (side) elements - gables. This type of roof is most often installed on low-rise buildings.
The design of a gable roof assumes the presence of load-bearing (mauerlat and roof truss system) and enclosing (roofing) elements. In addition, in the designs of gable roofs there are also various racks, crossbars, struts, struts and other fasteners that give the truss system additional rigidity.
The main part of the external weather influences on the building, as well as the entire mass of the roof structure, is assumed by the load-bearing elements, which distribute the load on the supports and walls of the building. They are subject to particularly stringent strength requirements. There are two elements of the supporting structure of roofs - the truss system and the mauerlat.
Features of the installation of Mauerlats and truss systems of gable roofs
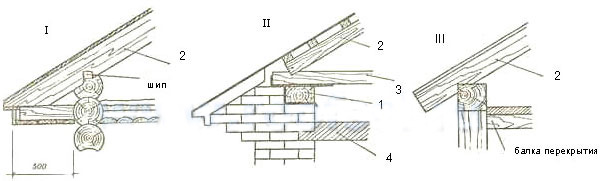 1 - Mauerlat; 2 - rafter leg; 3 - puff; 4 - overlap.
1 - Mauerlat; 2 - rafter leg; 3 - puff; 4 - overlap. Before analyzing in detail the roof truss system, let's consider a slightly different, but no less important load-bearing element - the Mauerlat.
- a kind of foundation for the roof of the house; support beam for inclined rafters, the main function of which is a balanced distribution of loads created by the roof of the building. This structural element of the roof is a bar with a section of at least 10x10 cm (usually 15x15 cm).
Mauerlat is placed under the rafter leg or installed along the entire length of the building. It is mounted on the upper wall edge, and depending on the structural features of the wall and roof of the building, it can be installed either along the axis or closer to the edge of the wall (internal or external, but not less than 5 centimeters from the outer edge).
In the manufacture of Mauerlat, wood is usually used. But if a metal roof frame is being built, channel, I-beam and other metal-profile mauerlats can be used. In fact, the roof is a large sail, therefore, in order to avoid its deformation by the wind, the mauerlat beam must be attached to the wall as securely as possible.
Mauerlat is laid on top of roofing material or other waterproofing material at a distance of at least 40 centimeters from the top of the attic floor. The runs are supported by racks cut into the beds at intervals of 3-5 meters. The angle between the rafter leg and the strut should be close to a straight line (90 degrees). Additional support struts, which rest on the beds, are installed with a greater length of the rafter legs.
In general, the mauerlat is a system of interconnected links that are attached to the rafters, thereby creating a very reliable and stable pitched structure along the perimeter of the roof. In separate segments, the Mauerlat can be placed under the rafters themselves.
If narrow rafter legs were used, then this exposes the structure to the risk of sagging. In order to prevent this, a special reinforcing grid is used, which consists of a rack, crossbar and struts. For its manufacture, boards 25 mm thick and 150 mm wide are used, or wooden plates made of logs with a diameter of at least 130 mm.
The roof truss system is a supporting structure of a pitched roof, which consists of rafter legs, inclined struts and vertical posts. With the help of fasteners (racks, crossbars, struts, struts, etc.), the rafters are connected into the actual rafter system. The material from which the rafters are made can be the most diverse: wood, metal, reinforced concrete or mixed.
The design of the roofs and the truss system of the gable type is based on a triangle, since this is the most rigid and stable geometric figure.
The cross section of the beam for rafters recommended for a simple roof structure can vary from 40x150 mm to 100x250 mm. This indicator depends on the installation step of the rafters, the length of the rafter legs, as well as the calculated value of snow and wind loads for a given region.
| Rafter installation step (m) | Rafter element length (m) | ||||||
| 3,0 | 3,5 | 4,0 | 4,5 | 5,0 | 5,5 | 6,0 | |
| 0,6 | 40x150 | 40x175 | 50x150 | 50x150 | 50x175 | 50x200 | 50x200 |
| 0,9 | 50x150 | 50x175 | 50x200 | 75x175 | 75x175 | 75x200 | 75x200 |
| 1,1 | 75x125 | 75x150 | 75x175 | 75x175 | 75x200 | 75x200 | 100x200 |
| 1,4 | 75x150 | 75x175 | 75x200 | 75x200 | 75x200 | 100x200 | 100x200 |
| 1,75 | 75x150 | 75x200 | 75x200 | 100x200 | 100x200 | 100x250 | 100x250 |
| 2,15 | 100x150 | 100x175 | 100x200 | 100x200 | 100x250 | 100x250 | - |
Below are the sections of the beams of other elements of the gable roof truss system (all indicators are in millimeters).
- Mauerlat: 100x100, 100x150, 150x150;
- diagonal legs and valleys: 100x200;
- runs: 50x150;
- racks: 100x100, 150x150;
- support crossbars for racks: 100x150, 100x200;
- filly, struts, boards of the cornice box: 50x150;
- puffs: 50x150;
- frontal and hemming boards: 22 ... 25x100 ... 150.
The basis of the roof truss system are rafter legs or just rafters. They are laid at an angle that is equal to the slope of the roof slope, and the lower ends are attached with metal brackets or strips to the Mauerlat.
You should also pay attention to the material from which the roof will be built. First of all, whatever material you choose, it should not have cracks and rot. Knots are also undesirable, but if perfectly even material is not available to you, the allowable length of knots should not exceed a third of the thickness of the board.
The rafter board must be at least 50 millimeters across. The width of the material depends on its length. For example, if a board is 6 meters long, it should be 15 centimeters (150 millimeters) wide. If the length of the beam exceeds 6 meters, then its width, respectively, must be at least 180 millimeters. The optimal ratio of all parameters of the source material for the rafters will prevent bending and breaking of the entire structure.
The final stage of the installation of the roof truss system is the connection of all its elements with the help of fasteners. For these purposes, metal corners or staples are most often used, although bolt fastening has also recently gained popularity.
The construction of a "warm" gable roof has its own characteristics. In this case, the rafter legs should be installed from each other at such a distance as to cut off the heat-insulating material as little as possible, which is laid in the inter-rafter space.
Types of truss systems for gable roofs and their calculation
The structural features of the truss structure of a gable roof depend on a number of factors, such as: the shape of the roof, the number of internal supports, the size of the span between the supports, the nature and intensity of the action of loads and external factors on the crate, etc.
Rafter legs are the main element of the truss structure. They are placed along the slope of the roof and act as a support for the crate. The gable roof sheathing is mounted from boards and battens, while the second option will be more economical.
Roof rafters in such structures have two varieties - hanging (they rest on the walls of the building only with the ends, without intermediate supports) and layered (they rest on the walls of the building with the ends and the middle part). Let's briefly consider the features of each of the two types of rafters.
Hanging roof rafters are used in the construction of buildings with light walls. One of the main advantages of this type of rafters is that they can be used to span long spans. This element of the truss system works in compression and bending.
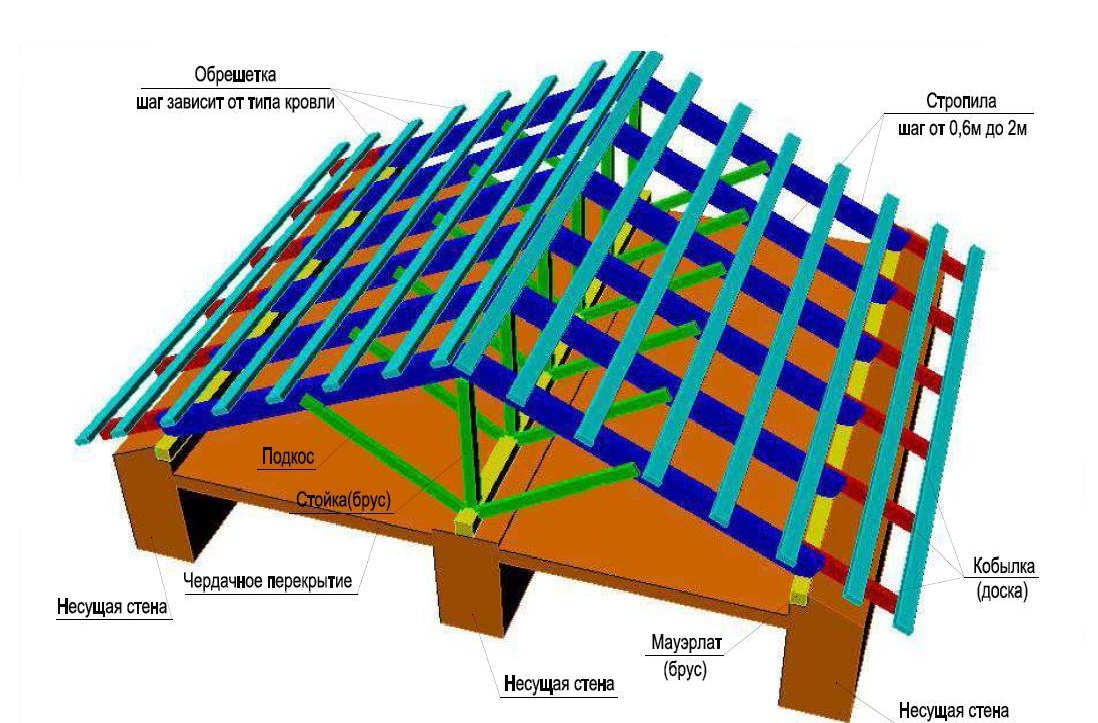
Due to their structural features, hanging rafters can only transfer the load to the two extreme supports, which are often the walls of the building. A strong horizontal bursting effect acts on the rafters.
In order to reduce this and prevent the rafters from moving around, wooden or metal puffs are used. They are attached at the base of the rafters. With a span of more than 8 meters, a beam with struts is installed parallel to the tightening. If the span is less than 8 meters, a crossbar is inserted between the top of the rafters and the puff parallel to the latter.
The higher the fastening puff is set, the more reliable and durable its connection with the rafters should be, regardless of what material they are made of. All this is aimed at reducing the deflection and containment of the spreading of the rafter legs. Such a scheme of supports is most often used in roof truss systems of mansard roofs.
The layered type of rafters is applicable in buildings where there are columnar intermediate supports or an average load-bearing wall. They can be installed with a span between supports of no more than 6.5-7 meters. Installation of additional supports will increase the width of the ceiling: one support - up to 11.5-12 meters, two supports - 15-15.5 meters. To increase the rigidity of the rafter system and expand the opening between the side supports, a rack with struts is installed under the ridge run.
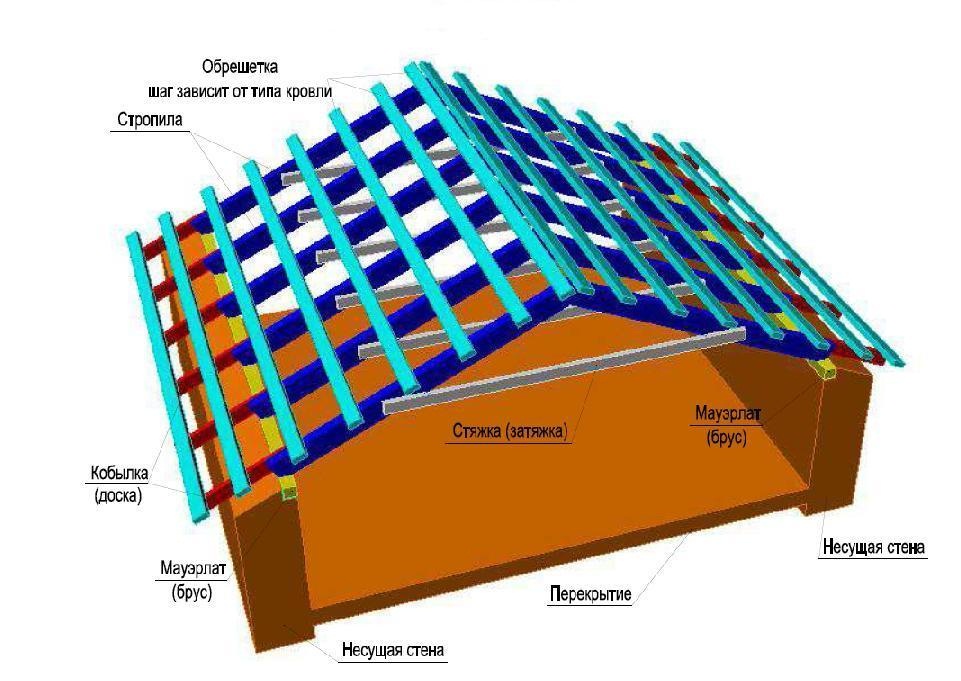 Scheme of layered rafters
Scheme of layered rafters Depending on the material from which the house is built and the structure of the building itself, the nature of the support of the roof rafters depends. In frame houses, they rest on the Mauerlat, in chopped or cobbled houses - on the upper crowns, in stone buildings - on the upper trim.
Fire safety requirements are imposed on the truss systems of gable roofs of houses with gas boilers or stove heating. The minimum distance at which the outer walls of the chimneys and chimney should be located from the wooden elements of the building is 40 centimeters. Thus, the middle part of the rafters transfers the load to the internal walls or supports, and the ends - to the external walls of the structure.
A roofing system based on roof rafters is easier to assemble and lighter than similar systems with the same parameters. In addition, the use of a layered type of rafters saves lumber and, accordingly, the developer's financial resources. If, within the framework of one roof structure, layered and hanging rafters are installed over several spans at once, then in this case the option of alternating them in different combinations is allowed.
Installing the truss system is the most time-consuming and important part of the entire process of building a gable roof. It requires accurate calculations of the size and number of rafters, as well as their most optimal connection with other roof elements. Therefore, the calculation of the roof truss system requires a careful and responsible approach, since the safety and durability of the entire structure under construction depends on its accuracy.
There are various guides and web resources that can help the builder in calculating the truss system. But it is still recommended to leave this part of the installation of a gable roof into the hands of specialists, given that the project of the house still needs to be ordered. The finished project will have all the necessary calculations, and the roof scheme itself.
To calculate the roof truss system, the following conditions are needed. First, the roof must be strong. This requirement is due to the fact that both the weight of the roof and external weather factors (wind, precipitation) will affect the roof. This can also include the weight of a repairman. Secondly, the lightness of the roof structure. It is determined by the need to reduce its pressure on the walls, ceilings and foundation of the house.
 Masonry mortars for brick kilns
Masonry mortars for brick kilns Why do the windows fog up in the apartment
Why do the windows fog up in the apartment Construction and schemes of brick ovens
Construction and schemes of brick ovens How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks
How to lay paving slabs: tips and tricks How to drill bathroom tiles
How to drill bathroom tiles Monolithic slab on coarse soil
Monolithic slab on coarse soil Which electric heater is economical
Which electric heater is economical