Design and principle of operation of refrigeration units. Calculation of the main structural elements of a household compression refrigerator Household refrigerators classification modern range of compression refrigerators
2. Classification and characteristics of the range of household refrigerators. Directions for improving their parameters
Household refrigerators and freezers are designed for short-term as well as long-term storage of perishable goods. food products, semi-finished and ready-made meals, chilled or frozen. The market for household refrigeration equipment has grown by an average of 20% annually over the past three years.
Refrigerators are a high-demand product, a fairly representative group in the consumer market, since they include a wide range of refrigerators of various brands and technical characteristics, and the formation of a preferred structure for the range of these goods in trade is of certain interest. The modern Russian refrigeration equipment market began to take shape in the early nineties and currently continues to actively develop. Estimates of market capacity given in various sources vary quite significantly. Thus, according to experts from the consulting house “Grifon”, today the capacity of the Russian refrigeration equipment market is 800 million US dollars.
There are many parameters by which modern household refrigerators are classified. The main ones are by purpose, operating principle, layout options, etc.
In our country, the production of refrigerators is determined by the requirements of GOST 16317-87 “Household electrical refrigeration appliances.” The standard applies to household electric compression and absorption refrigerators and household electric compression refrigerators-freezers intended for storing and (or) freezing food products in domestic conditions.
According to their purpose, refrigeration appliances are divided into refrigerators, freezers and refrigerator-freezers.
According to the method of obtaining cold - compression, absorption and thermoelectric.
According to the number of cameras - single-chamber, two-chamber, three-chamber and multi-chamber.
According to the installation method - floor-standing cabinet type, floor-standing table type, built-in wall-mounted, block built-in.
Ability to work at maximum temperatures environment Refrigeration appliances are divided into the following classes:
Class A (refrigerators): SN, N - not higher than 32 °C; ST - not higher than 38 °C; T - no higher than 43 °C.
Class B (freezers and refrigerator-freezers): N - not higher than 32 °C; T - no higher than 43 °C.
Depending on the temperature in the low-temperature compartment (LTC), refrigerators are marked as follows: one star (cooling to -6°C); two stars (cooling to - 12 C); three stars (cooling to - 18°C).
The designation on the freezer door (MK) is a combination of one large and three small stars. Two-chamber refrigerators, as a rule, are marked with four stars, which indicates the possibility of freezing products in them with the required temperature, thereby preserving their cellular structure.
Depending on the functions performed, refrigeration appliances are divided into complexity groups.
| Function performed | Complexity group and presence of function performed | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Refrigerated food storage | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Storing frozen food at temperatures: minus 6 °C minus 12 °C minus 18 °C | ||||||
| Freezing food | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Defrosting food with a special device | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Automatic defrosting of the refrigerator compartment evaporator (if equipped) | + | + | + | - | - | + |
| Automatic or semi-automatic defrosting of the NTO evaporator | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| Manual defrosting of the NTO evaporator | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| Light signaling of operating modes | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| Sound alarm about violation of operating rules | + | - | - | - | - | - |
Foreign refrigerators are divided into three comfort classes: functional class; comfort class; premium class.
The functional class meets the most important functional requirements for food storage conditions and the efficiency of the refrigerator in operation with an optimal combination of price and quality.
Comfort class refrigerators, in addition to the basic functions, also have additional functions that increase comfort and ease of use.
Premium refrigerators have the largest selection of functions and comfort elements
In order to be able to compare the characteristics of energy consumption when purchasing, in European countries all refrigeration and freezing equipment is equipped with the so-called “Euro sticker”, indicating the energy consumption. Devices from all manufacturers are divided into “energy consumption classes” on a five-point scale from A to G:
economical models (color of stickers on the body from dark green to yellow-green) - A, B and C;
intermediate class (yellow sticker) - D;
models with high power consumption (sticker color from orange to red) - E, F and G,
The energy consumption of home refrigerators is about 24% of the total energy consumption of home electrical appliances, exactly the same amount as energy costs for lighting. In this regard, it can be assumed in the future that the production of more advanced devices in terms of energy consumption will increase while simultaneously reducing the market share of inefficient products
Household refrigerators can be classified according to their design options as:
Universal single-chamber version, classic.
Freezer.
Single-compartment refrigerator without low-temperature compartment.
Two-chamber (multi-chamber) refrigerator.
Refrigerator without frost (No Frost)
Universal single-chamber version (aka regular, classic). Refrigerators of this class are made according to the simplest design with one evaporator, which simultaneously serves as a low-temperature compartment; this is what is commonly called a freezer. Designed for storing small quantities of products at low temperatures, and storing other products at temperatures close to 0°C. Throughout the refrigerator, the evaporator temperature is as low as possible, serving as an evaporator for storing frozen food. Cooling of the remaining volume of the refrigerator occurs from the evaporator due to natural convection of air inside the working space of the refrigerator below it. The temperature regime is maintained by a thermostat, which periodically, when the set temperature is reached, opens the electrical circuit, stops the operation of the motor-compressor, as soon as the temperature rises, the thermostat turns on the motor-compressor, closing the circuit, and the cycle repeats. The thermostat setting is such that it maintains the temperature in the freezer compartment in the range from -12°C to –18°C. The surface area of the evaporator is small compared to the total volume of the refrigerator; this does not make it possible to cool the entire volume to undesirable temperatures at which the food in the refrigerator compartment would freeze.
Freezer. Its design resembles a universal single-chamber version, it is also made with one evaporator, the only difference being that the evaporator occupies the entire working volume of the chamber, the surface area is large enough in relation to the volume, which allows you to effectively cool the entire space. The thermostat is configured in such a way as to provide an operating temperature in the range from –18°C to –24°C. Designed for long-term storage of a sufficiently large amount of food at low temperatures.
Single-compartment refrigerator without low-temperature compartment. It is made according to a simple design, with one evaporator, usually located vertically along the rear inner wall of the refrigerator. Designed for storing products in the temperature range from 0°C to +10°C. The design contains a heating element attached to the evaporator, the purpose of which is to remove frost formed during the operating cycle of the motor-compressor. The defrosting process occurs every time the thermostat turns off the motor-compressor when the evaporator has cooled to the set temperature. The thermostat is configured in such a way that it turns off, like all refrigerators, when the set temperature is reached, and turns on after all the frost has thawed from the surface of the evaporator. The constant, cyclically repeating presence of drops on the surface of such an evaporator explains its name - a “crying” type evaporator. By its design, such a refrigerator is half of a two-chamber refrigerator without a low-temperature compartment.
Two-chamber (multi-chamber) refrigerator. In the usual version, it is a refrigerator with evaporators connected in series, with one compressor, assembled together in a single housing, but installed in different compartments (chambers). The evaporator that is cooled first is installed in the low-temperature compartment (LTE). The second cooled evaporator is installed in the positive temperature compartment. Defrosting of the evaporator in the positive temperature compartment occurs automatically. However, there are options for assembling two (several) independent cooling systems in a single housing, each having a separate evaporator for each chamber, the operation of which is ensured by a corresponding number of compressors.
There are also “two-in-one” layout schemes, when it is possible to connect, or vice versa separate, the body of the freezer and refrigerator without HTO.
Refrigerator without frost (No Frost). By its design, it can be either single-chamber or multi-chamber, with or without NTO, or it can simply be a freezer of the No Frost system. The design of such a system uses a highly efficient fin evaporator, fan, timer and heating element. The finned evaporator used, paired with a fan, ensures sufficient cooling of the entire volume of the refrigerator. The timer ensures that the refrigerator periodically switches on to defrost mode at certain intervals. A heating element with increased power in defrost mode quickly removes the amount of frost that accumulates on the evaporator during operation of the refrigerator in operating mode. Thus, the refrigerator operates in a cyclically repeating mode, which eliminates the need for the user to defrost it manually.
Mini refrigerators. This category includes compression, absorption and thermoelectric refrigerators small size(height less than 850 mm). Compression mini-refrigerators can be used in offices and hotels, as well as for installation in minibars and display cases. Absorption mini-refrigerators are preferable for use in the country or on a tourist trip. They operate from a 12-volt car cigarette lighter, from a 220 V, 50 Hz network or from a gas cartridge with gas consumption from 180 to 250 g per day. Thermoelectric mini-refrigerators (volume up to 20 l) are used both for automobiles and portable
Directions for improving the parameters of refrigerators.
Designers create all new “new products”, and production carries out their development. Today the market offers two-, three- and multi-chamber refrigerators and combined refrigerators with “freshness” chambers, vertical and horizontal freezers, as well as universal cold Il-freezers and refrigerators with universal chambers.
Double-chamber refrigerators with top, bottom and side freezer compartments, with natural and forced air circulation, combined refrigerators with independent control By controlling the temperatures in the chambers, with 1 and 2 compressors, multifunctional and universal refrigerators are able to satisfy the needs of the most demanding customers. Multifunctional and multi-chamber refrigerators provide the ability to freeze and store products in various states (fresh, chilled and frozen).
Universal refrigerators allow you to change operating modes in the chambers depending on changes in circumstances in the family. A universal refrigerator can be used to store frozen meat in one season, and in another to store fruit supplies in the “wet fresh” mode.
In order to improve the conditions of use and increase the shelf life of products, odor absorbers and lamps for infrared, ultraviolet and gamma radiation are installed in refrigerators. , as well as sections filled with nitrogen. Antibacterial irradiation helps slow down the proliferation of putrefactive and pathogenic bacteria.
For families who consume large quantities of chilled water and ice, the market offers refrigerators with built-in water coolers, ice makers and dispensers that allow Fill the glass with cold water, cubes or crushed ice without opening the refrigerator door. Prestigious models have bars with separate doors through which you can get chilled drinks without opening the large refrigerator compartment.
Refrigerators with increased comfort have a device for semi-automatic or automatic defrosting of the CC evaporator with removal of melt water, plus at least one more of the following devices:
Maintaining a certain humidity in the cold storage room;
Cooling drinks and dispensing them without opening the door;
Operating mode alarms;
Limitations on the door opening angle;
Forced closing of the door when opening at an angle of less than 10°;
Rearranging shelves in height at intervals of less than 5 cm;
Extending the loaded shelf to a distance of at least 50% of its depth.
Modern refrigerators also use other devices that improve the consumer qualities of the device:
sound alarm about too long open door;
removal of the temperature regulator to the external control panel;
installation of a mechanical or digital temperature indicator in the chamber on this panel, etc.
The refrigerator compartments of some foreign refrigerators are equipped with a defrost - a small compartment with a fan that provides intensive air circulation through this compartment. The fan is turned on via a time relay, which allows you to set a certain duration of its operation, depending on the mass of the defrosted product. This device allows you to speed up the defrosting process at low temperatures in the cold storage room.
It is also proposed to use built-in microwave defrosters and sublimators, as well as chambers for long-term storage of products in a gaseous environment.
Some foreign companies (Samsung, LG Electronics) install air purifiers and lamps coated with special ceramics inside the refrigerator to slow down the process of food spoilage, emitting in the infrared range.
Modern foreign models consider the prospects of microprocessor control systems in household appliances. The introduction of electronic diagnostics to monitor the operation of complex systems was a step towards the creation of computerized refrigerators. Computerized control allows you to set and control the storage conditions of products and the operation of the refrigerator, conduct electronic self-diagnosis of faults and promptly resolve , both troubleshooting problems and daily operation tasks.
Improving the design of electronic components opens the way for computerized refrigerators. Such models are already present in the markets of America and Europe. A built-in microcomputer with Internet access allows you not only to control the contents of the refrigerator, but also to place orders for products without leaving home.
It would be absolutely wrong to believe that the advanced technical solutions used today in the best refrigerator models are the prerogative of only distant foreign manufacturers. Firstly, recently the geography of refrigerator production has moved closer to the Russian consumer (Vestel, BEKO, LG, etc. have opened factories in our country), and secondly, manufacturers in Russia and neighboring countries are successfully mastering new technologies.
Appendix 1 presents different kinds refrigerators, with all sorts of innovations and functions.
Leading manufacturers of refrigeration equipment
The wide variety of brands and models of refrigerators on the market today sometimes confuses consumers. To understand this abundance, let’s walk through the exhibition. household appliances and electronics, which took place at the Crocus Expo IEC. The exposition of refrigeration equipment included household refrigerators and freezers of mass demand, produced in Russia and abroad.
Each manufacturer is trying to occupy a certain niche in the market and establish itself in it as firmly as possible, so the leaders in the development of, say, refrigerators with fast dry freezing of food, are true professionals in their field. It is clear that it is difficult to cover all manufacturers on the Russian refrigerator market, so we will focus on those who are current sales leaders or have earned some name for themselves through the deeds of the recent past.
The range of domestic models included:
Among the compatriots, the new “Biryusa” refrigerators stood out, which can be considered as a presentation of the plant’s proposals for Russian buyers for the very near future. Krasnoyarsk refrigerator plant "Biryusa" showed models Italian design with electronic and electromechanical control.
The Podolsk plant presented refrigerators under the EXQVISIT brand.
The ZIL refrigerator plant showed two-chamber Korean-design refrigerators with non-freezing walls.
The Minsk plant produces units - Atlant - these are the refrigerators that can be recommended; their quality is quite comparable to their Western European counterparts, they are reliable and durable.
Stinol - economy-class refrigerators are quite suitable for operation in conditions where there are no excessive owner requirements for the equipment.
The Velikoluksky plant offered Morozko compression and thermoelectric refrigerators with solid and transparent doors.
The near abroad was represented by models of the Ukrainian group Nord under the Nord and Dnepr brands. Interestingly, in all Nord products, the refrigerator compartment and the inner door panel are made of special plastic, which contains silver ions and has bactericidal properties.
European refrigerators were presented by the most famous brands to Russian customers: AEG, BOSCH, SIEMENS, ELECTROLUX, WHIRLPOOL, BEKO. In addition to free-standing refrigerators, more expensive models built into furniture were shown at the exhibition. In order to provide bactericidal protection and increase the shelf life of fresh products, all leading European companies use plastic containing silver ions for the manufacture of internal chambers and door panels of refrigerators.
Two-chamber refrigerators with a top freezer from the WHIRLPOOL brand, made in Brazil, were models of a higher price range. Refrigerators are equipped with filters that can capture bacteria and mold spores, as well as odors from their activity.
AEG refrigerators are distinguished by high German quality and efficiency in operation, confirmed by class A+. They are focused on the convenience and comfort of the consumer. AEG SANTO refrigeration technology is the market leader in built-in refrigerators and freezers.
The two-chamber BOSCH stainless steel had a display at the top of the refrigerator door.
The prestigious SIEMENS had a built-in TV.
The most expensive model is the prestigious two-chamber ELECTROLUX with hinged doors, leather handles and wicker baskets.
Japanese refrigerators were represented by the SHARP and TOSHIBA brands. The attention of visitors was attracted by the improved 5-door model of the 4-chamber SHARP refrigerator with non-freezing walls. Instead of an ice maker, TOSHIBA two-chamber refrigerators have a rotating ice mold with a hopper. When turned manually, the ice mold bends and ice cubes pour out of it into the hopper.
Haier's two-chamber models had a top, bottom and side freezer compartment. Prestigious models had mirrors on the doors.
In the Hisense refrigerator, the universal chamber has an operating temperature range from +4° to -10°C.
The range of household refrigerators reflected the state of demand on the Russian market. Relatively inexpensive models with improved consumer performance were greatest number exhibits. Compared to previous exhibitions, the assortment has increased the share of refrigerators with forced air circulation in the refrigeration chamber, with electronic control and digital indication of temperatures in the chambers, with antibacterial protection of fresh products.
List of used literature
1. Andronova L.N., Gerasimenko O.A., Kapitsyn V.M. Ways for the textile industry to emerge from the crisis // Problems of forecasting. - 2000. - No. 2.
2. Babajanov S.G. Economics of clothing industry enterprises / S.G. Babajanov, Yu.A. Domozhirov. – M.: Academy, 2005. – 225 p.
3. Guseinova T.S. Commodity research of clothing and knitted goods: Textbook for the commodity research faculty of trade universities / T.S. Guseinova, G.V. Zhiltsova. – M.: Economics, 2005. – 280 p.
4. Zhukov Yu.V. Very good after many // Garment industry. - 2001. - No. 2.
5. Kochegarov B.E. Household machines and appliances: tutorial Part 1 / Refrigeration equipment // B.E. Kochegarov, V.V. Lotsmanenko, G.V. Oparin. – Vladivostok: Publishing House of Far Eastern State Technical University, 2004. – 166 p.
6. Moreva A.L. Modern tendencies development of the Russian clothing market // Light industry market. – 2007. - No. 49.
7. Rodionova N.P. Factors for increasing business efficiency of clothing industry enterprises // Light Industry Market. – 2006. - No. 46.
8. Russian statistical yearbook. - M.: ANO IIC “Statistics of Russia” - 2004. – 1020 p.
9. Teplov V.I. Commercial merchandising / V.I. Teplov, N.V. Seroshtan. – M.: NORM, 2001. – 620 p.
10. Tselikova L.V. Marketing research and directions for forming a preferred assortment of refrigerators in the consumer market / L.V. Tselikova, V.E. Sytsko, T.I. Tsybrankova and others - Gomel: BTEUPK, 2007. – 95 p.
11. Shishkina I.V. Commodity research and examination of haberdashery goods: Proc. manual for students of higher educational institutions / I.V. Shishkina. – M.: Publishing Center “Academy”, 2003. – 192 p.
Application
Refrigerator is different from refrigerator
Among the variety of refrigerators, we can distinguish free-standing and built-in models, portable and car appliances, refrigerators for medicines, ice makers and wine coolers, ice cream makers and refrigerators for drinks. The most widespread in our kitchens are free-standing models (they are also called “solo” models), but recently more and more buyers prefer built-in appliances. Freestanding and built-in refrigerators can be single-chamber, double-chamber and three-chamber. Single-chamber refrigerators, for example ARDO MP 16 SA, have only a chamber for cooling food and a small freezer (in the model under review, its volume is 22 l, and the volume of the refrigerator compartment is 102 l). In two-chamber refrigerators, for example in the Bosch KGS 36V01 for 24,300 rubles, one chamber (volume 227 l) is used for cooling food, and the other is used for freezing (volume 84 l). And in three-chamber models, such as the Toshiba GR-L42FR, the third chamber can often work either as a refrigerator or a freezer, and can also serve as a special “freshness zone,” which will be discussed below.
Most multi-compartment refrigerators are quite high, which is not always convenient, because sometimes it is very difficult for the housewife to put something on the top shelf. Fortunately, wide and low refrigerators with a large useful volume - up to 700 liters - were invented in America and soon became popular. Such refrigerators, in which the refrigerator and freezer compartments are located next to each other, and not above each other, are called Side-by-side. An example of such a device is the FRS-U20FET refrigerator from Daewoo Electronics. Thanks to know-how such as nano-silver technology and antibacterial coating, it can keep food fresh for a long time. It does not need to be opened to take ice cubes or pour a drink. cold water, it will serve perfectly as a home bar. It is easy to find a common language with it thanks to the accurate and convenient LCD display and electronic sensors for collecting climate information in different compartments of the refrigerator. Optimally organized space, low noise level, No Frost cooling system, Magic Cool zone - this is the gentleman’s set of the FRS-U20FET refrigerator, the price of which, fully equipped, is 49,990 rubles.
Game of classes
All refrigerators differ in comfort, energy saving and climate classes. The climate class (denoted by the letters N, ST, T) is determined by the maximum ambient temperature at which the operating parameters declared by the manufacturer are ensured. Refrigerators for temperate climates (N) should operate normally at ambient temperatures up to 32 °C, models for tropical latitudes (T) can withstand room temperatures up to 43 °C.
Comfort class is a conditional concept; it determines how well the refrigerator meets consumer needs and how ergonomic it is. In high-class comfort refrigerators, the doors should open easily, there should be convenient shelves inside, pull-out boxes and drawers, a shelf for horizontal storage of bottles, etc. It is worth noting that shelves in refrigerators can be lattice (made of metal) or glass. Transparent shelves protect the products below from accidental spills and facilitate hygienic cleaning, but impede air circulation. Lattice shelves, on the contrary, do not interfere with air circulation and contribute to more uniform cooling of products.
The energy standard is completely arbitrary. There are nine energy consumption classes: from A++ to G. Classes A++, A+, A and B correspond to the most economical models, classes C and D - models with moderate energy consumption. An A++ class refrigerator is approximately twice as economical as a G class refrigerator (however, G class appliances are probably no longer found on the market today). An example of a refrigerator with energy consumption class A+ is the ARDO DPF 41 SHX model, which belongs to the Special design line. The device with electronic temperature control and LCD display has a refrigerator compartment with a volume of 310 liters, a freezer compartment with a volume of 76 liters, and a freshness zone with a volume of 27 liters. The refrigerator has a compartment for making ice (ice cube space) and an antibacterial system, and a super freezing mode is provided. The surface of the refrigerator is subjected to special anti-fingerprint treatment.
It should be remembered that actual energy consumption depends on the characteristics of the cooling system, the thickness and quality of thermal insulation. When choosing a refrigerator, be sure to consider how economical it is.
When the wall cries
Modern refrigerators are equipped with a lot of additional functions that turn their operation into a real miracle.
Perhaps the most important “refrigeration” miracle is the No Frost system, which helps housewives save a lot of time without manually defrosting the refrigerator. The No Frost system prevents the formation of frost in the freezer. It is formed on a special heat exchanger outside the freezer, and even there it is periodically melted heating element As its layer thickens, it turns into water, flows into a special bath on the compressor and evaporates. Thus, refrigerators equipped with a No Frost system do not need defrosting at all. The only thing housewives have to keep an eye on is the correct packaging of products: if its integrity is damaged, food can quickly dehydrate and dry out, because cold (about -18°C) and dry air constantly circulates in the freezer with the No Frost system. It is this that removes all moisture from the freezer that can turn into frost and then into ice.
The No Frost system has now received universal recognition. Such a system is equipped, for example, with an Indesit BAN 35 FNF SD refrigerator with a refrigerator compartment of 280 liters and a freezer with a volume of 118 liters, a Hotpoint-Ariston MBT 1912 FI/HA refrigerator with the same dimensions of the refrigerator and freezer compartments, a Siemens KG 49NA71 refrigerator with a refrigerator compartment with a volume of 307 liters and a freezer compartment of 82 liters, and even such a giant as a side-by-side refrigerator, such as the Electrolux 7388 KG with a refrigerator compartment of 267 liters and a freezer compartment of 198 liters.
To help housewives, it was invented and automatic system defrosting the refrigeration chamber, the cooling wall of which thaws during the period of mandatory shutdown of the compressor due to an increase in temperature. The resulting water flows through a special channel or along the back wall of the refrigerator into a tray, from where it evaporates, thanks to the heat from the operating compressor. It is because of the flowing melt water that the automatic defrosting system is often called “crying.” The automatic defrosting function is found in almost all modern refrigerators. It is equipped, for example, with the Daewoo FR-291 model for 13,000 rubles, Hansa RFAK 311F, BEKO DSA 25000, not to mention expensive models such as from Liebherr CN 38130 for 27,000 rubles.
The refrigerator goes on vacation
Modern refrigerators not only save time, but also money: when going on vacation or a long business trip, you can switch the device to the economical “vacation” or “vacation” mode. In this case, the refrigeration chamber is switched off, in which the temperature is maintained at about +15°C, and the air is constantly ventilated to avoid stagnation and the occurrence of bad odors. For example, the GA-479ULBA refrigerator with bottom freezer, manufactured by LG Electronics, is equipped with a “vacation” mode.
Other models with an economy mode function are, for example, AEG-Electrolux S 70358 KG at a price of about 36,500 rubles. and Ariston BCZ M 40 IX costing about 30,000 rubles.
Keepers of freshness
For modern refrigerators, it is important not only to preserve food, but to ensure that it remains fresh for as long as possible and does not lose its taste and aroma. And for this purpose many different technologies have been invented.
For example, refrigerators use a special antibacterial coating. Scientists have long discovered that food in refrigerators spoils due to bacteria and fungi. To extend the shelf life of perishable foods, many refrigerator manufacturers began to coat the internal surfaces of their products with antibacterial compounds containing silver ions, which has long been considered a disinfectant. In refrigerators with antibacterial protection, food is stored longer and better, and in addition, it prevents unpleasant odors arising during the life of microbes. This coating, called AgION, is, for example, in the Bosch KGP 36320 refrigerator, costing 25-26,000 rubles. The Electrolux ERB 40301 refrigerator (RUB 24,000) uses the Bacteria safe system.
It has been established that many products retain their freshness longer and do not lose their aroma, appearance and nutritional properties if stored at a temperature of about 0 ° C and at a certain humidity. To ensure such conditions, a so-called “freshness zone” (“zero chamber”) is created in refrigerators. Its “branded” names are BioFresh (in Liebherr refrigerators), Fresh zone (LG), Fresh Box (Ariston), Natura Fresh (Electrolux), etc.
The “freshness zone” can be represented either by a whole chamber or by a separate shelf or box in the refrigerator compartment. It is divided into a “dry freshness” zone and a “wet freshness” zone. In the “dry freshness” zone, the temperature is maintained just below zero and the humidity is no more than 50% - this optimal conditions for storing meat, fish, cheese, etc. And greens, vegetables and fruits are better preserved in the “moist freshness” zone, where air humidity is maintained at about 90% and the temperature is just above zero. In the refrigerator Siemens KI 26FA50 at a price of about 24,000 rubles. The volume of the “wet freshness” zone is 15 liters, and the “dry” zone is 45 liters.
The principle of action of the Vitamin Plus technology used in the new series of LG refrigerators, including the already familiar GA-479ULBA model, is to saturate the air with concentrated, specially processed vitamin C, known for its antioxidant properties, which slows down the spoilage of vegetables and fruits. One block of vitamin C is enough for 7 years of use, which corresponds to the optimal lifespan of the refrigerator. In addition, the OptiFresh compartment maintains a temperature of approximately 0 °C, which is optimal for short-term storage of fresh meat and fish.
The “forced cooling” function, which maintains food in the refrigerator and freezer compartments, also helps maintain food freshness. optimal temperature and uniform cooling of all products from all sides due to constant forced circulation of multidirectional flows of cold air inside the chambers. Constant air circulation also guarantees that products lying on adjacent shelves will not become saturated with each other’s odors. The “forced cooling” effect is enhanced by special absorbers and deodorizers - filters built into the air circulation system. Such a filter, called “Z-freshener,” can be found, for example, in the LG GR S 462 QVC model, which costs about 21,000 rubles.
Air circulation helps to extend the shelf life of foods stored in the refrigerator and preserve their freshness and flavors. But with “forced cooling” energy costs increase, because it is carried out constantly.
The “quick cooling” function also helps to increase the shelf life of products. Typically, the food stored in the refrigerator never runs out at the same time, and we are constantly adding food to the refrigerator that we just brought from the store. They are, of course, warmer than those already in the refrigerator, and when they are placed on shelves, the temperature in the refrigerator compartment increases. Thanks to the “quick cooling” function, when fresh food enters the refrigerator, the temperature in the refrigerator compartment drops to +2°C. Fresh food cools quickly, and already chilled food avoids unwanted temperature increases. The premium model AEG-Elelctrolux S 70408 KG with this function will cost 36-39 thousand rubles, and the middle class model Candy CFBC 3180 A will cost 17-19 thousand rubles.
The freezers of many refrigerator models have a “quick freeze” function. It allows you to preserve frozen products for a longer period without harming their quality. This is achieved by very fast and uniform freezing of products at a temperature of -25...-38 °C. At the same time, the products are not covered with an ice crust and do not freeze to the walls of the freezer, and upon further defrosting they do not produce juice. This means that they practically do not lose vitamins, taste and nutritional qualities, and natural color. Rapid freezing also prevents the temperature of food already stored in the freezer from increasing.
The premium refrigerator AEG-Electrolux S 86378 KG with the “quick freezing” function costs about 43,000 rubles, and the middle-class model Ariston MBA 45 D1 NFE costs about 29,000 rubles.
Ice, water and wine
Keeping the house clean at all times drinking water is the need of any modern person living in a large metropolis. Latest Research in this area pushed Electrolux specialists to create new models modern refrigerator that will be able to provide their owner with clean drinking water, both regular and carbonated and with ice. The Source and Glacier refrigerators were designed to be a perfect match. They can be installed side by side, offering water and ice through dispensers on the doors.
New refrigerator called Source is an inexhaustible source clean water, which can be used for drinking and cooking. To get water, simply place a glass or other container directly under the dispenser and lightly press the button.
The Glacier refrigerator has a compact ice making and dispensing device built into the door. Special technology prevents ice cubes from sticking together, and thanks to Frost-free technology, the owner of a Glacier refrigerator does not need to spend time defrosting - he can devote more time to other household chores.
Owners of new Hotpoint-Ariston refrigerators always have chilled drinks at hand. Now they won't have to open the refrigerator door to get a bottle of chilled wine. Hotpoint-Ariston's new two-chamber refrigerator MBZE 45 NF BAR/HA with energy class A is equipped with a minibar on the door, which until now could only be found in Side-by-Side refrigerators. The refrigerator is spacious (the volume of the refrigerator and freezer compartments is 280 and 118 liters, respectively), its No Frost system will relieve the owner from the grueling task of manual defrosting. The freezer can freeze up to 14 kg of food per day, and in case of a power outage, keep it cold for 21 hours.

Because, for a number of reasons, there are suppliers of goods on the world market that are more competitive than domestic producers. Increasing the role of 3. Increasing the role of customs duties in regulating the import of goods into the Russian Federation Customs duty as an economic category appeared at the stage of the emergence of the exchange of labor results between individual state entities, i.e. a little later...
The operation of refrigerators is based on the artificial removal of heat from the internal space to the environment.
I. By the method of heat transfer from the refrigerator to the environment. Household refrigerators are divided into:
Compression (K);
Absorption-diffusion (A);
Thermoelectric (TE);
Magnetic (M).
In compression and absorption-diffusion refrigerators, heat from the refrigerator cabinet is removed into the environment using a special working substance - refrigerant (in compression refrigerators - freon gas , in absorption-diffusion - a solution of ammonia with hydrogen), which, as it circulates through the closed system of the refrigeration unit, changes its state of aggregation, passing from liquid to gaseous and back to liquid.
The process of transition from a liquid to a gaseous state (the process of evaporation or boiling) takes place inside the refrigerator and is accompanied by the absorption of heat.
In compression refrigerators, the movement of the refrigerant (freon - 12, less often freon - 22, another name is freon - 12, 22) is caused by the operation of an electric motor and a compressor (a complex unit designed to compress and increase the temperature of refrigerant vapors).
The refrigerant under pressure caused by the operation of the electric motor enters the compressor, where it is compressed and heated. The heated vapor enters the condenser, the temperature of which is lower than the temperature of the refrigerant. In the condenser, due to the temperature difference, condensation occurs (steam into liquid). The refrigerant then enters the evaporator through a narrow capillary tube. Since the evaporator channels are much larger than the diameter of the capillary tube, a pressure drop and boiling of the refrigerant occur in it. Turning into vapor, the refrigerant absorbs heat in the refrigerator compartment and the temperature decreases. Then the vaporous freon is sucked from the evaporator by the compressor and the whole cycle is repeated. The condenser is cooled by ambient air.
The design of the refrigerating chamber of compression refrigerators allows you to create different temperature conditions in individual places. In a regular refrigerator compartment the temperature is maintained from +2 to + 10 o C, in some types -0 o C, in the freezer compartment from -6 to -24 o C (quick freezing), in the low-temperature compartment pre-frozen products are stored.
[ Foreign-made compression refrigerators may have additional temperature compartments (“wine cellar”, ice maker, etc.). ]
Defrosting of refrigerators can be carried out in the usual way or using special systems (No-Frost, Frost-Free, etc.).
Appliances with the No-Frost system defrost automatically due to the fact that air is distributed throughout the refrigerator using special fans. However, this system creates:
1) increased level noise and constant air circulation;
2) dries food.
In refrigerators with a “crying” evaporator, the latter is located in the refrigerator compartment. When the compressor is running, freezing occurs, and when it stops, thawing occurs due to the heat generated by the products. Moisture is removed through special channels.
Refrigerators with the Frost-Free system use both a “crying” evaporator and a No-Frost system.
Range of compression refrigerators:
1) domestic – Stinol-205 (107;110) – Novolipetsk Iron and Steel Works; Atlant – 355-0 (151-01); Nord – 233 (226; 234) – Belarus and Ukraine.
2) foreign – Bosch KGS 3202; Siemens KGE 3501; Indesit GC 2322 W; Ariston - 216; Sharp RFSJ-55; Samsung SR-V-43.
In contrast to compression refrigerators, absorption-diffusion refrigerators do not have an electric motor with a compressor, so the device operates silently. The movement of the refrigerant (a solution of ammonia with hydrogen) is carried out due to heating (electric, gas, etc.).
Cooling of the chamber is achieved, as in compression refrigerators, by absorbing heat from it by boiling liquid ammonia in the evaporator.
The freezer compartment of such refrigerators maintains a temperature of about -5 o C.
Absorption refrigerators are small in size, operate silently, consume a small amount of electricity, and are relatively cheap.
The assortment is represented by devices of domestic production (Iney, Morozko), as well as foreign companies - Whirpool, Electrolux, etc.
The production of cold in thermoelectric refrigerators is based on the Peltier effect, and refrigerators also do not have a refrigerant. The Peltier effect lies in the fact that when direct current flows through dissimilar semiconductors (i.e. materials with different conductivities - exp: selenium with bismuth, tellurium with antimony) a temperature difference is created at the places of their junctions (connections); one semiconductor is heated (it is located outside the refrigerator), and the other is cooled by the same amount (it is located inside the refrigerator).
The temperature inside the refrigerator is up to +5 o C.
Thermoelectric refrigerators consume a lot of electricity and have a high price. They are used primarily as car refrigerators.
Assortment: Chaika, Voronezh, Krokha, etc.
II. According to climatic version:
1) (up to 40 o C) refrigerators for temperate climates (U);
2) (up to 45 o C) for tropical (T).
III. By number of refrigeration chambers:
Single chamber;
Two-chamber;
Three-chamber;
Multi-chamber.
IV. According to the temperature regime in the low-temperature compartment:
1) up to -6 o C;
2) from -6 to -12 o C;
3) from -12 to -18 o C;
4) from -18 to -24 o C.
V. At the installation location:
1) floor-mounted in the form of a cabinet (W);
2) floor in the form of a table (C);
3) built-in desktop (H);
4) block-built (B);
5) portable.
VI. By difficulty group – from 0 to 5.
VII. By comfort level:
1) refrigerators with ordinary comfort;
2) with increased comfort (automatic defrosting; automatic door closing (if not closed at an angle of up to 10 o), light indication of the operating mode, device for cooling and dispensing drinks, computer control and monitoring system, clock-timer, sound alarm for an open door and etc.).
VIII. According to the internal volume of the chamber:
In the marking of refrigerators, the total volume in liters is indicated by numbers separated by a fraction, the numerator is the total volume, the denominator is the volume of the low-temperature mode.
IX. Based on materials of manufacture: metal, plastic, etc.
X. By the nature of the coating and finishing.
XI. By model: model number – two digits, modification number – a digit separated by a hyphen).
Refrigerator markings contain:
1) brand – Stinol;
2) difficulty group (0-5);
3) model serial number (two digits);
4) serial number of the modification (digit separated by a hyphen);
5) type of refrigeration device (compression);
6) number of cameras;
7) total volume;
8) nature of installation (floor-standing in the form of a cabinet);
9) standard number;
10) temperature in the lower temperature compartment.
In foreign models of refrigerators, the level of energy consumption is indicated, which is reflected in the letters: A, B and C - very economical, D - economical, E, F and G - with high energy consumption.
Refrigerated structures, or refrigerators, are specially equipped industrial buildings with a refrigeration compressor unit that provides them with temperature and humidity conditions that correspond to technological standards for the storage or production of food products.
In refrigerators they support reduced temperature air (from +4 to -30 °C) and high relative humidity (80 - 95%). To create and maintain such parameters, they are built without windows, they have a powerful thermal insulation roofs, external and internal fences, doors, are equipped with equipment for cooling the premises and devices to prevent freezing of the soil at the base of the building.
Classification of refrigerators by purpose. The following types of refrigerators are distinguished by purpose: procurement, production, distribution, basic, for storing vegetables and fruits, food depots, ports, transhipment, retail and catering enterprises, mixed purposes.
Procurement refrigerators constructed in areas where perishable food products are stored. They are intended for initial refrigeration treatment, short-term storage and preparation of prepared products for transportation to retail establishments or distribution refrigerators and other types of refrigerators.
Industrial refrigerators - an integral part of food enterprises (meat processing plants, fish processing plants, canning plants, dairies, etc.). They provide refrigeration for production processes. They are used for cooling, freezing and storing raw materials and finished products.
Distribution refrigerators are intended for the creation and storage of reserve, seasonal, current and insurance stocks of perishable raw materials and finished products, ensuring the rhythm of production of food industries and a uniform supply of food products to the population throughout the year.
Distribution refrigerators can be universal or specialized depending on the range of goods stored. Distribution refrigerators, especially those with a capacity of 7,000 to 20,000 tons, may include workshops for the production of ice cream or frozen food products (berries, etc.), dry and water ice, oil packaging, production of semi-finished products. Such refrigerators are called cold storage facilities.
Basic refrigerators designed for long-term storage of reserves of perishable products (state reserve). These refrigerators are built in places that are remote from populated areas and are reliably protected.
Refrigerators for storing vegetables and fruits can be independent enterprises or be part of fruit and vegetable and food bases. They are located in rural areas, playing the role of procurement, or in places of consumption (in cities, towns).
Refrigerators for food stores designed to serve the retail chain of small towns. They receive food products from production and distribution refrigerators.
Port refrigerators used for storing food products transported by water. They carry out transshipment of food products from refrigerated ships to railway and automobile transport and vice versa, therefore they are classified as transport and forwarding.
Transfer refrigerators are designed for short-term storage of goods when transferring them from one type of transport to another, for example from rail to road and vice versa.
Refrigerators for retail and catering establishments are intended for storing stocks of products that are sold by enterprises within several days.
Mixed-use refrigerators perform several functions. For example, industrial and port refrigerators in large cities can simultaneously perform distribution functions. And port refrigerators in fishing ports can serve as industrial refrigerators in fish processing plants.
Classification of refrigerators by cargo capacity. Based on cargo capacity, refrigerators are divided into small (up to 100 tons), small (up to 300 tons), medium (up to 500 tons), large (up to 10,000 tons) and extra-large (over 10,000 tons).
The carrying capacity (capacity) of refrigerators is expressed in tons of conventional cargo. Meat in half carcasses is taken as a conditional load, having a volumetric mass of 0.35 t/m 3 when placed on the floor in a stack or when placed on overhead tracks, a load of 0.25 t per 1 m of track (excluding distribution tracks and switches). Depending on the nature of the cargo, its packaging and stowage, the calculated volumetric mass of the cargo may be more or less than indicated. The conditional cargo capacity of the refrigerator is determined by the formula
E x = E k.o + E k.z + E k.p,
Where E k.o And E k.z- conditional cargo capacity of all storage rooms for refrigerated and frozen cargo, respectively, t; E k.p - conditional cargo capacity of all chilled meat storage chambers equipped with overhead tracks, tons;
E k.o= 0,35 V year; E k.z = 0,35 V g.z; E k.p= 0.25L,
Where V year, V g.z– cargo volume of storage chambers for refrigerated and frozen cargo, respectively, m 3 ; L- load length of overhead tracks, m.
Conditional cargo capacity can be converted into actual (for a specific cargo) by dividing it by the conversion factor. Thus, the conversion factor, for example, for eggs in cardboard boxes is taken equal to 1.35, for butter in cardboard boxes - 0.44.
When determining the cargo capacity of a refrigerator, cooling and freezing chambers, refrigerated rooms not intended for food storage (expeditions, storage chambers, loading and unloading rooms, ice storage facilities), as well as uncooled rooms (utility rooms, corridors, lobbies, elevator shafts and staircases) are not taken into account ).
The cooled building volume of the refrigerator chamber, m3, is determined by the formula
Vc = FH,
Where F- chamber floor area, m2; N - chamber height from floor to ceiling, m.
Cargo volume of the chamber V g, less construction:
V g = F g H g< V c ,
Where F g - area of the chamber floor on which the load is placed, m 2 ; N g- cargo height of the room, m;
F g = F - ∑ f,
Where ∑ f- total floor area occupied by columns, passages and driveways, refrigeration equipment, m2;
H g = H – h,
Where h- distance from the top of the stack to the ceiling or beams, cooling devices and air ducts (0.2 - 0.3 m).
The load capacity of distribution refrigerators is established on the basis of annual freight turnover. The distribution refrigerators available in our country are designed for a freight turnover rate of 4-6 per year.
In the refrigerator of meat processing plants, the capacity of the chambers for storing frozen meat must correspond to the 40-60-shift capacity of the meat production plant, and the storage chambers for chilled meat must correspond to a two-day production supply. The carrying capacity of a refrigerator at a city dairy plant is assumed to be equal to the 10-15 shift production volume of products to be stored.
Refrigerators with a cargo capacity of up to 700 tons belong to class I, over 700 tons belong to class II of the building capital with a service life of 50-100 years, from 250 to 700 tons belong to class III with a service life of 25-50 years, less than 250 tons belong to IV class with a service life of 5 - 25 years.
The main load-bearing structures of buildings of classes II and III are made of reinforced concrete or steel.
Refrigerator buildings - single-story and multi-story; sometimes they have a basement floor.
In single-story refrigerators, where there is no need for floor-by-floor vertical movement of cargo, it becomes possible to increase the spans of the building's load-bearing structures to 24 - 30 m (compared to a grid of columns of 6 · 6 m in multi-story refrigerators), two to three times the payload on the floors due to their location on the ground, which allows you to store cargo at a greater height (10 - 20 m). However, single-story refrigerators are characterized by increased heat inflows through external fences compared to multi-story ones (by 20 - 40%), especially through the roof, the surface of which can account for up to 70% of the entire surface of their external fences.
For multi-storey refrigerators, the issue of protecting the soil at the base of the building from freezing is easier to solve. They occupy a smaller area, and the heat inflow through the roof in the overall balance of heat input into them is less than in one-story buildings.
The space-planning solution and the number of refrigeration chambers for one purpose or another (cargo capacity structure) should allow the introduction of advanced technology for refrigeration processing and storage of food products, organizing rational cargo flows in the building, achieving a high level of mechanization of loading and unloading and transport and storage operations, minimal heat inflows and cold consumption.
In Russia, refrigerators with a cargo capacity of over 4000 tons are mainly equipped with chambers with a cargo capacity of more than 400 tons (over 90%). The load capacity of frozen food storage chambers (-20 °C) of distribution refrigerators is 50 - 70%, chilled food storage chambers (+4...-3 °C) - 20 - 35%, universal (0...-20 °C ) - 10-15%, freezing chambers (-30°C) - 0.5-1%. The sizes of the chambers are different. For example, in single-story refrigerators, chambers for storing frozen foods have an area of 300-600 m2, and chambers for storing chilled foods have an area of up to 300 m2. In multi-storey refrigerators, the chamber area is larger - up to 1000 m2.
Cameras with the same temperature conditions form blocks (compartments) horizontally (on floors) and vertically (in a building). In the basement there are chambers with a temperature not lower than -3 0 C so that the ground under the floor does not freeze.
Multi-storey refrigerators are built with a width of up to 40 m, single-storey ones - 24 - 72 m. The length of the refrigerator is determined mainly by the front of loading and unloading operations, i.e. the length of railway and automobile platforms, which depends on the capacity of the refrigerator and cargo turnover. For refrigerators with a capacity of over 3000 tons, the length of the railway platform must be at least 120 m, i.e. sufficient to unload a 5-car refrigerated section.
For cooling meat, up to 3 chambers are used, for freezing - 5 - 7, for storing chilled meat - 1 - 2 (area 200 - 300 m2), frozen meat - 3 - 4 (area 300 - 1000 m2). Depending on the need, universal chambers (from 1 to 3) are used for refrigeration processing and storage.
With the establishment of market relations in our country, the operating conditions for refrigeration enterprises provided for in the projects changed, primarily distribution refrigerators designed and built during the period of planned distribution economy and intended for the one-time long-term storage of food products in large quantities.
Due to the increase in cargo turnover caused by a reduction in the shelf life of goods, their irregular arrival, and small consignments of goods, the use of existing refrigerator capacities does not exceed 25 - 35%, while previously it reached 100%. There was a need for small capacity cells that could be rented by small trading companies. It is necessary to redesign existing refrigeration chambers, which will increase the load rate of refrigerators, reduce the cost of cargo turnover, and increase profits.
The creation of refrigeration chambers with a capacity of 100 tons based on the refrigeration capacities of existing distribution refrigerators makes it possible to increase the number of refrigerated volumes and the efficiency of their use.
In Fig. 14 shows a diagram of the restructured refrigeration chamber.
Rice. 14. Restructured cold room:
1 - thermal insulation fencing; 2, 9 - side guards; 3 - air cooler;
4 - movable partition; 5- wall batteries; 6- monorail tracks;
7 - doors; 8 - seal made of elastic material; 10 - autonomous compartments
When creating new refrigerators, it is rational to arrange them in the form of modules of various cargo capacities, adapted both for cold processing of goods and for their storage.
As an example in Fig. Figure 15 shows the layout of the refrigeration chamber module for cooling, freezing and storing half carcasses with a capacity of 6 tons/day of cold processing and 80 tons of storage.
Such modules can also be used on existing production and distribution refrigerators when receiving small batches of meat for cooling and freezing carcasses and their subsequent storage in refrigeration chambers, as well as for storing meat with short sales periods. These modules can also be installed in remote areas where transport communications are not developed to ensure supplies to the local population.
Let's give specifications refrigeration modules with freezing capacity 1; 3 and 6 tons of meat per day (Table 1).
Unlike existing refrigerators, the frames of which are made of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures with multilayer enclosing walls made of brick or reinforced concrete panels with thermal insulation, the frame of the modules is made of metal frames, profiled iron and pipe racks, and the walls are made of thermally insulated polyurethane foam sandwich panels. . This design allows the module to be transported disassembled railway and road transport.
Cooling supply is provided by 4 refrigeration machines with air-cooled condensers, allowing you to regulate the temperature by turning off individual units depending on the load of the chambers and the outside temperature. The maximum power consumption at a temperature in the chambers is -3°C 1.2 kW.
Comparative characteristics of the range of cotton and linen fabrics and directions of its development
Assortment of cotton and linen fabrics
All fabrics are divided depending on the raw materials used: cotton (cotton), linen, silk, wool.
Cotton fabrics differ varied design as a result of the use of various weaves and types of finishing, also good hygienic properties, wear resistance, lightness, beautiful appearance. Most of the fabrics are made from pure cotton, the rest using chemical fibers.
Classification:
Depending on the yarn structure: combed, carded, carded-combed, carded-carded;
By production method: multi-colored and melange;
By the nature of the finish: harsh, bleached, plain-dyed, printed;
By groups: calico, calico, linen, satin, dress, clothing, lining, teak, pile, shawl, blanket;
By purpose:
1) linen fabrics (calico, calico, special fabric);
2) dress and shirt fabrics (chintz, calico, satin);
3) dress fabric: summer subgroup (chio fabric - chio san), demi-season (spark), winter (flannel, flannel);
4) pile fabrics (corduroy, velvet);
5) lining fabrics;
6) suit and coat;
7) towels, furniture and decorative fabrics and piece goods (handkerchiefs and head scarves).
Cotton fabrics are mainly made from yarn of various thicknesses, various weaves, but mostly plain.
Quality requirements: cotton, linen, woolen fabrics are grades 1 and 2, silk - grades 1, 2, 3
Placed on counters. The distance from the floor is at least 20 cm.
Linen fabrics have unique hygienic properties: they quickly absorb and release moisture, are vapor and breathable, and thermally conductive. Linen fabrics are indispensable for sewing summer clothes; they have high wear resistance and wash well. The disadvantage of linen fabrics is their high creaseability.
Classification:
Ingredients: flaxseed and semi-linseed;
By weave: plain, satin, finely patterned, large patterned;
By finishing: harsh, bleached, boiled, multi-colored, melange;
By purpose: linen, costume and dress, furniture and decorative, trim, linen, piece goods;
By width: canvases, narrow, wide canvases;
By groups: (16 groups):
1) linen (linen and canvas)
2) suit and dress fabrics (linen and semi-linen fabrics)
3) furniture and decorative (curtain, furniture, mattress, terrace fabrics)
4) fabrics for special purposes (sideboards, covers, harsh rough, mattress)
5) piece goods (tablecloths, napkins, bedspreads, towels)
Napkins are:
White (36x36, 62x62), tea (32x32), table (80x80)
Household refrigerators: classification, modern range of compression refrigerators
The most widespread classification of refrigerators is based on the method of “obtaining cold”:
Compression refrigerators and freezers;
Absorption-diffusion refrigerators;
Thermoelectric refrigerators.
Compression refrigerators are the most widely used. In these refrigerators, heat is taken from the internal chamber when the working substance (refrigerant) boils in the evaporator. Freons were previously used as working substances, which have now been replaced by other hydrocarbons.
Absorption-diffusion refrigerators use ammonia as a refrigerant and water, which serves as an absorbent. Heat is also taken from the refrigerator chamber when the refrigerant boils in the evaporator.
Thermoelectric refrigerators do not have a refrigerant; their operation is based on the use of the Peltier effect, which consists in the fact that when passing a constant electric current Through a thermoelement made of two series-connected (soldered) materials with different thermoelectromotive forces, heat is released at one of its contacts (junction), and heat is absorbed at the second. The cold junctions of the thermopile are placed in the refrigerating chamber, and the hot junctions are placed outside the chamber.
In the marking of domestic refrigerators, the type is designated as follows:
K - compression;
A - absorption-diffusion;
TE - thermoelectric.
Refrigerators, according to the current standard, can be classified according to a number of other characteristics, the main ones being purpose, installation method, number of chambers, temperature in the low-temperature compartment, complexity group, etc.
According to their purpose, all devices for storing food by cooling or freezing methods are divided into:
Refrigerators - devices for storing chilled products;
Freezers - devices for storing frozen foods;
Refrigerator-freezers are devices for storing chilled and frozen food products (they differ from two-chamber refrigerators in the large size of the low-temperature chamber - from 40 liters, and the presence of two independent refrigeration units).
Refrigerators are classified according to installation method:
"Ш" - floor-standing in the form of a cabinet;
"C" - floor-standing in the form of a table;
"N" - built-in;
"B" - block-built;
"side-by-side" - cameras are placed parallel in a vertical plane.
According to the number of cooled chambers, refrigerators are: 1; 2 (D); 3 (T) and multi-chamber (M).
Based on the temperature in the low-temperature compartment, refrigerators are divided into 6°C intervals from -6 to -24°C (and below), every 6 degrees is usually designated by one snowflake. In the labeling of refrigerator-freezers with a temperature
in the NTK - 24°C, one large snowflake and three small ones are introduced, i.e. in normal storage mode the temperature in them is -18°C, and in freezing mode - 24°C.
Refrigerators can also be classified according to their climatic design (according to their ability to operate at maximum ambient temperatures):
SN, N - not higher than 32°C;
ST - not higher than 38°C;
T - not higher than 43°C;
Freezers:
N - not higher than 32°C;
T - no higher than 43°C. The chambers included in refrigerators can also be divided into types:
Chambers for storing vegetables and fruits - have high humidity;
Refrigerated chambers for storing chilled products;
Low temperature chamber (LTC) - for storing frozen food products;
MK - freezer;
Universal camera - a general purpose camera.
According to the degree of comfort, refrigerators are distinguished between regular and superior. Deluxe refrigerators must have a device for automatic or semi-automatic defrosting of the evaporator, and in addition, one or more devices that increase ease of use:
A device for maintaining a certain humidity in the refrigerating chamber or part thereof;
A device for cooling drinks and dispensing them without opening the door;
Alarm about operating modes;
Device for forced automatic closing of doors when they are opened by 10°;
Door opening angle limiter;
Ensuring the rearrangement of shelves with a height interval of no more than 50 mm or extending the shelf to a distance of at least 50% of its depth while maintaining the horizontal position of the shelf;
Possibility of re-hanging the door.
The standard also provides for other comfort elements.
Depending on the functions performed, refrigeration appliances are divided into complexity groups from 0 to 5. Group zero is assigned to the most complex models, and 5 is the least difficult.
Compression refrigerators account for about 90% of the refrigerator market. The principle of operation of a refrigeration compression machine is as follows: when the refrigerator is turned on, the compressor starts working, refrigerant vapor (freon) flows from the evaporator into the compressor cylinder, where it is compressed by a piston. Compressed and superheated vapors are supplied under pressure to the condenser.
In the Condenser, the refrigerant vapors are cooled by the ambient air, condensed - they turn into a liquid state. Liquid refrigerant flows through the capillary tube into the evaporator, and the refrigerant pressure drops. In the evaporator, liquid refrigerant boils at low pressure, turns into steam and absorbs heat from the refrigeration chamber. The vaporized refrigerant again enters the compressor and the cycle repeats. The thermostat maintains the set temperature. During operation, the evaporator is covered with a “snow coat”. If the frost layer is more than 5 mm, this leads to greater energy consumption and heating of the low-temperature compartment.
Parameters of compression refrigerators. Electrical parameters determine the quality of the functional properties of refrigerators. Total internal volume (measured in dm3 and l) - the volume limited by the internal walls of the refrigerator with the door closed and removable elements removed. The total volume of refrigerators according to the standard is from 60 to 500 dm3.
The freezer capacity indicates how much frozen food can be stored in the freezer compartment.
Functional properties include total energy consumption. For the consumer, this indicator has great importance, since the refrigerator operates 24 hours a day.
In Europe, since 1995, refrigerator manufacturers have been required to indicate annual electricity consumption on a special information sticker. For clarity, each energy consumption class is highlighted in color and designated by letters - from A to G: A, B, C - very economical; D - intermediate; E, F, G - with high and very high power consumption. Electricity consumption classes:
A 266-351 kW/year;
B 379-427 kW/year;
From 415-516 kW/year.
The ergonomic properties of refrigerators are determined by ease of use, degree of comfort, the strength of shelves, trays, dimensions, occupied floor space, light and sound alarms are important.
The aesthetic properties of a refrigerator are the color scheme, the proportionality of the forms of the refrigerator, the location of the chambers, and the expressiveness of the brand names.
The refrigeration unit must be safe in fire, sanitary (noise and vibration levels), electrical and mechanical terms.
Range of compression refrigerators. Compression refrigerators come in single, double and multi-chamber types. Such refrigerators are produced as combination refrigerators, such as “refrigerator-freezers”. The range of refrigerators entering the trade includes a large number of models of different designs, from various manufacturers: Atlant (Belarus), Electrolux (Sweden), Arston (Italy), Stinol, Nord, etc. Marking refrigerator designations: name, model designation, serial number, type and amount of refrigerant, volume of the refrigerating chamber, production date.
 Dream interpretation dreamed of shit
Dream interpretation dreamed of shit How to squeeze a lemon: tips and methods How to squeeze juice from a lemon at home
How to squeeze a lemon: tips and methods How to squeeze juice from a lemon at home Representatives and characteristics of the order insectivores
Representatives and characteristics of the order insectivores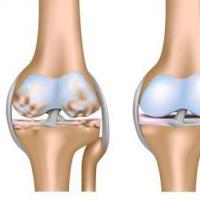 DOA of the knee joints: stages, symptoms and treatment
DOA of the knee joints: stages, symptoms and treatment Dimexide - detailed description and use at home Dimexide if it enters the stomach
Dimexide - detailed description and use at home Dimexide if it enters the stomach Andrey Stygar: How to make inventory profitable?
Andrey Stygar: How to make inventory profitable?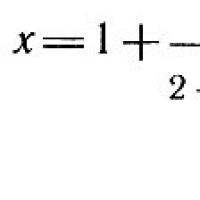 Meaning of continued fractions in Collier's dictionary
Meaning of continued fractions in Collier's dictionary