Can ureaplasma pass after mud therapy. Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)? Ureaplasma: what is it
Thanks to new medical research technologies, such as polymerase chain reaction and enzyme immunoassay, many new microorganisms have been identified. Among them - ureaplasma (Ureaplasma urealyticum).
Many patients who have been diagnosed with ureaplasmosis are interested in the type of pathogen, wondering how dangerous ureaplasma is, what it is and how to quickly recover from the disease.
The bacterium lives on the genitals and in the human urinary system. Bacteriological studies reveal the activity of the microorganism in various inflammatory diseases: prostatitis, cystitis, colpitis, adnexitis, cervical erosion and other diseases of the urogenital area in men and women.
The microorganism is introduced into the cytoplasm of leukocytes, epithelium, spermatozoa, disrupting their functions. Often, ureaplasma is found along with other pathogenic microflora: chlamydia, gardnerella, Trichomonas and others.
Symptoms of the disease may be acute or be of a sluggish nature. There are no specific symptoms characteristic exclusively of ureaplasmosis. Symptoms of a disease caused by ureaplasma are easily confused with manifestations of other microbes. It is possible to determine specifically what it is - ureaplasma or, for example, chlamydia using diagnostic studies.
Symptoms of male ureaplasmosis:
- burning and pain in the genitals during urination;
- pain in the head of the penis during sex;
- pulling pains in the perineum and lower abdomen;
- pain in the scrotum (testicles);
- not abundant discharge from the penis;
- decreased sexual desire.
Symptoms of female ureaplasmosis:
- there is pain, burning and pain when urinating;
- pulling pains in the lower abdomen may appear;
- profuse discharge from the vagina;
- a woman experiences discomfort during sex;
- partial or complete lack of libido;
- after sexual intercourse, an admixture of blood may appear in the discharge;
- pregnancy does not occur for a long time.
Ureaplasmas can harm the body asymptomatically. In this case, the disease passes into the chronic stage, bypassing the acute one.
How is ureaplasma transmitted, and what factors contribute to the development of diseases
 The main routes of transmission of Ureaplasma spp are unprotected sexual contact, and infection of infants from the mother in utero or during passage through the birth canal. Intrauterine infection is possible due to the presence of ureaplasma in the amniotic fluid. The infection enters through the skin, the urethrogenital tract, or the digestive tract.
The main routes of transmission of Ureaplasma spp are unprotected sexual contact, and infection of infants from the mother in utero or during passage through the birth canal. Intrauterine infection is possible due to the presence of ureaplasma in the amniotic fluid. The infection enters through the skin, the urethrogenital tract, or the digestive tract.
According to statistics, almost a third of female newborns are found to have ureaplasma on the genitals.. Among boys, this figure is much lower. In the process of growth and development of the body, the infection disappears, especially in male children. Among schoolgirls, ureaplasma is detected only in 5-20 percent of the subjects. In boys, this figure is practically reduced to zero. Unlike children, the percentage of adults suffering from ureaplasmosis is increasing, since the sexual route of infection is the most common.
Another way of transmitting a microorganism is household. How ureaplasma is transmitted by household means has not been studied, so this statement is controversial. But still there are prerequisites for the fact that not only sexual intercourse is the cause of infection of adults. For example, a microbe is able to maintain its activity on wet household items for two days.
Frequently asked questions about modes of microorganism transmission:
- Is it possible to get infected with ureaplasma through a kiss?
Microbes live and multiply on the organs of the genitourinary system. They are not in the mouth. Therefore, a kiss cannot be a source of infection with ureaplasmosis. But if the partners have oral sex, then the microorganism, getting into the oral cavity, can be transmitted to the partner during a kiss. And if he has ulcers on the mucous membranes, then the ureaplasma is able to enter the bloodstream, and, accordingly, infection is possible. - Is ureaplasma transmitted through saliva?
We have already found out how ureaplasma is transmitted through a kiss. Therefore, we can say that saliva itself does not contain a microbe, but it can temporarily appear in its composition during oral caresses.
If an infection has entered the body, this does not mean that a person will get sick.
To activate ureaplasma, special conditions are required, including:
- reduced immunity;
- frequent stress;
- violation of the balance of the microflora of the body;
- the presence of other infections of the genitourinary system;
- radioactive exposure;
- poor nutrition and quality of life in general;
- insufficient hygiene of the genital organs;
- long-term use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs;
- pregnancy, childbirth.
A decrease in the body's defenses is almost always accompanied by the development or exacerbation of diseases that have a bacterial etiology. But the ailments themselves reduce immunity: frequent colds, chronic diseases, etc. During pregnancy, the woman’s body is rebuilt, and this is an additional burden on the immune system.
Malnutrition, alcohol abuse, heavy physical exertion and stress - all lead to the depletion of the body, which means it contributes to the development of ureaplasmosis. The most dangerous factor for the manifestation of the disease is promiscuity.
In addition to many different pathogenic microorganisms that enter the mucous membranes of the genital organs, the frequent change of sexual partners disrupts the natural microflora present in the urogenital area of a woman, increasing the risk of developing inflammatory processes.
Types of ureaplasma in women and men
 Ureaplasmas have recently begun to be isolated as a separate type of microorganisms. Previously, they were classified as mycoplasmas (mycoplasma). Among the species, ureaplasma urealiticum, parvum and spices are distinguished. Latin names: urealyticum, parvum, species. In total, there are 14 species of microorganisms, but only three types differ in the composition of membrane proteins. Thanks to typing by type, you can choose an effective treatment for ureaplasmosis.
Ureaplasmas have recently begun to be isolated as a separate type of microorganisms. Previously, they were classified as mycoplasmas (mycoplasma). Among the species, ureaplasma urealiticum, parvum and spices are distinguished. Latin names: urealyticum, parvum, species. In total, there are 14 species of microorganisms, but only three types differ in the composition of membrane proteins. Thanks to typing by type, you can choose an effective treatment for ureaplasmosis.
Realiticum type.
It has a weakly expressed membrane, due to which it is easily introduced into the mucous membranes of the genital organs and urinary tract. This type of ureaplasma is capable of destroying immune cells, since the basis of the microorganism is immunoglobulin Iga. But the biggest danger of the urealyticum microbe is that it penetrates the cytoplasm of sperm and blood, destroying them.
Variety of parvum.
Specialty type.
Treatment varies depending on the type of microbe. Most often, diseases caused by ureaplasma urealiticum and parvum are diagnosed. Usually the second does not require treatment, it all depends on the number of microbes that live on the mucous membranes.
If the ureaplasma pravum exceeds the permissible norm several times, then inflammation develops and antibacterial therapy is carried out against the bacteria. The urealiticum type requires rapid intervention, as it can cause complications. Based on the patient's complaints, PCR molecular diagnostics are carried out, and after the detection of a variety of a microorganism, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
It is especially important to diagnose these types of ureaplasma in women during childbearing, as they disrupt the normal process of pregnancy.
Spice tests are prescribed in the following cases:
- pregnancy is planned;
- there are pathologies of previous pregnancies;
- during infertility treatment;
- the presence of urogenital infections.
Ureaplasmosis is treated with antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics are usually prescribed tetracyclines or macrolides: Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Josamycin and others. As an addition, a course of treatment with immunomodulators is prescribed: Dikaris, Takvitin, etc. Sexual contacts and drinking alcohol are prohibited while taking medications. Pregnant women undergo therapy under the supervision of the attending physician.
Diseases caused by different types of ureaplasma in women and men:
- women: damage to the fallopian tubes, adnexitis, endometriosis, cervicitis, vaginitis, ectopic pregnancy, infertility;
- men: prostatitis, urethritis, infertility.
Ureaplasma infection: diagnosis and features of the disease during pregnancy
 Treatment of ureaplasmosis is possible only after diagnostic studies. As mentioned earlier, the disease has no distinctive symptoms, and, therefore, the pathogen that provokes the inflammatory process must be identified. It is advisable to undergo diagnostics before conceiving a child, since bacteria can infect the fetus.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis is possible only after diagnostic studies. As mentioned earlier, the disease has no distinctive symptoms, and, therefore, the pathogen that provokes the inflammatory process must be identified. It is advisable to undergo diagnostics before conceiving a child, since bacteria can infect the fetus.
Ureaplasma infection is detected by different methods:
- Enzyme immunoassay (ELISA). With it, you can differentiate the types of infection: Ureaplasma urealyticum and pravum. The method allows you to identify antibodies to the microbe and the titer (number) of bacteria.
- Cultural method (bacterial culture). Longer method, but more accurate. Allows you to identify the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibacterial substances.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Pretty expensive method. With its help, even a small amount of bacteria or viruses in the blood serum can be determined long before the clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Immunofluorescence (RNIF - indirect, RPIF - direct). One of the most inexpensive methods for detecting pathogenic microflora.
Late diagnosis before pregnancy or infection during childbearing can cause various complications. This is especially dangerous in the 1st trimester, since antibiotic therapy cannot be carried out during this period. Antibiotics can harm the fetus by inhibiting its growth and causing developmental abnormalities.
Complications associated with pregnancy:
- Ureaplasma urealyticum can lead to ectopic pregnancy, and in the early stages - to provoke a miscarriage.
- In the later stages, the subspecies ureaplasma spensis contributes to premature birth.
- Both during pregnancy and during childbirth, the baby can be infected with bacteria.
- Ureaplasma infection can cause inflammatory processes in the uterus, which adversely affect the process of bearing a child.
- Many doctors associate the low weight of the child after birth with the presence of Ureaplasma urealyticum. But it is still too early to assert this as a fact, as research continues.
Can ureaplasma pass by itself, or does it always need treatment? Unfortunately, there is no unequivocal answer to this question, because to date this infection has not been sufficiently studied. But if you rely on medical practice and medical experience, then we can say the following:
 It's just that an infection that enters the body sexually settles on the mucous membranes of the urethra, on the walls of the vagina, uterus, and prostate gland. Decreased immunity, high physical activity, stress, hypothermia, a cold or inflammatory disease, and other negative circumstances will instantly refute the assertion that ureaplasma has passed on its own.
It's just that an infection that enters the body sexually settles on the mucous membranes of the urethra, on the walls of the vagina, uterus, and prostate gland. Decreased immunity, high physical activity, stress, hypothermia, a cold or inflammatory disease, and other negative circumstances will instantly refute the assertion that ureaplasma has passed on its own.
“Is ureaplasmosis completely cured?”, “Is it necessary to treat ureaplasmosis?” and in general "Will we cure ureaplasmosis?". Discussions on these issues...
Reviews and comments
PCR showed a negative result for ureaplasma, and three years later it was positive. The partner is the same. Does this mean that the partner brought this ureaplasma after infidelity?
Does anyone know what kind of animal ureaplasma is and whether it should still be treated? and got the best answer
Answer from Anna Matveeva[guru]
In principle, it is believed that ureaplasma is one of the manifestations of dysbiosis (dysbacteriosis) of the vagina. It should be treated if there are symptoms - scanty clear vaginal discharge;
lower abdominal pain. It often happens that after persistent treatment with several courses of antibiotics, ureaplasma still continues to be detected in smears. Well, leave her alone.
Source: Family doctor practice
Answer from gin[guru]
Personally, I treated her during pregnancy and everything is fine.
Ureaplasmosis - is caused by microorganisms that are close in size to large viruses and have neither DNA nor a cell membrane. They are sometimes considered as a kind of transitional stage from viruses to single-celled ones. The infection is transmitted mainly through sexual contact, but intrauterine infection from a sick mother is also possible, and in addition, microbes can enter the child's genital tract during childbirth and remain there all their lives, for the time being in an inactive state. Ureaplasmas can cause inflammation of any parts of the genitourinary tract - the urethra, prostate, bladder, testicles and their appendages, and in women - the vagina, uterus and appendages. In addition, some studies have found that ureaplasmas can be fixed on spermatozoa and disrupt their motor activity, and in some cases simply kill sperm. Finally, microbes can cause joint inflammation, especially in rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment of ureaplasmosis.
Ureaplasmosis can occur in both acute and chronic forms. As with many other infections, the disease does not have symptoms specific to this pathogen. Clinical manifestations of ureaplasmosis depend on the affected organ. At the same time, the pathogen is often detected by modern methods in completely healthy women who do not present any complaints, and often in combination with other infections.
Some symptoms of ureaplasmosis
Symptoms of ureaplasmosis occur 3-5 weeks after infection. It should be noted that ureaplasmosis is manifested by minor symptoms that bother patients little, and often do not appear at all (especially in women).
Symptoms of ureaplasmosis in men:
scanty clear discharge from the urethra;
moderate pain and burning during urination;
with damage to the prostate - symptoms of prostatitis.
Symptoms of ureaplasmosis in women:
scanty clear vaginal discharge;
moderate pain and burning during urination;
pain in the lower abdomen (with inflammation of the uterus and appendages).
Do not start treatment for ureaplasmosis
Without treatment, ureaplasmosis can occur from time to time. Repeated exacerbations can be associated with drinking in large quantities, colds, emotional overload. Chronic infection can cause urethral stricture over time. If left untreated in men, ureaplasmosis can cause inflammation of the prostate gland (see Prostatitis).
In women, untreated ureaplasmosis causes inflammation and adhesions in the fallopian tubes, leading to infertility and increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy. In pregnant women, ureaplasmosis can cause pathology of pregnancy and the fetus.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis with antibiotics is quite effective, but at the same time, a person's own (useful) microflora is destroyed.
Answer from N[guru]
Ureaplasmas are microorganisms that cause various inflammatory processes in the body. For some time, they can be passive, and during the period of weakening of the immune system, due to the influence of various adverse factors, they can become more active and provoke both male and female diseases. Here are some inflammations that can occur as a result of ureaplasma entering the body: prostatitis, colpitis, vaginitis, cervical erosion, etc. Ureaplasma in men is more pronounced than in women. The presence of a microorganism is evidenced by burning, itching and mucus discharge from the urethra.
Answer from Ўliya[guru]
It is necessary to cure first what spravotsiroval her. And then it might go away on its own...
What you need to know about this disease in order to protect yourself and prevent infection of your loved ones?
Why is it so special that it is worth talking about it?
The international classification has identified the following forms of this disease:
- Manifest amebiasis, in which clinical symptoms can be observed.
- Asymptomatic amoebiasis.
Manifest amoebiasis has several manifestations:
- Intestinal.
- Extraintestinal. This includes the genitourinary, cerebral, pulmonary, hepatic.
- Cutaneous.
The main type of manifest amebiasis is intestinal, and the rest are derivatives of it. This happens when the disease is severely neglected, pathogens multiply a lot. They penetrate the walls of the intestine, and the blood carries them throughout the body. Amoeba settle in different organs, contributing to the occurrence of amoebic abscesses.
Transmission routes
The disease is transmitted in the same way as any other intestinal infection. It happens through:
- Infected water.
- Infected food.
- Dirty hands.
In summer, you can become infected by swallowing amoeba cysts while swimming in an open body of water.
Development of the disease
The development of the disease occurs gradually, since not living amoebas, but cysts penetrate into a person. They will take some time to develop: there are no favorable conditions for cysts in the external environment, so many types of bacteria fall into a state of sleep, having previously been covered with a hard shell. Precisely because the cysts are in a dormant state, they can pass through the aggressive environment that is present in the stomach and small intestine.
As soon as the environment changes for the better for them, and the large intestine has the most acceptable climate for them, the cysts “wake up”. Then they are embedded in its walls. Lucky for those who have increased stomach acidity, lucky in this matter - amoebas do not survive in such an environment. Although you shouldn’t be especially happy - there are highly pathogenic amoebas, whose cysts are not even afraid of hydrochloric acid.
Intestinal amoeba can have the following life forms:
- Large vegetative.
- Small vegetative.
- Cyst.
The size of large forms is about 30-60 microns, and cysts are from 8-9 to 23-24 microns.
Intestinal amoebiasis - what is it?
So, if intestinal amoebae are "habitual residents", when do they become dangerous and begin to cause harm? This happens when the host's body is weakened, which is facilitated by stress, SARS, acute respiratory infections and other similar effects on the immune system.
Distinctive features of amoebiasis
A distinctive symptom of the disease is stool and localization of pain. So, the stool will have the consistency and color of raspberry jam. As for the pain, it, unlike the defeat of the dysenteric amoeba, will not be localized in the left side of the abdomen. The stomach will hurt on the right side, because with a disease of this type, other parts of the large intestine are affected - higher ones.
Ulcers form on the intestinal mucosa. Then abscesses may appear in their place. In addition, other organs may also be affected. Lung and liver damage may occur.
signs
Various symptoms will help diagnose the intestinal type of amoebiasis:
- Heat.
- Blood in stools.
- Weakness.
- High fatigue.
- Headache.
These symptoms are already a reason to call an ambulance. If amoebas are distributed throughout the body, they may additionally manifest themselves:
- Jaundice.
- Pain in the liver.
The liver can hurt and jaundice can appear, for example, with cholangitis, so to clarify the diagnosis, symptoms alone are not enough, you will need to do an ultrasound.
But it is not necessary to observe nausea among the symptoms, since it is not characteristic of this disease.
The symptoms also depend on the stage of the disease. So in an acute form, all the signs appear very pronounced and constantly disturb a person. The chronic course is less pronounced - the temperature is normal, the pain that occurs in the abdomen does not have an exact localization. Periodically, the patient is concerned about not pronounced flatulence.
To treat or not to treat?
Attention: “Of course, this is not fatal, but self-treatment of the disease can have disastrous consequences, in particular, contribute to its transition to a chronic form.”
In addition, it is very difficult for a non-specialist to determine the symptoms of amoebiasis, since they are similar to the symptoms of many other diseases.
If the disease is acute, and the necessary treatment is not provided, it is possible that amoebas, penetrating into the walls of the intestine, contribute to the appearance of ulcers. If they occur at the site of large vessels, bleeding may open. And this is a threat to the life of the patient. You will need immediate surgery. It will be necessary to turn to surgeons even when amoebiasis has passed into an extraintestinal form.
How to overcome the disease?
Treatment in medical institutions begins with diagnostics, for which samples of feces, urine, and blood are taken for analysis. Further, the treatment process is already in the hospital controlled by a doctor. Most often, a specialist prescribes an appointment:
- Metronidazole, which must be taken for at least a week. If the patient is diagnosed with a severe case of the course of the disease, then treatment with metronidazole continues for 14-15 days. No less effective is Furamid.
- Salt solutions. This is necessary to restore water balance.
- Antispasmodics.
- Enzyme preparations to stop the colitis syndrome. This is Panzinorm, Digestal.
- Antibiotics. Necessary in the course of treatment to change the microbial biocenosis in the intestine.
If the disease is diagnosed in a chronic form in remission, then Quinamine, Ambilgar, Dihydroemitin, Emetin are also used for treatment.
But the treatment will be incomplete without observing certain food restrictions. Table No. 4 is recommended for such patients and the following are prohibited:
- Baking, bread.
- Any kind of sweets.
- Soda.
- Salty, spicy.
- Fruit.
- Vegetables.
Then the return to the usual food should be slow. This process should take at least two weeks.
It's worth reading
Ureaplasma in men: treatment regimen, effective drugs
Competent and timely treatment of ureaplasma in men allows you to avoid a number of complications and unpleasant consequences. Initially, ureaplasma was considered a type of mycoplasma. But then scientists found out that ureaplasma can break down urea, so it was brought out into a separate species. Ureaplasma in its normal state does not need to be treated. It is present in approximately 70% of all men who are sexually active. If the microflora of the genitourinary system is normal, ureaplasma does not carry any threat. If immunity falls, the microflora is disturbed, this can lead to infections.
Symptoms and consequences of ureaplasma
You need to be treated for ureaplasma if it has begun to negatively affect the health of a man. Alas, in order to treat ureaplasmosis, patients sometimes turn to specialists late. This is largely due to the fact that ureaplasmosis is often asymptomatic and does not make itself felt until complications arise in the form of chlamydia or other infectious diseases.
You can pay attention to the fact that ureaplasma threatens men's health by several characteristic signs or symptoms:
- when urinating, pain is observed;
- urination is not rarely accompanied by a strong burning sensation;
- pain occurs in the genital area;
- pain can also be observed in the lower abdomen;
- discharge from the urethra.
If ureaplasmosis is detected or suspected, treatment should be started without fail. Otherwise, ureaplasma, which is called parvum or urealiticum, can entail quite serious consequences in the form of:
- prostatitis;
- nonspecific urethritis;
- inflammation of the egg appendages;
- infertility.
In order to maximize the effective treatment of ureaplasma in men, a woman should also undergo therapy if she is the only permanent sexual partner. It is especially important to undergo joint treatment if the couple is planning a pregnancy.
With ureaplasma in men, treatment is prescribed only by a doctor on an individual basis. It is important to understand that antibacterial agents and antibiotics play a major role in the treatment. Each body reacts differently to certain drugs. Therefore, some drugs are excellent for one, but are completely useless for other men.
In order for the treatment regimen to be drawn up correctly, you must first pass the appropriate tests and undergo examinations. This will help determine how a man's body reacts to certain substances, as well as which medications will be most effective in his particular case.
Medications against ureaplasma
How to treat ureaplasma in men? Currently, the disease is treated with antibiotics of certain groups. Such treatment in men as a means of therapy is optimal, since it allows you to cope with microorganisms as efficiently as possible.
It is difficult to say what the most effective drugs are called, since the question is largely individual. After the man undergoes the necessary examinations and passes the tests, the doctor will be able to determine which specific medicines are best to treat him.
The most effective from ureaplasma are:
- tetracycline antibacterial drugs;
- azalides;
- macrolides;
- nitroimidazoles.
As practice shows, having diagnosed ureaplasmosis in men, correctly prescribed and carried out treatment gives the desired result. It may take a long time to recover, although a course of antibiotics usually lasts no more than 10 days.
Often, urologists in the treatment of male ureaplasmosis use one of several types of drugs and individually prescribe a therapy regimen.
- Doxycycline. This is a drug of the tetracycline group, which should be taken 1 tablet twice a day. The approximate duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
- Josamycin. Belongs to the group of macrolides and azalides. Take it 1-2 grams during the day. The drug should be taken between meals. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
- Erythromycin. Another representative of macrolides and azalides. The regimen includes 2 tablets four times a day. Treatment lasts a week (7 days).
- Azithromycin. azalides and macrolides. The drug is taken only 1 time per day (daily dose - 250 mg of the drug). Usually the course of treatment lasts about 6 days.
- Metronidazole. Nitroimidazole group. Depending on the nature of the disease, men are recommended to take the drug three times a day, and the duration of the course is 7 days.
It would be ideal if the sexual permanent partner of a man who has experienced ureaplasmosis also undergoes a similar course of antibiotics. After 2 weeks after completion of therapy, you need to undergo a follow-up examination.
But there are cases when the treatment of ureaplasmosis in men does not give the desired result.
- The patient did not follow the doctor's instructions. Often, the doctor himself prescribes the frequency and amount of medication taken. If such instructions were not given, then you need to rely on the manufacturer's manual. But men tend to violate the recommendations, forgetting to take pills on time or completely abandoning treatment;
- Incomplete course of medication. The doctor tells in detail how to treat ureaplasmosis in men, but they still do not follow these tips. One of the most common reasons for the lack of effect of treatment is insufficiently long-term use of drugs. In simple terms, instead of the prescribed 5-10 days of taking medication, a man drinks them for several days. Feeling relieved, this misleads him that the problem is solved and drops the medication;
- Re-infection. If a man became infected from a woman with whom he constantly lives, or closely communicates with infected people, then re-infection is quite possible if the carrier of ureaplasma has not been treated. This is why couples are encouraged to do therapy together.
Just do not rush to your soulmate with accusations of treason, if she turned out to be the carrier of ureaplasma. The fact is that this microorganism is not only spread sexually, and therefore the fact of infection is not evidence of infidelity.
Often, with ureaplasmosis, treatment is carried out at home. Therefore, the entire responsibility for the result lies with the patient himself. The doctor's task is to correctly prescribe therapy for ureaplasma. It is also recommended that a man periodically visit a doctor during the entire period of treatment at home to confirm the effectiveness of the chosen treatment regimen.
- Antioxidants. The easiest way to get them is from green tea, which doctors recommend to patients to drink in order to avoid diseases such as urethritis or prostatitis. The substances contained in tea protect against inflammatory processes and help strengthen the immune system. Some people enjoy just drinking 2 cups of green tea a day. But there is an alternative - these are certified extracts that need to be taken up to 500 mg during the day;
- Genital care. Since with ureaplasma we are mainly talking about the threat of the genitourinary system of men, personal hygiene plays an important role here. The doctor may prescribe a special antibacterial ointment that can suppress the activity of ureaplasma. In parallel with this, it is imperative to follow the rules of hygiene and maintain a minimum level of humidity in the genital area. To do this, wipe the genitals dry after water procedures and wear underwear only and natural fabrics. This will allow the area to breathe. Moisture is a favorable condition for the growth and reproduction of ureaplasma;
- Immunity and ureaplasma. The stronger your immune system is, the less likely the ureaplasma is to lead to any unpleasant consequences. Immunity is considered the main tool in the fight against ureaplasma and ureaplasmosis. To this end, doctors usually prescribe vitamin complexes and simple medicines to raise the protective functions of the body;
- The fight against dysbacteriosis in ureaplasma. Ureaplasmosis, which becomes chronic, often leads to dysbacteriosis. Antibiotics prescribed by a doctor also kill not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microflora. In order not to provoke complications against the background of dysbacteriosis, it is very important to take probiotics, yogurt and other means to maintain normal microflora;
- Individual appointments. How to cure ureaplasmosis in one case or another depends on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease. Therefore, the specific nuances of the disease play a role here, in which doctors prescribe medications for related problems or choose drugs whose substances do not cause allergic reactions, for example.
Ureaplasma can be safe with strong male immunity. But if ureaplasma is activated, it threatens with ureaplasmosis and serious complications. Therefore, ureaplasma requires increased attention from men.
Often, as a result of the examination, the patient learns that he has found ureaplasma. Naturally, he has questions: “Where does the infection come from, is it curable and what should be done so as not to infect a partner?”.
To begin with, do not panic, but ask the doctor: where does women come from.
- Ureaplasma: what is it
- Diagnosis of ureaplasmosis
- Symptoms of ureaplasmosis
- Treatment of ureaplasmosis
- How to be during pregnancy?
Ureaplasma: what is it
 In fact, the bacterium belongs to opportunistic microbes. And it can be present in the human body without causing any concern.
In fact, the bacterium belongs to opportunistic microbes. And it can be present in the human body without causing any concern.
If the bacteria does not exceed 10 * 4, then this is not a disease and the patient does not require treatment. But there are times when bacteria seem to be absent. But patients complain about and discomfort when urinating. In this case, an additional examination is carried out and adequate therapy is prescribed.
Ureaplasmosis: causes of the disease
The causes of ureaplasmosis in men and women do not differ.
The most common mode of transmission is through unprotected sexual contact. There are two types of microorganisms that are found in women and men. These are ureaplasma ureatilicum and parvum.
A person who often changes sexual partners does not even make sense to think about where the infection came from. Since any of them can be a potential source of infection.
In some cases, such a situation occurs. The man complains that "during the examination, my wife was found to have ureaplasma, but I have no pathology in the analyzes."
How can this be?
 The thing is that normally the infection may be present, but not manifest itself in any way. Under certain conditions, the pathogen is activated and begins to multiply.
The thing is that normally the infection may be present, but not manifest itself in any way. Under certain conditions, the pathogen is activated and begins to multiply.
The causes of the appearance of pathology in women is a change in the acidity of the vaginal flora. When the number of rods (lactobacilli) decreases and mixed flora begins to develop, including ureaplasma.
To the question: "Where do the patients who have never had sexual intercourse get the ureaplasma from?"
Moreover, in 5-25% of cases, the pathogen is detected even in schoolgirls - virgins.
Even a specialist cannot give a definite answer to this question. The thing is that there are other ways of penetration into the body. Including the contact-household way of infection is not excluded. Other causes of the disease in women are:
- decreased immunity;
- Availability ;
- exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the body;
- after monthly, surgical interventions;
- in the postpartum period;
- against the background of the use of the IUD (intrauterine device).
Among the common causes of ureaplasmosis in men are:

Ureaplasma: how the pathogen is transmitted
Ways of infection can be as follows:
- sexual intercourse with an infected partner;
- vertical (ascending) way, i.e. from the vagina and urethra to other organs;
- infection can occur during labor when the fetus moves through the mother's birth canal. In newborn babies, infection is often diagnosed in the nasopharynx and genitals, especially in girls;
In very rare cases, transmission of the infection to the fetus during pregnancy can occur. Even less often, ureaplasma can be infected by contact of a healthy person with a sick person.
Diagnosis of ureaplasmosis
Already after the presentation of complaints and examination by a doctor, the specialist may suspect that the patient has ureaplasmosis. In order to clarify the proposed diagnosis, an additional examination of the patient is carried out. To do this, the doctor may prescribe a number of studies:

If a woman has:
- inflammatory processes of the genitals;
- burdened obstetric history
- or she suffers from infertility,
- violation of the menstrual cycle,
- erosion of the cervix,
- cervicitis or colpitis,
then it is necessary to conduct a study on the presence of ureaplasma infection.
Symptoms of ureaplasmosis
Microorganisms, destroying the cell wall, penetrate into the cell.
The duration of the incubation period for men and women is at least fourteen days.
In some cases, the incubation period for parvum ureaplasma increases to several years. Therefore, if one of the partners has a pathogen, then the other also has it.
Preventive and preventive treatment of the pathological process will help to quickly cope with the infection even at the stage of the development of the disease. In most cases, there are no signs of the disease. Or patients feel mild discomfort when urinating and the presence of weak vaginal discharge. Moreover, such symptoms do not last long and soon disappear.
The disease becomes chronic. With a decrease in the body's resistance, an exacerbation of the disease occurs. And there are pronounced symptoms of the inflammatory nature of the genitourinary system. Such manifestations can be:

If there is a concomitant infection, such as chlamydial, mycoplasma, etc., the symptoms will be more pronounced. If the patient is a carrier of ureaplasma, then the following factors can trigger the development of infection:
- the presence of other sexual infections;
- shift in hormonal status associated with the menstrual cycle;
- decrease in the immune defense of the body;
- during pregnancy;
- in the postpartum period.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis
The causes of ureaplasmosis in women can be very diverse. But regardless of them, treatment should be carried out immediately. To prevent possible complications of the disease, therapy must be carried out without fail:
- if patients present complaints that are symptoms of ureaplasmosis;
- in the presence of a high concentration of infection in the test material during inoculation or according to the results of PCR;
- at the stage of pregnancy planning;
- in the presence of burdened obstetric history;
- with infertility.
What to treat?
A feature of the treatment of the disease is an integrated approach to prescribing medications.

At the end of the course of therapy, control tests are prescribed.
The indicators of the effectiveness of the treatment carried out are as follows:
- absence of complaints and symptoms;
- negative results of PCR and bacterial culture;
- restoration of the vaginal flora.

It often happens that the symptoms of the disease go away spontaneously without treatment. True, in some people the disease never manifests itself again, in others it gives relapses.
Possible causes of self-healing from ureaplasma are not yet fully understood and remain a mystery.
When a disease is detected, both sexual partners should be treated, otherwise it is impossible. The presence of an infection in some cases is not a disease. So the decision on the need for therapy should be made by the attending physician.

Found ureaplasma: what is dangerous infection
Even if the infection in women does not manifest itself in any way, it still carries a certain danger to her health:

If a woman is affected by ureaplasma urealiticum and parvum, negative consequences may develop, the causes of which are caused by:
- decreased immune responses;
- the duration of the pathogen in the urogenital tract;
- physiological instability of protective reactions during pregnancy.
Is it necessary to treat if ureaplasma is found
- With the defeat of the genitourinary system, the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy and infertility increases. The reasons are associated with inflammatory changes in the structure and the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, which contributes to the violation of their patency and prevents the penetration of the egg into the uterine cavity.
- In the postpartum period, pathology can be complicated by endometritis. With the defeat of ureaplasma parvum, chorionamnionitis can serve as the cause of the pathology.
- If the infection spreads upward, it can provoke the development of urolithiasis.
- If ureaplasma is adjacent to mycoplasma infection, then acute hemorrhagic cystitis may develop, leading to damage to the overlying sections of the urogenital system.
How to be during pregnancy?
At the stage of pregnancy planning, a woman needs to go through. This should be done because:
- The presence of even a normal ratio of microorganisms during pregnancy can provoke their reproduction and cause ureaplasmosis.
- The use of antibiotics in the early stages of pregnancy is highly undesirable.
What should a woman do if she has a ureaplasma infection during pregnancy? Most likely, the doctor will postpone treatment until the baby is born. In extreme cases, he will prescribe immunostimulants.
 Ureaplasma in the body in pregnant women is a high risk. And not only for the bearing of the fetus, but also for the possible consequences for the health of the newborn. At the same time, very strong antibacterial drugs are used to treat the disease. But pregnant women are prescribed drugs that do not give a teratogenic and toxic effect. Josamycin is such a drug.
Ureaplasma in the body in pregnant women is a high risk. And not only for the bearing of the fetus, but also for the possible consequences for the health of the newborn. At the same time, very strong antibacterial drugs are used to treat the disease. But pregnant women are prescribed drugs that do not give a teratogenic and toxic effect. Josamycin is such a drug.
How to prevent the possibility of complications during pregnancy and in the postpartum period?
And also infection of the baby at the time of birth?
For a period after 22 weeks, antibiotic therapy is carried out with the simultaneous administration of immunostimulants.
If you suspect ureaplasma, contact a competent venereologist.
 Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?
Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?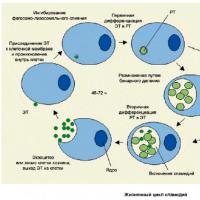 PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do
PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs
COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat
Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials
Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials How to tell the time in English?
How to tell the time in English? Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis