Is it possible to catch syphilis in a household way. Domestic syphilis infection - pathogen, incubation period, stages, treatment and prevention. Household method of spreading the pathogen
Each person needs to have information about how syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted in order to exclude the possibility of infection. Despite the fact that medicine has made a huge leap forward, these diseases still exist in society. Everyone can face them, regardless of the level of wealth and social status.
An analysis for the detection of antibodies to this infection is mandatory during pregnancy and preparation for surgery in order to exclude possible complications that this systemic disease leads to. Syphilis without proper treatment can cause irreparable harm to the human body and even cause death.
The price of the analysis is not high, and if there is a risk of infection, then it is worth diagnosing even if there are no symptoms of the disease. Just keep in mind that the incubation period for a spirochete is 3-4 weeks. If the analysis is carried out earlier, then it most likely will not be informative.
During the latent period of infection with syphilis, the disease can be asymptomatic for years, and then, when the body's immunity fails for some period, attack the body. In venereological practice, early and late latent syphilis are distinguished. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to know how much time has passed since the infection.
The causes of latent syphilis lie in the ability of pale treponemas to turn into L-forms and hide inside the body in the form of cysts that have a dense shell, resistant to antibiotics and effects on them from the immune system. With a decrease in its protective reserves, the microbe can turn back into a spiral shape and attack the body.
The main ways of transmission of infection:

How you can get syphilis and what you need to know about its pathogen
 Most often, pale treponema enters the human body through the mouth, rectum or vagina through sexual contact, from a sick mother to a child, and also through blood transfusion. Other ways of infection, fortunately, are much less common. Infection through dishes and household items is very rare. Everyone needs to know how you can become infected with syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases, and what to do if there is a suspicion of the presence of this infection in the body.
Most often, pale treponema enters the human body through the mouth, rectum or vagina through sexual contact, from a sick mother to a child, and also through blood transfusion. Other ways of infection, fortunately, are much less common. Infection through dishes and household items is very rare. Everyone needs to know how you can become infected with syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases, and what to do if there is a suspicion of the presence of this infection in the body.
Features of pale treponema, what is this microbe really afraid of?
Pale treponema is not very resistant to the effects of the external environment. This infection lives and multiplies in the human body, which is its carrier. Animals do not get syphilis. Once in the air, when the liquid in which it is located dries, the bacterium dies.
It got its name "pale" because, unlike other saprophytic treponemas, it does not stain with aniline dyes. Other types of treponema do not penetrate into the lymph nodes. The study of material from lymph nodes using a microscope can be very informative.
The causative agent of syphilis, once in the body, manifests itself as follows:
- With primary syphilis, a chancre is formed at the site of infection, then the infection penetrates into the lymph nodes that are nearby. In them, its reproduction and accumulation takes place. The patient at this stage of the disease is very contagious to others. The ulcer does not hurt and after a while disappears on its own even without treatment.
- When treponema enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body, forming a pale rash, the disease passes into the second stage. It is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions. This process may take several years.
- In the third stage of the disease, gummas appear around the mouth and on the genitals, which can be localized in different parts of the body. They cause great discomfort to the patient, in contrast to the ulcers and rashes in the earlier stages, which do not hurt or itch. If left untreated, the disease leads to a deep disability of a person with damage to the central nervous system or spinal cord.
Outside the body, pale treponema quickly dies. It is very sensitive to external influences such as heating, drying and chemical reaction. On household items, it dies when it dries. Exposure to a temperature of 60 degrees kills it in 15 minutes, and at 100 ° C, the causative agent of syphilis dies immediately. Low temperatures are not detrimental to this microbe; this pathogenic strain persists in an anoxic environment from −20 to −70 °C.
The probability of contracting syphilis at different stages is not the same. The most dangerous carriers with primary syphilis, when they develop ulcers in the mouth, on the genitals and in the rectum. Knowing how you can get syphilis through sexual contact can protect your body from this aggressive infection.
The incubation period for syphilis is 2 to 6 weeks. Most often, the disease begins to manifest itself 3-4 weeks after infection.
Why does congenital syphilis appear, what harm can it cause to a child?
Congenital syphilis in a child appears if a woman is sick or becomes infected during pregnancy. The causative agent of this disease is transmitted by the transplacental hematogenous route (through the vessels of the affected placenta), but infection can also occur during childbirth. Often, intrauterine infection of the fetus leads to its death or severe damage to all systems of the child's body.
Infection of the fetus can occur as early as the 10th week of pregnancy, but usually occurs at 4-5 months of pregnancy. Especially dangerous is an acute infection in the mother after 24 weeks. With a latent infection, intrauterine infection does not occur.
With timely treatment of the mother, many complications in the child can be avoided. Expectant mothers simply need to know how to get syphilis, as they are responsible not only for their lives, but also for the health of their child.
Analysis for syphilis, ways of transmitting this infection from a sick person to a healthy one
 There are many ways of transmission, since syphilis is highly contagious, but according to statistics, 95% of patients become infected as a result of unprotected intercourse, so sexual contact with an unverified partner is a major risk factor.
There are many ways of transmission, since syphilis is highly contagious, but according to statistics, 95% of patients become infected as a result of unprotected intercourse, so sexual contact with an unverified partner is a major risk factor.
How not to get syphilis? Syphilis is a highly contagious infection. During sexual contact with its carrier, the risk of infection is about 50%. Unfortunately, it is transmitted at all stages of its development and even in a latent state of infection.
Methods of protection against infection with syphilis are the use of barrier contraception during sexual intercourse and the absence of casual relationships, as well as the observance of personal hygiene measures when visiting public places. Other methods of prevention (except for a condom) in contact with a random partner do not give any guarantees.
What to do if there was unprotected sexual contact?
There are several options for what to do if you feel you may have been infected:
- Drug prophylaxis of infection, which will prevent the development of bacterial sexually transmitted infections. The drug regimen is the same as in the treatment of the manifested disease at the initial stage without complications.
- Testing and examination by a venereologist in a month. It does not make sense to conduct laboratory tests earlier, since most pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases, including pale treponema, are in the incubation period.
- Ask a partner, contact with which caused anxiety for their health, to be examined by a venereologist. As practice shows, this option is usually difficult to implement.
Testing for syphilis is not the most pleasant procedure, especially for a pregnant woman. But for the sake of her health and the safety of the unborn child, this is necessary, even if she has had only one sexual partner, and there are no external signs of the disease. In the case of a positive result for syphilis, the transmission routes through which the infection entered the body fade into the background.
The first step is to make sure that this is not a mistake, and if the presence of an infection in the body is confirmed, then adequate treatment carried out in time will help maintain health and even save the life of both the mother and the unborn baby.
Tests for the detection of antibodies to pale treponema are also prescribed during the preoperative examination of patients.
A blood test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach, eating and tonic drinks are excluded, you can only drink water. The turnaround time for analysis is usually 1 day.
How blood tests for syphilis are evaluated:
- A negative result usually means no infection. It should be borne in mind that early primary and late tertiary syphilis is not excluded in this case, so the doctor may prescribe a second test after some time, if necessary.
- A positive result can be in the first year after recovery, since antibodies will still be present in the blood, as well as in primary, secondary, tertiary and seropositive syphilis.
- A false positive result can be obtained during pregnancy, oncology, the presence of the hepatitis virus, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus and the state of the vaccination field.
If a positive result is obtained in the RPR test, it is imperative to contact a venereologist for an additional examination and the appointment of adequate therapy. Knowing how syphilis manifests itself, how the disease is transmitted, and how to prevent infection will help keep you and your loved ones healthy. Syphilis still refers to sexually transmitted diseases and the likelihood of contracting it in the pool is much less than during unprotected intercourse.
Publication date: 03-12-2019
How is syphilis transmitted?
Taking care of yourself and your health is the vital position of every sane person. And to know how syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted is important not only for yourself, but also for people around you of the opposite sex. Don't forget about protective gear either. They can save you from a mass of diseases transmitted by blood and sexual contact. Some of them are incurable even today. But we will not talk about a whole group of diseases transmitted in a similar way, we will focus on one of the most dangerous - syphilis. Everyone knows that syphilis is contagious. In society, you can get syphilis anywhere.
Not everyone knows in what ways syphilis can be transmitted, what symptoms it has, and who and under what circumstances can become infected with the disease. Many are concerned about the question: is syphilis transmitted through a handshake, etc.
Syphilis was first diagnosed in the 15th century. Until the moment antibiotics were found, the disease was bedridden, leading to death.
In the modern world, antibiotics are widely used for many diseases. In this regard, as a rule, syphilis proceeds latently, and its clinical picture is much blurred. Consider the ways of transmission, how to protect yourself if there are signs of illness in another person. And what if frequent contact with a person with syphilis is expected?
Transmission routes
The most basic is the sexual way. Pale treponema multiplies well in semen and in the vagina. Infection with syphilis occurs during unprotected sexual intercourse (lack of barrier protection - contraception). Any sexual intercourse (without protection) can guarantee (with 50% certainty) infection.
That is why any unprotected sexual contact is dangerous for infection. Women are more prone to the risk of infection.
Syphilis is transmitted at any stage of development. It is also dangerous during the incubation period, when the sick person does not yet feel symptoms, which increases the risk for surrounding potential partners. There are no manifestations, and a person can infect everyone unconsciously, without even knowing about his infection.
Anal sex is also dangerous due to the fact that there is a high risk of injury to the mucous membrane. The main ways of transmission of syphilis:
- sexual contact;
- through the blood;
- infected medical instruments.
Various types of infection
Is syphilis transmitted by an innocent kiss? Yes, this option is possible if there are lesions of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity of a sick person, wounds, all kinds of rashes on the lips. If the integrity of the mucosa is violated, pale treponema migrates in large quantities into the saliva. The presence of wounds in the infected cavity, various dental procedures also increase the risk of infection. The better the condition of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity, the lower the risk of infection.
Despite all these warnings, according to medical statistics, syphilis is transmitted through saliva in very rare cases. A greater degree of risk with "French kissing", when there is penetration and contact with saliva, the area of \u200b\u200bcontact increases, and syphilis can be transmitted. It is realistic to get syphilis through a kiss, but in this case a very small percentage is exposed to infection. In order for syphilis to enter the human blood during a kiss, wounds (injuries) are needed in the oral cavity. Those who have contact with a patient with syphilis need to remember this, because the methods of transmission and infection with syphilis are known.
The breast milk of a sick woman also has pale treponema. This means that during breastfeeding, the child may become infected. Mothers who have been diagnosed with syphilis are advised to formula feed their baby so as not to put the baby at additional risk. Infants, due to the fact that their immune system has not yet formed, are especially susceptible to infection.

Due to the fact that the causative agent of the disease is constantly in the blood of a person, a blood transfusion to another person will give one hundred percent infection with syphilis. The same applies to organ transplantation, the importance of cleanliness of medical instruments. Medical workers know about it, remember, but there is always a human factor. It is very easy to get infected with AIDS, syphilis or hepatitis during dental procedures.
The risk group in this case is drug addicts and military personnel. Drug addicts due to the fact that they use one syringe for several people, and military personnel sometimes use other people's razors. There are also reusable syringes in the army, and they are being boiled.
You can also get infected (or infect others) during a fight, when body parts broken to blood are a common thing. Here the factor of chance plays an important role.
Pale treponema, getting into the blood of a person, multiplies rapidly. At blood transfusion and storage stations, all biomaterial is checked by a laboratory. Therefore, blood infected with syphilis will never be transfused to another person, it is immediately discarded.
Occupational-related infection
This category includes people working in medicine, cosmetologists, etc. The risk is especially high for surgeons, gynecologists, venereologists and junior medical personnel of blood transfusion stations. Although they are all well protected, there is a degree of risk of infection due to carelessness during the manipulation of the instrument. In any work there is an injury, and among doctors it is not excluded. Although how to prevent the possibility of infection, they know well.

Transmission of syphilis through household items also occurs. This question is primarily of interest to those who live in direct contact with a sick person. The household way is possible with prolonged and constant contact with towels, cutlery and dishes, when hygiene rules are not observed. People nearby should remember this, follow the rules of hygiene and use separate devices. With tactile contact, you can also become infected with syphilis, especially in the terminal stages of the development of the disease. This is the period when treponema is actively released, sores appear on the body. Remember that treponema dies in a dry environment. Activity is manifested only in wet secretions (saliva and blood).
Infection during pregnancy and childbirth
This is infection of the fetus during pregnancy by the mother, because syphilis is contagious. If the expectant mother does not receive drugs to treat the disease, the infection of the child occurs in 100% of cases. The circulatory system during pregnancy is one for two. At the very beginning, treponema affects the placenta, and then passes into the body of the fetus. A woman is especially contagious in the first years of the disease. Therefore, with the conception of a new life, if syphilis is detected, one should wait a little, knowing how syphilis is transmitted.
Another way of infection with a 100% probability is infection during childbirth.
After all, the child is in direct contact with the affected environment of the mother. If the fetus is not infected in the womb, then during childbirth there is simply no chance of avoiding infection.
.jpg) The fact that venereal diseases are transmitted not only through sexual contact, but also through everyday contact, did not immediately become known, but there were enough rumors and unconfirmed speculations about this. Immediately a lot of questions arose: how can you get infected with household syphilis, through what objects and under what conditions it is transmitted, is it possible to get infected in public places, etc. In fact, household is a somewhat simplified concept, meaning only that infection occurs even without direct contact between a healthy person and a sick person. The fact is that the causative agent of syphilis - treponema, feels great in a warm and humid environment, but from dryness and high temperature it immediately loses its activity, dying within a few hours. Therefore, the probability of getting syphilis by household means, for example, when traveling by public transport, is extremely low.
The fact that venereal diseases are transmitted not only through sexual contact, but also through everyday contact, did not immediately become known, but there were enough rumors and unconfirmed speculations about this. Immediately a lot of questions arose: how can you get infected with household syphilis, through what objects and under what conditions it is transmitted, is it possible to get infected in public places, etc. In fact, household is a somewhat simplified concept, meaning only that infection occurs even without direct contact between a healthy person and a sick person. The fact is that the causative agent of syphilis - treponema, feels great in a warm and humid environment, but from dryness and high temperature it immediately loses its activity, dying within a few hours. Therefore, the probability of getting syphilis by household means, for example, when traveling by public transport, is extremely low.
What household syphilis looks like: symptoms and signs
If you were already interested in this issue and searched the Internet for pictures or photos that would show signs of domestic syphilis, then you probably noticed that there is no specific group of photos and pictures. This is due to the fact that the signs, like the symptoms of this disease, are always the same, regardless of how the pathogen entered the body. The only difference is that such pictures, as well as photos taken by real patients, show how household syphilis manifests itself not on the genitals. .jpg) organs, but in those parts of the body where contact with treponema occurred. This does not mean that household syphilis can be transmitted simply by touching a person: the pathogen is not able to overcome obstacles in the form of human skin, for this it needs direct entry in the form of trauma or microdamage.
organs, but in those parts of the body where contact with treponema occurred. This does not mean that household syphilis can be transmitted simply by touching a person: the pathogen is not able to overcome obstacles in the form of human skin, for this it needs direct entry in the form of trauma or microdamage.
There are no specific signs and symptoms that the patient has a domestic form of the disease. As a rule, when a disease is detected, intimate contact with the carrier is primarily implied, which often becomes a cause of distrust between partners. Meanwhile, any doctor should not only prescribe and carry out treatment, but also explain to the patient and his relatives that there is a household way of transmitting syphilis, and it is not at all necessary to have a promiscuous sex life in order to become infected with it.
This form of the disease manifests itself similarly to others: the primary stage is most often asymptomatic, the second is manifested by the appearance of a hard chancre and inflammation of the lymph nodes, and the third irreversibly affects the internal organs. Therefore, if you find any manifestations that are unusual for the normal state of health of the body, as well as in the presence of symptoms and signs that were previously absent, you should immediately seek the advice of a doctor.
Domestic infection with syphilis: conditions and factors
In order to understand where the symptoms of a sexually transmitted disease came from, if sexual contact with unverified partners did not occur, you should know under what conditions syphilis is infected by household means. The causative agent of this disease lives and actively multiplies in a warm and humid environment. Of course, in the human body, the conditions for it are ideal, but there are other places where treponema lives, although less, but nevertheless quite active. The danger of a household method of infection with syphilis can be:
.jpg)
It is through such and similar objects that most often become infected with this disease. At the same time, given that it does not appear immediately, a person, without suspecting it, becomes the reason that it is transmitted further. Unfortunately, it is impossible to advise anything here other than to study photos and pictures in order to know what the disease looks like, what symptoms and signs are characteristic of it, and at the first manifestations, it is impossible to immediately consult a doctor. In addition, even a doctor will not be able to determine at a glance what kind of disease these or those signs are, but, in any case, the patient will be prescribed tests.
Household syphilis: treatment
In different forms of syphilis, only the way in which the pathogen entered the human body differs. Treatment does not imply any features - antibiotic therapy is prescribed, aimed at destroying the causative agent of the disease. The specific method of treatment is chosen by the doctor, after a preliminary examination. The only point is that in case of domestic infection, it is important to examine absolutely all family members (if the infection occurred at home) or the work team (if syphilis was detected at work). Even in the absence of obvious symptoms and direct signs of the disease, it is possible that the doctor may prescribe preventive treatment in order to prevent the development of the disease. Sexual contact during treatment should be excluded.
Sexually transmitted diseases remain an urgent problem to this day. Syphilis is the third most common sexually transmitted infection. According to official statistics, this disease is registered annually in at least 12 million people. How is syphilis transmitted, what are the first symptoms of this disease and what methods are used to diagnose it? This knowledge will help protect against a dangerous infection or timely detect the fact of infection.
What is syphilis
Syphilis is classified as a chronic sexually transmitted infection that affects the skin, mucous membranes, bone and nervous system, and internal organs. Its causative agent is a bacterium from the genus of spirochetes called "pale treponema", which instantly penetrates the body, even if there are only imperceptible microdamages on the skin or mucous membranes. In severe cases, the disease leads to irreversible lesions that are difficult to treat and often end in disability.
How is the disease transmitted
The main ways of transmission of the infection are sexual, household, blood transfusion (infection through the blood) and transplacental (infection of the child from the mother). Sexual transmission of the disease is most common, but in rare cases, even those who treat their health with due responsibility and do not allow unprotected sex can become infected with syphilis. How is syphilis transmitted?
sexual
Syphilis can be transmitted through unprotected sexual contact. The causative agent of the disease is present not only in the blood, but also in some body fluids, such as semen or vaginal discharge. For this reason, the risk of infection is very high even after one sexual intercourse. At the same time, syphilis can be transmitted during any type of sex - traditional, oral or anal, in which the partners did not use a condom.
Household
Pale treponemas do not have a high viability when outside the body and die quickly, so the household route of infection with syphilis is a relatively rare way of infection. It is possible with close contact with a carrier of infection with open sores on the body. How is syphilis transmitted in this case? The causative agent of the infection may be on the dishes, towels or linens used by the infected, and if hygiene standards are not observed, it can pass to a healthy person.
Many are interested in how syphilis is transmitted through such contact with the patient as a kiss or a handshake. Transmission of infection through saliva can only occur when the carrier has syphilitic rashes on the oral mucosa. As for bodily contact, such cases of infection, although very rare, occur when there are wounds or microtraumas on the hands or other parts of the body that have come into contact with the infected surfaces of the patient's body. Syphilis is not transmitted by airborne droplets.
Through the blood
Blood transfusion transmission of a sexually transmitted infection is possible through blood transfusion from an infected person or the use of shared injection syringes. In everyday life, this type of infection can be caused by the joint use of personal hygiene items on which the patient's blood can remain, for example, shaving accessories or a toothbrush.
From mother to child

Transmission of syphilis to a child can occur directly during pregnancy. The placental barrier is able to protect the fetus from some pathogens of infectious diseases, but pale treponema is not among them. With this route of infection, the disease is congenital. The infected fetus often dies or is born dead. If the infection does not lead to death, the newborn has a very high risk of severe damage to all body systems.
In addition to the transplacental route, the infection can be transmitted to the child during childbirth or feeding along with mother's milk. Knowing how syphilis is transmitted helps prevent infection of the baby, unless it has already occurred during pregnancy. In cases where a woman is diagnosed with a disease, she is given a caesarean section, and the baby is prescribed artificial nutrition.
The first signs of the disease
The clinical symptoms of syphilis are varied. They depend on the stage of the disease, the timing of the start of treatment and the adequacy of the therapy prescribed to the patient. In addition to information about the primary signs of the disease, a person suspecting infection should know how long syphilis manifests itself. The incubation period of the disease is about 3-6 weeks.
The primary signs of syphilis appear as single skin lesions that occur at the site of contact. In medicine, such a formation is called a hard chancre. It is a dense round ulcer, which is painless and can have a diameter of 0.5 to 2 cm. Within a week after its appearance, an increase in lymph nodes occurs. In some cases, there are no external signs of the disease, since a hard chancre can form in places invisible to the eye (on the internal genital organs) or not appear at all.

The secondary stage of the disease occurs 2-3 months after infection. The primary foci of syphilis by that time disappear, and a rash appears on the skin and mucous membranes. It can be localized on the face, torso, legs and arms, palms and soles. Sometimes the appearance of a rash is combined with a slight malaise, fever, sore throat. After a few days or later, after 1-2 weeks, all these manifestations disappear without a trace.
If untreated, syphilis acquires a chronic course, which is characterized by a complete absence of symptoms. This stage can last for months or years, and in some cases the latent course of the disease drags on for up to 10-20 years. Some patients remain carriers of the infection, but in about 30% of cases, after a long asymptomatic stage, the development of tertiary syphilis begins.
The last stage of the disease is characterized by multiple progressive lesions that can affect a number of systems and organs: the skin, mucous membranes, large vessels, the musculoskeletal system, the brain and spinal cord. The most rapid development is distinguished by such a form of the disease as syphilitic meningitis, which mainly affects the membranes of the brain.
In men
The primary manifestations of syphilis in men can be located on the head and body of the penis, foreskin or scrotum. Sometimes the formation is localized inside the urethra, but it is worth noting that its location does not depend on gender. Chancre is able to appear on any part of the body, and all the main symptoms of the disease in both men and girls develop the same way.
Among women
In the female part of the population, the primary sign of syphilis is sometimes not a hard chancre, but its atypical form - indurative edema. It manifests itself in the form of an increase and a noticeable change in the color of the labia and clitoris. Edema can persist from 1-2 weeks to a month. This phenomenon accompanies many sexual infections in women, and such characteristic manifestations as an increase in lymph nodes and the absence of signs of an inflammatory process in a blood test help to distinguish it from other diseases.
Express test for syphilis

Blood tests for genital infections in men and women are carried out using several laboratory methods, and the cardiolipin test and enzyme immunoassay provide the fastest results. To ensure the reliability of the analyzes, these two methods are often combined, and if the results are unclear, additional tests are used.
Passing a laboratory test for syphilis is available at the hospital at the place of registration or in a paid medical laboratory or clinic. The cost of an express test in non-state clinics is about 250-350 rubles. However, this type of analysis often gives too vague or ambiguous results, so for accurate diagnosis, more in-depth types of research may be required, the prices of which reach 1800-2000 rubles.
Treatment Methods

Syphilis is treated with mandatory use of specific antibiotic therapy. When prescribing treatment, penicillin is a priority drug. If the patient is allergic to penicillin antibiotics, therapy is carried out using antibacterial agents from a number of cephalosporins or macrolides. Depending on the stage of the course of the disease, drugs can be prescribed in tablet form or as injections. Active forms of syphilis are treated in a hospital setting. The duration of therapy can take from several weeks or months to several years.
Video how a dangerous infection is transmitted
For more information on the specifics of syphilis infection, see the videos below. In them, experts tell how the infection is transmitted through a kiss, what external manifestations can serve as signs of infection, and how long the incubation period of the disease lasts. This knowledge will help protect yourself from a sexually transmitted infection or timely identify its signs and seek qualified medical help.
Through a kiss
Incubation period
Attention! The information provided in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not call for self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give recommendations for treatment, based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Did you find an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we'll fix it!Such a disease as syphilis became known to mankind as early as the 15th century, and before the discovery of antibiotics, it was a disabling and severe pathology that significantly shortened a person's life.
But today, the active use of antibiotics in the treatment of other diseases in certain cases leads to a blurring of the clinical picture and, as a result, the development of latent syphilis.
In our time, syphilis has become widespread. The main age group is people 15-40 years old (there is a peak incidence at 20-30 years old). The risk of infection is much higher than in women (microtrauma of the vagina contributes to infection), but today the increase in the number of homosexuals leads to the fact that there are more cases of syphilis in men.
Syphilis is one of the most common venereal infections (third place in the world), with about 12 million people becoming victims of it every day. But these statistics cannot be called accurate, since some of the sick prefer to be treated secretly, or on their own, without turning to doctors. And many people think about how infection with this disease occurs other than through the sexual route. Can syphilis be transmitted through saliva, by household means, can it be transmitted to a child?
When do symptoms of infection appear?
The incubation period is usually calculated from the moment of penetration into the body of pale treponema and until the formation of a hard chancre, which averages 3-4 weeks.
During the latent phase, the following options may occur:
Shortening up to 8-15 days when infected from several sources;
Removal up to 100-190 days against the background of taking various antibiotics aimed at treating another pathology.
Thus, a person after infection for 2-6 weeks does not experience any symptoms, which, in the presence of a large number of sexual partners, greatly complicates the establishment of the source of infection.

How is syphilis transmitted?
By knowing how syphilis is transmitted, you can protect your loved ones and yourself from this unpleasant disease.
Infection through sexual contact.
The sexual route during unprotected intercourse without the use of barrier contraception is the main one in the epidemiology of the disease, as a result of which it belongs to the STI group. Vaginal secretions and semen are an excellent medium for Treponema pallidum to live, and one sexual intercourse (with oral, anal, or vaginal penetration) with a sick person is enough to become infected (average 50% of cases).
All types of sexual intercourse are equally dangerous, but anal penetration has the highest risk of infection, since there is a possibility of injuring the rectal mucosa. During vaginal intercourse, a woman has a higher risk of contracting syphilis than a man, since the vaginal mucosa can be easily injured during intercourse.

Syphilis is a very insidious disease. A sick person is contagious at his every stage. During the incubation period, not knowing about his illness, a sick person can infect all new partners with whom he has sexual intercourse.
Transmission of syphilis through saliva.
Unfortunately, syphilis can be transmitted through saliva if there are rashes on the lips or in the oral cavity - only in this case there is pale treponema in the saliva. Naturally, such patients pose a great danger of infection when kissing, when the oral cavities are in contact with each other.
According to statistics, syphilis is most often transmitted through a kiss and only in some cases through saliva. All this for the reason that syphilitic rashes on the lips and oral mucosa are quite rare. Moreover, a healthy person must have microtraumas of the oral mucosa, otherwise the causative agent of syphilis will not be able to penetrate into the bloodstream.
Transmission of syphilis through breast milk.
There are treponemas in the mother's milk of a sick woman, so she can easily infect her baby while breastfeeding. Infants, especially newborns, have a very underdeveloped immune system and are therefore at particularly high risk of disease.

Infection with syphilis through the blood.
If the causative agent of syphilis is present in the blood, then organ transplantation, or transfusion of the blood of a sick person, will necessarily lead to infection of this pathology, but this route of transmission of syphilis is unlikely, since today transplanted organs and blood are carefully checked for various infections, including syphilis.
Especially often, infection with syphilis through the blood passes after the use of one syringe by drug addicts, for one container for preparing a solution of a narcotic drug. If the skin and mucous membranes are damaged, for example, during a fight, it can also become infected from a sick person.

From the first day of infection to the last day of the course of the disease, the patient's blood is contagious. This means that infection is possible not only through transfusion, but also through injury to the skin or mucous membranes with medical instruments, instruments in beauty centers (pedicure and manicure parlors) that have been contaminated with infected blood. All external manifestations of syphilis (erosions, ulcers, papules) with poor separation in a patient are contagious. Therefore, if there are microcracks on the skin of a healthy person, in contact with the skin of a patient, they can lead to infection with syphilis by contact (household) way.
Infection during professional activity.
This way of transmission of the disease takes place among the following professions: cosmetologists, medical personnel and others whose activities are directly related to invasive procedures, as well as contact with vaginal secretions, saliva, blood of infected people. Infection among physicians most likely occurs when injuries are caused by tools used in a patient with syphilis. Beauticians can become infected with syphilis when using undisinfected instruments that were used during procedures on a patient with syphilis.
But keep in mind that a prerequisite for transmission is a violation of the integrity of the skin in a healthy person. The mere contact of infected blood with healthy skin does not lead to infection.

Domestic infection.
Many people are interested in whether syphilis can be transmitted by household means - after all, someone has to live next to a sick person. Transmission of syphilis through household items (personal hygiene items, cigarettes, linen, dishes, cutlery, towels) is likely with prolonged and close contact with the patient, and at the thermal stages of the disease, during the period of active release of infection into the external environment (decaying ulcers, pits) . When dried, treponema may lose its pathogenicity, for this reason, the transmission of syphilis can only be with saliva, or other liquid on objects.
Infection during childbirth.
Since the pathogen is in the vaginal environment, and the birth itself is accompanied by contact of maternal blood with the fetus, the transmission of syphilis is easily realized. In the event that the child was able to avoid intrauterine infection, then during natural childbirth it is almost impossible to prevent it. In this case, a caesarean section is required, in which the likelihood of infection of the baby is significantly reduced.
The infection is transplacental.
This path is realized during the pregnancy of a sick woman - the pathogen is transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. First, treponema affects the placenta and, after the protective barrier is destroyed, it penetrates through the lymphatic system, or the umbilical vein, into the organs and tissues of the fetus. In the first 3 months of the disease, a woman is especially contagious, but the likelihood of the disease remains in the future.

How to avoid contracting syphilis?
Compliance with elementary hygiene rules will help to avoid this shameful and unpleasant disease. By knowing how syphilis is transmitted, you can protect yourself from situations in which the likelihood of infection is especially high.
The use of local antiseptics intended for the treatment of the oral cavity, genitals, rectum after sexual intercourse ("Chlorhexidine", "Miramistina"). This measure is mandatory for both unprotected and protected sexual intercourse - in the first case, there are no guarantees that infection will not occur, but the likelihood will significantly decrease.
Use of a condom in a variety of types of sexual relations.
Consult a doctor within two hours after unprotected intercourse, who will prescribe you preventive treatment, namely antibiotic therapy.
Body care and individual use of personal hygiene products.
Artificial feeding of babies born to a mother who is sick with syphilis.
Strict observance of safety rules for persons at risk.
The use of disposable syringes for different types of injection (subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, and others).
Mandatory treatment of a pregnant woman in case of detection of syphilis.
Regular, timely preventive examination for sexually transmitted diseases.
Evaluation of a blood test for syphilis
It should be noted that the diagnosis of syphilis is a rather difficult task for specialists, for the reason that the results may be negative at the stage of the incubation period, or false positive (they may be as a result of malaria, or against the background of pyelonephritis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, tuberculosis lungs, chronic hepatitis, pregnancy, oncological diseases, antiphospholipid syndrome). For this reason, the tests should be performed again, after the treatment of somatic diseases and the relief of chronic foci of infection.
To establish the diagnosis of syphilis and evaluate the cure, tests such as:
passive hemoagglutination reaction (RPHA - TPHA) - treponemal tests;
immunofluorescence reaction (RIF-FTA) - treponemal tests;
non-treponemal test - RPR / VDRL, a fourfold decrease in such titers within one year after treatment is a criterion for cure.
Treponemal tests are used solely to establish the diagnosis, but not to monitor cure. In Russia, the Wasserman reaction and the immobilization reaction of pale treponema are still used to establish the diagnosis. The performance of the RPR test, as a rule, is supplemented by PCR, RIBT, RIF analyzes.
|
Result evaluation |
|||
|
or early stage or incubation period or no syphilis |
|||
|
or recent treatment for syphilis or have syphilis and it is not treated |
|||
|
or primary syphilis or a false positive result of RPR and RIF |
|||
|
or false positive RPHA and RIF or false negative RIF |
|||
|
or treated syphilis or late untreated |
|||
|
biological false positive reaction |
|||
|
or early primary syphilis or recently treated or false positive RIF analysis |
|||
|
or treated syphilis or false positive RPHA |
After infection at the end of the incubation period may be positive:
one to two weeks after the onset of the chancre (four to five weeks from infection), non-specific bodies may be positive;
antitreponemal IgM bodies often appear in the second week of illness;
IgG to treponemal antigens becomes plus four weeks after the disease;
when symptoms of syphilis appear, total IgG + IgM antibodies become positive in blood tests.

Throughout the course of drug treatment, test results may change, with well-chosen therapy in blood tests, IgM rapidly decreases, but IgG will remain in the blood for a long time (in some cases, even until the end of the patient's life).
For a mass survey of the population, simple, inexpensive and fast non-treponemal tests will be used. The following categories of citizens are subject to examination:
Pregnant women.
Military personnel.
Serving time in prison.
Donors of blood and organs for transplantation.
Upon admission to the hospital for treatment and before surgery.
Workers in the field of medicine, education, nutrition.
 Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?
Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?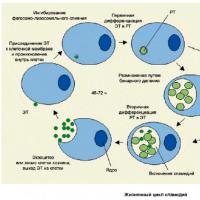 PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do
PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs
COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat
Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials
Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials How to tell the time in English?
How to tell the time in English? Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis