Ancient Rome. Roman Empire History of the Ancient World. Presentation on the theme of the early empire the first emperors

1. Early empire 30 BC e. - Octavian - 1st emperor (August). Beginning of an empire. Formally, “restorer of the republic”. provincial reform. Officials have power. Army reform. Strengthening the borders. «Return to the values of ancestors». Cult of August. Rise of culture – Horace, Ovid, Virgil. Heirs - despotism, civil war, weakening of the senate. Nero. Octavian August

1. Early empire Antonine dynasty II c. BC e. – Rise of the empire. Trajan (AD) is the “best” emperor. Support for the poor, agriculture, defeat, Dacians and Parthians. Marcus Aurelius (161 - 180) - a philosopher on the throne, following ethical standards. Victory over the Parthians and Germans. Edict of Caracalla in 212 - citizenship to the free inhabitants of the empire. Emperor Trajan

1. The early empire The emergence of Christianity Jesus Christ in Judea under the emperors Augustus and Tiberius. Convicted by Pontius Pilate and executed in Jerusalem. (Sacrifice for the atonement of the sins of mankind). The leaders of Christianity are the apostles. Gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke and John - New Testament. Christian communities. Pre-sweaters. Bishops. Peter and Paul - Church. Persecution - Nero, Diocletian (I-III centuries). Rembrandt. Resurrection of Christ

1. Early empire 3rd century AD e. - The systemic crisis of the empire. External danger. Reduction of slaves. The impoverishment of farmers - Colony (for life). Slave uprisings. Reducing trade. Tax increase. "Soldier" emperors. In the army - the provincials. Lack of funds for maintenance. The provinces are trying to get out of the control of Rome Germanic warriors

2. Late Empire 284 - 305 — Diocletian. Dominat. Honor as Jupiter. The three assistants are part of the empire. Single land tax. Division into 12 regions. Ranking of officials. Taxpayers are included in the qualification (inventory). The population is attached to the place of residence and profession. The process of the collapse of the empire slowed down. Emperor Diocletian

2. Late Empire 306 - 337 - Constantine I the Great. 313 - Ediolan Edict - religious tolerance. Church support. Arianism: God the Son is not equal, but “like in essence” to God the Father. 325 - Council of Nicaea - Creed (book of dogmas), condemnation of Arianism. 330 - Capital in Constantinople. Columns to the ground. 395 - Division into Western and Eastern empires. Western and Eastern Roman Empires

2. Late Empire IV - V centuries. The Great Migration of Nations. The main enemies are the Germans (Goths, Vandals) and the Huns. 378 - The Goths defeated the Roman army. 408, 410 - Alaric to Rome. Ransom. Liberation of 40 thousand slaves. Again, fall, ruin. 451 - Catalunian fields. Huns. Death of Attila. But: 476 - Odoacer overthrew Romulus Augustus. Imperial regalia to Constantinople. Romulus Augustus presents the crown to Odoacer

To use the preview of presentations, create a Google account (account) and sign in: https://accounts.google.com
Slides captions:
Roman Empire under Constantine
1. Invasion of the barbarians. Since the time of Trajan, the Romans have not waged wars of conquest. But barbarians constantly invaded the empire. This was the name of the peoples whose language the Greeks and Romans did not understand, which seemed to them wild and uneducated.
Emperor Constantine at the beginning. 4 centuries in the struggle for power won one of the generals - Constantine.
Read paragraph 2 of §59 and answer the questions: How did Konstantin dress? What was the power of Constantine? How did the army change under him? Who could serve in the army under Constantine?
By his order, the Arc de Triomphe was erected in Rome. For the first time, such an arch was installed not in memory of the defeat of an external enemy, but in honor of the victory of some Romans over others.
3. Attaching the columns to the ground. Remember - who are the columns? In addition to part of the harvest to the owner of the land, they now had to pay tax to the imperial treasury. The columns began to leave their sites. In response to this, Constantine issues a decree forbidding the columns to leave their lands, thereby attaching them to the ground.
4. Changes in the position of Christians. Constantine realized that Christians were not calling for the overthrow of the emperor and the destruction of the Roman state. After all, even the Apostle Paul taught: "There is no power except from God; he who opposes the authority opposes God's establishment." In 313, Constantine issued a decree allowing Christians to build temples and openly pray. Apostle Peter - crucified on the cross upside down
Enrique Simone, The Beheading of St. Paul (1887)
Note: The bishop is the leader of the Christians of an entire area. Soon the bishops got together and agreed to create a single church for the entire empire - an organization of Christians.
Church leaders have determined which books written about Jesus and his teachings are considered sacred. These books were brought together to form the second part of the Bible, the New Testament.
Among the Christians, the bishop of the city of Rome gained great influence. He began to call himself the pope (in Greek "papas" - 2 "father"). According to legend, the first bishop of Rome was the disciple of Jesus, the apostle Peter, so the popes consider themselves his successors.
Baptism of Emperor Constantine. niistali.narod.ru
Holy Equal-to-the-Apostles Emperor Constantine. During the reign of the Roman Emperor Constantine, the persecution of Christians ceased. Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire in 325.
Agreement
Rules for registering users on the site "QUALITY SIGN":
It is forbidden to register users with nicknames like: 111111, 123456, ytsukenb, lox, etc.;
It is forbidden to re-register on the site (create duplicate accounts);
It is forbidden to use other people's data;
It is forbidden to use other people's e-mail addresses;
Rules of conduct on the site, forum and in the comments:
1.2. Publication of personal data of other users in the questionnaire.
1.3. Any destructive actions in relation to this resource (destructive scripts, password guessing, violation of the security system, etc.).
1.4. Using obscene words and expressions as a nickname; expressions that violate the laws of the Russian Federation, the norms of ethics and morality; words and phrases similar to the nicknames of the administration and moderators.
4. Violations of the 2nd category: Punishable by a complete ban on sending any type of messages for up to 7 days. 4.1. Placement of information falling under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation and contrary to the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
4.2. Propaganda in any form of extremism, violence, cruelty, fascism, Nazism, terrorism, racism; inciting interethnic, interreligious and social hatred.
4.3. Incorrect discussion of the work and insults to the authors of texts and notes published on the pages of "QUALITY SIGN".
4.4. Threats against forum members.
4.5. Placing deliberately false information, slander and other information discrediting the honor and dignity of both users and other people.
4.6. Pornography in avatars, messages and quotes, as well as links to pornographic images and resources.
4.7. Open discussion of the actions of the administration and moderators.
4.8. Public discussion and evaluation of existing rules in any form.
5.1. Mat and profanity.
5.2. Provocations (personal attacks, personal discrediting, the formation of a negative emotional reaction) and harassment of participants in discussions (the systematic use of provocations in relation to one or more participants).
5.3. Provoking users to conflict with each other.
5.4. Rudeness and rudeness towards interlocutors.
5.5. The transition to the individual and the clarification of personal relationships on the forum threads.
5.6. Flood (identical or meaningless messages).
5.7. Intentional misspelling of nicknames and names of other users in an offensive manner.
5.8. Editing quoted messages, distorting their meaning.
5.9. Publication of personal correspondence without the express consent of the interlocutor.
5.11. Destructive trolling is the purposeful transformation of a discussion into a skirmish.
6.1. Overquoting (excessive quoting) messages.
6.2. Use of red font, intended for corrections and comments of moderators.
6.3. Continuation of the discussion of topics closed by the moderator or administrator.
6.4. Creating topics that do not carry semantic content or are provocative in content.
6.5. Creating the title of a topic or message in whole or in part in capital letters or in a foreign language. An exception is made for titles of permanent topics and topics opened by moderators.
6.6. Creating a caption in a font larger than the post's font and using more than one palette color in the caption.
7. Sanctions applied to violators of the Forum Rules
7.1. Temporary or permanent ban on access to the Forum.
7.4. Deleting an account.
7.5. IP blocking.
8. Notes
8.1. The application of sanctions by the moderators and the administration can be carried out without explanation.
8.2. These rules are subject to change, which will be reported to all site members.
8.3. Users are prohibited from using clones during the period of time when the main nickname is blocked. In this case, the clone is blocked indefinitely, and the main nickname will receive an additional day.
8.4 A message containing obscene language can be edited by a moderator or administrator.
9. Administration The administration of the site "ZNAK QUALITY" reserves the right to delete any messages and topics without explanation. The site administration reserves the right to edit messages and the user's profile if the information in them only partially violates the rules of the forums. These powers apply to moderators and administrators. The Administration reserves the right to change or supplement these Rules as necessary. Ignorance of the rules does not release the user from responsibility for their violation. The site administration is not able to check all the information published by users. All messages reflect only the opinion of the author and cannot be used to evaluate the opinions of all forum participants as a whole. The messages of the site staff and moderators are an expression of their personal opinion and may not coincide with the opinion of the editors and site management.
slide 1
Description of the slide:
slide 2
Description of the slide:
slide 3
Description of the slide:
slide 4
Description of the slide:
slide 5
Description of the slide:
slide 6
Description of the slide:
Slide 7
Description of the slide:
Slide 8
Description of the slide:
Slide 9
Description of the slide:
German emperors… The imperial title did not give the kings of Germany much additional power, although theoretically they stood above all the royal houses of Europe. The emperors ruled in Germany using already existing administrative mechanisms, and interfered very little in the affairs of their feudal vassals in Italy, where their main support was the bishops of the Lombard cities. Beginning in 1046, Emperor Henry III gained the right to appoint popes, just as he held in his hands the appointment of bishops in the German church. He used his power to introduce in Rome the ideas of church government in accordance with the principles of canon law (the so-called Cluniac reform), developed in the area lying on the border between France and Germany. After Henry's death, the papacy turned the principle of freedom of the "divine state" against the authority of the emperor in matters of ecclesiastical government. Pope Gregory VII asserted the principle of the superiority of spiritual over secular power and, in what went down in history as the "struggle for investiture", which lasted from 1075 to 1122, launched an attack on the emperor's right to appoint bishops.
Slide 10
Description of the slide:
slide 11
Description of the slide:
Hohenstaufen on the imperial throne. The compromise reached in 1122 did not lead to final clarity on the question of supremacy in state and church, and under Frederick I Barbarossa, the first emperor of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, who took the throne 30 years later, the struggle between the papacy and the empire flared up again, although with a specific the reason for it was now disagreements about the ownership of Italian lands. Under Frederick, the words "Roman Empire" for the first time added the definition "Sacred", which indicated the belief in the sanctity of the worldly state; this concept was further substantiated during the revival of Roman law and the revival of contacts with the Byzantine Empire. This was the period of the highest prestige and power of the empire. Frederick and his successors centralized the system of government in their territories, conquered the Italian cities, established feudal suzerainty over states outside the empire, and, as the Germans moved east, extended their influence in this direction as well. In 1194, the Kingdom of Sicily passed to the Hohenstaufen - through Constance, daughter of King Roger II of Sicily and wife of Emperor Henry VI, which led to the complete encirclement of papal possessions by the lands of the Holy Roman Empire.
slide 12
Description of the slide:
slide 13
Description of the slide:
Slide 14
Description of the slide:
slide 15
Description of the slide:
slide 16
Description of the slide:
Slide 17
Description of the slide:
Slide 18
Description of the slide:
 Substances and their physical properties
Substances and their physical properties Classification, structure, nutrition and the role of bacteria in nature
Classification, structure, nutrition and the role of bacteria in nature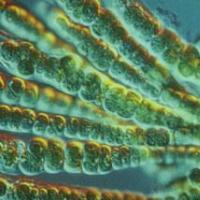 Bacteria - the most ancient organisms on Earth Bacteria - the oldest group of living organisms
Bacteria - the most ancient organisms on Earth Bacteria - the oldest group of living organisms Epithets, metaphors, personifications, comparisons: definitions, examples
Epithets, metaphors, personifications, comparisons: definitions, examples Bronchial asthma Bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma Bronchial asthma Roman Empire Ancient History
Roman Empire Ancient History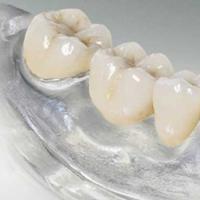 Flexible removable dentures: design, features and benefits Varieties of soft dentures with photos
Flexible removable dentures: design, features and benefits Varieties of soft dentures with photos