How to get rid of papilloma virus. Is it possible to cure the human papillomavirus forever. Removal of growths on the body
Human papillomavirus is not a scratch that you can get rid of with a leaf of medicinal herb, but also not a serious disease that threatens a person's life. It's just an infection. The infection, which has more than 100 species, is incredibly contagious, does not look back at the age / social status of a potential carrier, and is present in the body of more than 80% of the population.
Each patient who treats in the first place should understand: what he is dealing with, what threatens him with self-treatment, which doctor should seek help, and how much time / effort / money it will cost a full-fledged attempt to get rid of this disease.
HPV: what is it? Disease symptoms. Is it worth it to treat
But, as practice shows, the result of the invasion of papillomavirus, in fact, can be twofold:
- Infected people become carriers of the virus, but they themselves, thanks to the body's defenses, do not notice any symptoms of the disease.
- Almost immediately, the body of an infected person begins to cover papillomas. Depending on the main location of their localization and the type of virus itself, they can be of different shapes / colors, cause itching / pain, or cause absolutely no discomfort.
Accordingly, with the existing variant of the manifestation of symptoms, the issue of treating or ignoring the papillomavirus is resolved by itself. However, there is a special study using. Its results will help determine the type of pathogen, choose the right drug (for a particular strain), find out if it is treated at all.
As for the medical point of view, it was also divided into two halves. Some experts are of the opinion that it is basically impossible to get rid of the papillomavirus. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the symptoms, examining "problem" tumors in time. The only treatment option for this side is / other radical therapeutic methods. The main indications for this approach are:
- regular relapses of the disease;
- pronounced symptoms of the disease, especially on the genitals (genital warts) and mucous membranes (larynx, bronchi, nose, eyes, oral cavity);
- preparation for pregnancy;
- high viral load according to the results of the polymerase chain reaction.
The rest believe in the independent removal of the virus from the body. To do this, it is enough to support his immune system, which will block the pathogenic microorganism. This can be done with the help of vitamin complexes, immunostimulants, a healthy lifestyle (meaning good nutrition / giving up bad habits).
IMPORTANT! This theory is valid for patients under 30 years of age. After reaching the mentioned age, the immune system weakens somewhat and cannot remove the virus from the body on its own, having coped with several strains of HPV at once.
Reasons for the development / progression of HPV
 Before puzzling over how to treat HPV, where to find a good specialist, how much time / money it will take and whether it will be possible to cure papillomavirus in principle, maybe focus on prevention and try not to get infected?
Before puzzling over how to treat HPV, where to find a good specialist, how much time / money it will take and whether it will be possible to cure papillomavirus in principle, maybe focus on prevention and try not to get infected?
It is good if the attending physician explains to the patient in advance that this is almost impossible. For the simple reason that every second person around him can be a carrier of the virus, without having a single papilloma. Thanks for this, he can say to his immunity, which has the strength to block the symptoms of the disease. Whether your body's defenses are so powerful can only be known after infection with HPV itself. This often happens in three main ways:
- From mother to child. During pregnancy, infection is practically excluded, since the placenta is a reliable barrier that protects the baby from any external influence. But during birth, when the baby passes through the birth canal, the risk of transmitting the virus is incredibly high. Moreover, it penetrates, first of all, into the mucous membrane of the eyes / nose / oropharynx of the child. As a result, the first papillomas in a small patient may appear in the first few days. Especially dangerous are those that are localized on the glottis, endangering the life of the baby due to possible strangulation. They are also called papillomatosis of the larynx.
- Contact-household way. It is especially relevant in case of non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, using other people's towels / cups / clothes, shaking hands, kissing, hugging, etc. The risk of infection increases in enclosed spaces with high humidity (pool, sauna, bath), as well as in preschool / school institutions.
- Autoinfection. It is observed in small children who pull everything into their mouths without first washing their hands. The same applies to the habit of biting nails, as well as burrs on the fingers. In place of the latter, characteristic outgrowths appear in the form of flat plaques with a pinkish tint. Do not forget about small scratches / abrasions / other mechanical damage to the skin, through which the virus quickly penetrates into healthy epithelium.
In the absence of any actions, as well as concomitant causes of a decrease in immunity (inflammatory processes, chronic diseases, viral / colds, lack of vitamins / useful micro- and macroelements, living in unfavorable conditions, low environmental level, poor-quality / unbalanced nutrition), papillomatosis rapidly spreads throughout the body, affecting more and more healthy cells. In this case, treatment is inevitable. It remains only to choose the fastest and most effective method.
Treatment of the papillomavirus: the most effective methods

This is how cervical cancer develops
ATTENTION! Treatment of the human papillomavirus should begin with a consultation with a trusted specialist! Only he, after considering your complaints, conducting an examination and making an accurate diagnosis, will be able to draw up an effective treatment plan. He will answer all your questions, including “is it possible to cure papillomatosis in principle?” and “should it be treated at all?”.
If you don’t know who to contact specifically, pay attention to where the papillomas are located that cause you the most inconvenience:
- Are the growths "scattered" on the arms, legs, and/or neck? Then a dermatologist can help you.
- Worried about genital warts? Such papillomas are dealt with by a gynecologist / urologist.
- Tumors were found in, near the anus? Contact a proctologist.
It is worth remembering that at the very start of treatment it would be wrong to set the goal of “removing HPV from the body”. No, you have symptoms that cause some inconvenience and also threaten. We must start with them, minimizing the risk to life and health. Often, a complex method of treating papillomas is used for this:
- Destruction of "problem" papillomas.
- Body support with immunomodulators.
- Healthy lifestyle.
Such an HPV treatment regimen will not only help get rid of the manifestations of the disease, but will also be able to eliminate the virus from the body as such. But you should not count on its rapid removal: if a complete cure is possible, then it will take at least years.
Hardware cosmetology/surgery
 This method of removing papillomas is considered a priority not only in medical circles, but also in cosmetology. After all, this is the only way to quickly / without a trace / effectively remove those papillomas that cause physical discomfort, develop complexes due to an unsightly aesthetic appearance.
This method of removing papillomas is considered a priority not only in medical circles, but also in cosmetology. After all, this is the only way to quickly / without a trace / effectively remove those papillomas that cause physical discomfort, develop complexes due to an unsightly aesthetic appearance.
The most popular are:
- . The essence of the procedure is the "dissolution" of pathological cells, sealing the walls of blood vessels, as well as the rehabilitation of the damaged epithelial layer. The process is absolutely painless, fast and quite effective (from 60 to 92% of papillomas disappear without a trace, without recurrence). However, with regard to wound healing after removal of growths larger than 5 mm, it stretches up to 4 weeks and leaves small depigmented spots.
- "Surgitron" (radio wave therapy / radio knife). This method involves the use of high frequency radio waves to remove skin lesions. Allows you to cure papillomatosis by coagulating blood vessels, and without bleeding and pain. Eliminates recurrence of the disease, acts extremely pointwise, without damaging healthy tissues. More suitable for removing single tumors.
- Cryodestruction. It implies exposure to papilloma with liquid nitrogen, as a result of which the growths dry out, turn black and fall off. If their dimensions are more than 5-6 mm, several sessions will be required to achieve the desired result. IMPORTANT! The likelihood of relapse is quite high.
- Chemolysis. Removes neoplasms with trichloroacetic acid. It is used only for the treatment of genital warts. And then with an efficiency of 30-40%.
- . Papillomas are exposed to high-frequency electric current, as a result of which protein tissues coagulate, destroying the pathological layer. The procedure is quite painful, but allows the use of local anesthesia. As for relapses, they are quite likely, so you should immediately pay attention to this. ATTENTION! The specialist performing the procedure must be extremely careful: the smoke during electrocoagulation may contain particles of the human papillomavirus and, if it enters the upper respiratory tract, infect him.
- "Good old scalpel". Surgical intervention, despite the abundance of more modern methods, continues to occupy one of the first places in medicine. Only now they use it mainly to remove genital warts of large sizes. Also, this method is effective in getting rid of malignant tumors.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. In addition, the patient's fear of hardware therapy/surgery often plays a significant role. In this case, all these methods can be categorically rejected, despite their high efficiency. An exception is, perhaps, oncogenic formations. But even in this case, the patient may insist on other, more “humane” therapeutic methods.
Removal of papillomas using pharmaceutical products
 How to remove pathological formations with medicines? Simple enough. Consult your doctor, who will prescribe a suitable topical product for you. Regardless of the name and price, the active substance of each of them is an acid or alkali, under the influence of which the tissues of epithelial formations are destroyed. In other words, necrosis of pathological cells occurs.
How to remove pathological formations with medicines? Simple enough. Consult your doctor, who will prescribe a suitable topical product for you. Regardless of the name and price, the active substance of each of them is an acid or alkali, under the influence of which the tissues of epithelial formations are destroyed. In other words, necrosis of pathological cells occurs.
The most popular are Solcoderm, Supercleaner, Dermavit, Ferezol, Solkovagin, Wartner Crio, lapis pencil, Isoprinosine. The use of each of them is prohibited for self-medication, as there are a number of contraindications that should not be overlooked:
- None of the pharmaceutical products is allowed for self-treatment of genital papillomas. Solcoderm and Solkovagin are theoretically suitable, but are applied only in the treatment room by an experienced specialist.
- Dermavit is strictly forbidden to be applied to the face / neck / chest / armpit.
- Wartner Cryo turned out to be an excellent analogue of cryodestruction. Its use is allowed at home, but only after consulting a dermatologist and carefully studying the attached instructions. The tool is really effective, but the surface of the skin affected by it heals for a long time and painfully.
- The lapis pencil acts on papillomas with silver nitrate, which helps to remove growths with the maximum destruction of pathological bacteria. Already at the end of the first week of use, necrosis of neoplasms is observed. But you should be prepared for "residual" scars, as well as burns. On closed areas of the body, this is not critical, but it is better not to experiment on the face / neck / chest.
- The most "gentle" agent is Isoprinosine, as it has an antiviral effect. No one will tell you for sure how to get rid of papillomas with these pills. But the body's defenses, in particular the lymphocytic warehouse of blood, will be noticeably strengthened. And with a small spread of papillomatosis, this increases the chances of self-elimination of the virus.
- Ferezol. This solution specializes in skin warts, as well as genital warts, cauterizing their first manifestations. Dangerous for healthy skin and is used no more than 5 times.
How to get rid of papillomatosis folk methods
Traditional medicine is dearly loved by many patients, especially those who prefer self-medication. It is not surprising that they ask neighbors, grandmothers and the good old Internet the question “how to treat HPV”.
This is not to say that such methods of treatment are ineffective. No, many will be able to demonstrate a self-cured ailment with the help of decoctions, tinctures and lotions. But there are also those who folk remedies did not help or only aggravated the condition.
Therefore, before you start using all the collected homemade recipes for papillomatosis, do not forget to consult a specialist and undergo the necessary examination. Most likely, you will be given a “green light” to use certain means, or even advised by those that traditional medicine itself recommends:
| Just a few fresh stems of the plant are enough, from which the juice came out. They lubricate the surface of the growths, trying not to hook on a healthy epidermis. The procedure is somewhat painful, but the result is visible after a few days. | |
| Iodine | You will need a solution (available at any pharmacy) and cotton swabs (for ease of application). HPV is often treated with iodine and is considered one of the most effective/inexpensive remedies. |
| Contains acid that can destroy pathological papillomavirus cells. Allowed for the treatment of growths on the face. It is enough just to lubricate the warts with castor oil twice a day and seal with a plaster. | |
| Any elderly person will tell you how to treat papillomas with garlic. And not about one option, since you can apply a cut clove of garlic to the growth or prepare a “garlic ointment”. | |
| Dandelions | Heads of plants are harvested, filled with cologne and infused. The resulting mixture of papillomas is processed 6-7 times a day. |
Each of the suggested options has the right to life. And he proves that often in order to get rid of the human papillomavirus, it is not necessary to schedule treatment for several years in advance.
Video: How to treat papilloma virus
Content
Like herpes or HIV infection, human papillomavirus (HPV or HPV) is transmitted sexually during unprotected intercourse. Infection can also occur through household contact, but such cases are rare. As a rule, HPV infection appears and disappears imperceptibly, only in 5% of the fairer sex the virus continues to develop, causing various disorders of the reproductive system. A terrifying complication of the disease is cervical cancer. therefore, proper treatment of HPV in women is extremely important. Read and consult a doctor in time.
What does the diagnosis of papillomavirus infection in women mean?
Over the past half century, medical science has discovered more than 150 types of HPV. 80 of them are pathogenic for the human body. According to statistics provided by the World Health Organization, 70% of women are infected with the papillomavirus. If you are diagnosed with HPV in the hospital, this does not mean that you need to sound the alarm. Remember: it is highly likely that the virus will go away on its own, leaving no trace. But to avoid depressing consequences, be observed by a doctor. If the virus begins to show activity, it will be immediately noticed.
Where does papilloma virus come from
How is HPV infection transmitted? Doctors call the following ways of infection:
- sexual - during vaginal / anal / oral sex;
- contact - with kisses;
- household - through common dishes, toilet lids and / or hygiene items;
- vertical - transmission of infection to the child from the mother during childbirth.
According to statistics, infection can occur in childhood when microdamages are received - through scratches / abrasions. HPV infection enters the body, and after the end of the incubation period, it is manifested by the appearance of warts on the skin. The consolation is the fact that papillomaviruses transmitted by contact do not threaten the appearance of cancer.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus
The incubation period of this infection varies from 3 weeks to 10-15 years, so it is not always possible to determine exactly when the infection occurred. As for clinical manifestations, they are also not always expressed clearly. However, doctors call a number of symptoms by which HPV can be preliminarily diagnosed:
- Cervical intereptilial neoplasia.
- Small characteristic growths on the genitals, under the mammary glands, in the armpits, on the eyelids and on the neck.
- Genital warts (genital warts). In women, they appear on the vulva, in men - on the glans penis.
HPV typing and viral diseases as a consequence
Medicine has studied in detail each of the 150 known varieties of HPV and conventionally divided them into several categories that differ in the degree of threat to a woman's health. After establishing a general diagnosis of the papillomavirus, the doctor prescribes a series of tests to clarify the type of infection so that the HPV treatment in a woman gives the desired effect.
High oncogenic risk
With an average level of risk of oncology
|
papillomavirus subtype in women |
Abnormalities seen in women with HPV. |
|
Malignant neoplasms of the larynx, cervical dysplasia. |
|
|
Cervical dysplasia, cervical cancer (rare). |
|
|
Dysplasia and malignant neoplasms of the cervix. |
|
|
Dysplasia of the cervix. |
|
|
Warts in the area of recipients of the genital organs. |
|
|
Features of this type of papillomavirus in women are not fully understood. |
With a low level of cancer
Non-oncogenic
This category of HPV infection in women is less dangerous, since it does not threaten the appearance of oncological diseases. These subtypes of the papillomavirus are expressed in the appearance of warts on the skin, which are easily removed using a special medical laser. Non-oncogenic HPV infection does not cause changes in the structure of human DNA, so the risk of malignant tumors is completely excluded.
Diagnosis of papillomavirus
To detect the papilloma virus in women, special laboratory methods have been developed. The purpose of these tests is not only to determine the presence / absence of HPV infection in a woman, but also to clarify its type. In order to prevent the uncontrolled development of complications, doctors recommend being screened for papillomavirus at least once every two years.

PCR for papillomavirus in women
Polymer chain reaction is a very effective, and therefore a common method for diagnosing many diseases, including papillomavirus. The quantitative PCR test identifies pathogens of infectious diseases by detecting their DNA or RNA in the cells and tissues of the human body. The maximum degree of diagnostic certainty is achieved in the study of vaginal discharge. This HPV test is completely safe. The doctor takes a smear of vaginal discharge and submits it for examination. A few days later, the woman receives a response.
HPV DNA test
In a wide range of medical professionals, this method of research is called Digene (digen test). It is designed to detect papillomavirus in women by the so-called hybrid capture. Digene-test finds DNA fragments of HPV infection and determines its type with high accuracy. Immediately after this analysis, the patient can find out if there is a threat of developing cancer.
Analyzes in gynecology
A doctor may prescribe a Digene test or PCR analysis for HPV in women only if there are good reasons for this. The need for such studies may arise if diseases caused by the papillomavirus are detected:
- erosion of the cervix - an acute inflammatory process, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the epithelium and a change in its properties;
- metaplasia - a reversible pathology of the cervix, characteristic of many types of papillomavirus;
- genital warts - outgrowths on the mucous membrane of the cervix and other organs of the reproductive system;
- warts - harmless signs of the presence of the papillomavirus, manifested in the form of skin defects;
- dysplasia - an irreversible change in the epithelium of the cervix, occurring at the cellular level;
- cancer in situ - malignant oncological tumors that do not extend beyond the basement membranes of the mucous membranes (often observed with constant contact of the patient with carcinogens);
- cancer is a complication of dysplasia that has arisen due to the lack of a fight against the papillomavirus.

Medical practice notes a negative trend of uncontrolled development of diseases associated with HPV in gynecology. The vast majority of patients go to the hospital with complaints of the symptoms of the diseases listed above, undergo an examination and find out that papillomavirus has been raging in the body for a long time. PCR and Digene tests always complete the diagnostic procedure. Doctors prescribe them with disturbing results from primary studies. These are analyzes such as:
- Colposcopy. Inspection of the mucous membrane and tissues of the cervix. This study is the only way to detect changes and understand that they can be caused by the papillomavirus.
- Cytological study. Plain smear from the wall of the mucous membrane of the cervix. The study of such a sample reveals a large number of epithelial cells for analysis. By examining them under a microscope, the doctor accurately determines the changes characteristic of an HPV infection.
- Biopsy. This diagnostic method is more invasive. It is carried out as follows: the doctor takes a fragment of the mucous membrane and slightly cuts the tissue to obtain a sample of the internal material. In this case, the patient may experience discomfort, but the effectiveness of this study is worth it. Deciphering the biopsy reveals atypical epithelial cells that have been altered under the negative influence of the papillomavirus.
How to treat the human papillomavirus
Existing strategies for combating the papillomavirus cannot be called perfect, but there are a number of methods that provide treatment efficiency of up to 90%. To successfully treat HPV, you must first pass all the necessary tests, and then get the doctor's prescriptions and follow them. When prescribing medications and procedures to a patient, doctors study his genotype in detail.

Preparations
The main striking force of medicine against HPV is pharmaceuticals. The patient is prescribed drugs that destroy the cells of the virus and strengthen the immune system. Based on medical practice, the following drugs demonstrate the greatest effectiveness:
- "Allokin-alpha". Antiviral immunomodulator. It is prescribed for patients infected with HPV of high oncogenic risk. The drug is administered intravenously. Mixing with the blood, the active ingredients of this drug have a powerful rebuff to the virus.
- "Groprinosin" and analogues: "Panavir", "Epigen intim". Antiviral immunostimulant, available in the form of tablets. Widely used throughout the world to combat papillomavirus. The drug effectively fights the virus inside the body and quickly eliminates the external symptoms of HPV in women.
- "Viferon" (ointment, spray, suppositories). Effective against HPV infection as a local immunomodulatory drug. It is used as part of a complex course of treatment. Subject to strict observance of the doctor's instructions, "Viferon" helps to quickly stop the development of the virus and get rid of external skin manifestations.
- "Genferon". A powerful antiviral drug based on interferon, taurine and benzocaine, which will help you quickly recover from HPV and improve immunity. It is used strictly according to the doctor's prescription.
- "Isoprinosine". Another representative of the group of immunomodulators, which has established itself as highly effective. "Isoprinosine" can be treated for HPV and carried out prevention. These tablets strengthen the body's internal defenses and enhance the effect of Allokin-alpha injections.
Surgery
It is prescribed in combination with medication. Modern medicine uses destructive methods to quickly eliminate warts and growths on the skin. The main disadvantage of surgical removal of defects is the high probability of recurrence, which is 45-55%. This is due to the fact that the papillomavirus often reactivates. Drug treatment, which was described in the previous section, is aimed at preventing the recurrence of growths and warts.

Folk remedies
If you manage to detect the virus in time, try to do without drug treatment. Keep in mind that you have already become a carrier of the papillomavirus, so you should abstain from sex until you are fully recovered so as not to become pregnant and infect your partner. In addition, it is worth refusing to visit the solarium, otherwise skin defects will become fixed and it will be more difficult to cope with them. By adhering to these restrictions and using folk remedies, you can quickly overcome the papillomavirus. If you are interested, write down some recipes for HPV home remedies:
- Herbal herbal tea against the papillomavirus in women No. 1. Combine in equal parts a plantain leaf, horsetail, lemon balm, nettle, rose hips and lemon balm (6-7 grams each). It will turn out about 3 tablespoons of the dry mixture, which must be poured with a liter of water, put on a burner with a medium-intensity fire, bring to a boil and detect for 10 minutes. Let it brew for 3-4 hours. Take the resulting medicine half an hour before a meal. In just a few weeks, a natural collection will help to cope with the papillomavirus without pharmaceuticals.
- Herbal herbal tea against papillomavirus in women №2. Combine hop cones, valerian root, swamp cudweed, coriander fruits, lemon balm, oregano, lime blossom and motherwort (in equal proportions) in a small metal bowl. Pour 25 grams of the resulting mixture with a liter of boiling water and let it brew for 4-5 hours (preferably in a thermos). To cope with the papillomavirus, take this remedy every 8 hours, exactly 170 ml. For pregnant women, this recipe is contraindicated.
- Castor oil. This unique product of natural origin will help to cope with the external manifestations of the papillomavirus in women and men. Rub castor tree oil into problem areas of the skin, and you will not know the problems. This folk technique will be especially relevant for those who have cosmetic defects on the lips, cheeks and chin.
- Proteins of chicken eggs. The most simple and at the same time extremely effective remedy for combating warts that occur due to the papillomavirus. To avoid cosmetic problems, simply lubricate problem areas of the skin with egg white.
Video: HPV and pregnancy - what to do
Attention! The information provided in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not call for self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give recommendations for treatment, based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Did you find an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we'll fix it!Human papillomavirus (HPV, HPV) is a DNA virus that contributes to the active division of body cells, which leads to the appearance of genital warts, warts and papillomas on the skin of the anorectal zone. Today, more than 100 types of human papillomavirus are known to exist, each of which has a different degree of oncogenicity.
The greatest danger of this infection lies in the fact that the papillomavirus in women can cause the development of a malignant tumor of the cervix, vulva or anus. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment of human papillomavirus infection minimizes the risk of developing cancer, especially of the cervix.
Given the danger of this infection, we want to tell you where the human papillomavirus comes from, how papillomavirus infection manifests itself and how to cure it. We will also introduce you to modern methods of diagnosing and preventing human papillomavirus in women.
The type of human papillomavirus determines how papillomavirus infection will develop and manifest itself in the future, as well as the choice of treatment methods.
 Human papillomaviruses are usually divided according to the degree of their oncogenicity. Thus, all types of virus can be divided into three groups. HPV typing makes it possible to identify a group of patients with a high risk of developing cancer.
Human papillomaviruses are usually divided according to the degree of their oncogenicity. Thus, all types of virus can be divided into three groups. HPV typing makes it possible to identify a group of patients with a high risk of developing cancer.
The first group includes five types of non-oncogenic HPV, namely 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The listed types are not oncogenic, therefore they cannot cause cervical cancer.
The second group consists of human papillomavirus types 6, 11, 42, 43 and 44, which have a low degree of oncogenicity. By themselves, representatives of this group cannot cause cancer of the cervix, vulva or anus, but they can prepare fertile ground for the appearance of malignant tumors.
The most dangerous is the third group of HPV, which consists of types such as 16, 18, 31, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 59 and 68. The listed types of HPV have the highest degree of oncogenicity. Almost 80% of women infected with these types of human papillomavirus sooner or later develop cancer of the cervix, vulva or anus, and the risk of breast cancer is also significantly increased.
Human papillomavirus in women: causes
Human papillomavirus DNA is the causative agent of human papillomavirus infection. This virus penetrates not only the mucous layer, but also the deeper layers of the skin.
There are a number of factors that contribute to human papillomavirus infection, namely:

Ways of transmission of human papillomavirus can be as follows:

The main way is sexual transmission. The infection can be transmitted to girls not only during unprotected vaginal and anal intercourse, but also during petting.
If a woman suffers from papillomavirus infection and there are condylomas or papillomas on the walls of the vagina or labia, then the child can also become infected with them during childbirth.
Also, HPV infection through handshakes, personal hygiene items, pool water, sauna, etc. is not excluded.
Why is the human papillomavirus dangerous in women?
Human papillomavirus, if the immune system is strong, 90% heals itself. But in the presence of favorable soil, which is created by the above factors, human papillomavirus infection can transform into cancer of the vulva, cervix, labia or anus.
As we have already said, in 70% of women with cervical cancer, human papillomaviruses, which belong to the third group, were identified in the blood. Type 16 and 18 HPV are considered the most dangerous.
The human papillomavirus in women on the cervix requires immediate treatment to exclude the development of dysplasia, and then cancer.
In addition, papillomavirus increases the risk of contracting other genital infections, and can also be transmitted to the child during passage through the genital tract.
Each type of human papillomavirus has its own characteristics and specific symptoms. Let's consider them.
Human papillomavirus type 16 in women
Human papillomavirus 16 is a common type of HPV that is found in more than half of infected people. This type has a high oncogenicity.
 The pathogenesis of papillomavirus infection caused by HPV 16 is that the pathogen invades the genome of the cells of the body and blocks the processes of natural antitumor defense, as a result of which papillomas, condylomas or warts appear on the skin.
The pathogenesis of papillomavirus infection caused by HPV 16 is that the pathogen invades the genome of the cells of the body and blocks the processes of natural antitumor defense, as a result of which papillomas, condylomas or warts appear on the skin.
In infected women with HPV 16, gray or brown, flat, rough patches of various sizes appear on the skin of the genitals and anorectal zone. Such rashes are called bowenoid papulosis.
The second sign of a papullovirus infection caused by HPV 16 can be genital warts, which appear not only in the genital area, but also in the eyelids, hips, neck, armpits, etc.
The most dangerous manifestation of HPV 16 is intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervical mucosa, which belongs to precancerous conditions.
Human papillomavirus type 18
HPV 18 is another oncogenic virus that, by integrating into the DNA of human cells, blocks the immune system and promotes the formation of benign tumors. Such tumors are prone to malignancy.
Papillomavirus type 18 in women can cause cervical cancer. This trend was proven by scientists who identified this type of virus in 70% of women with cervical cancer.
Signs of HPV 18 activation:
- genital warts on the skin of the genitals and anus. When injured, these neoplasms can bleed. Condylomas are most prone to malignancy;
- papillomas. These rounded neoplasms do not differ in color from the skin, but rise above its level. Most often, papillomas affect the skin of the armpit and genital organs, but in advanced cases, they can spread to other areas.
- warts, rounded rashes that rise above the skin and are red or dark in color.
HPV 31 is not only dangerous, but also an insidious oncogenic virus, since it can persist in the body asymptomatically for a long time.
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection appear when favorable soil is created in the body, that is, the immune system weakens under the influence of various factors (hypothermia, hormonal failure, exacerbation of chronic diseases, acute infections, sexually transmitted diseases, etc.). Moreover, this type of virus is equally dangerous for both females and males.
Papillomavirus type 31 in women is manifested by papillomas and condylomas in the genital area and anorectal region. There may also be vaginal discharge, soreness during intercourse, discomfort in the vagina, and others.
Human papillomavirus type 33
HPV 33- This is another dangerous virus that can provoke the appearance of a carcinogenic process.

Symptoms of the human papillomavirus type 33 in women can manifest as warts on the genitals. The incubation period of this type of papillomavirus infection is 12-16 weeks. After this time, genital warts on a wide stalk are determined on the labia, the walls of the vagina and the cervix. A feature of warts caused by HPV 33 is that they do not have clear boundaries and a flat surface.
Also, this type of virus can cause a precancerous condition called intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix.
Human papillomavirus type 35
Human papillomavirus type 35 in women may present with the following symptoms:
- the formation of warts, which is more common in girls;
- genital warts that occur on the genitals and tissues of the anorectal region. This type of neoplasm progresses very quickly, turning into large spots;
- flat warts rarely appear with type 35 papillomavirus infection. But, nevertheless, this type of genital warts is dangerous, because it often degenerates into a cancerous tumor.
These neoplasms are accompanied by severe itching, soreness and discomfort. Women may also have symptoms of intoxication of the body in the form of fever, chills, excessive sweating and general weakness.
Human papillomavirus type 39 is also included in the group of viruses with a high risk of oncogenicity. It should be said that this type of virus is most dangerous for women, since men are mainly carriers of the infection.
 Type 39 papillomavirus in women can cause the formation of both warts and papillomas or condylomas, which are prone to degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Most often, such neoplasms are localized on the walls of the vagina and the cervical canal.
Type 39 papillomavirus in women can cause the formation of both warts and papillomas or condylomas, which are prone to degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Most often, such neoplasms are localized on the walls of the vagina and the cervical canal.
Human papillomavirus type 45
The papillomavirus type 45 in women is also highly oncogenic. Moreover, the first signs of papillomavirus infection can appear even 20 years after infection.
During the course of papillomavirus infection caused by type 45 virus, three stages are distinguished. The first stage is characterized by the appearance of genital warts and genital warts. The second stage of the disease is accompanied by dysplasia of the epithelium of the cervix. The most dangerous third stage, which is characterized by the development of cancer of the cervix, vulva or anus.
Human papillomavirus type 51
Symptoms of human papillomavirus type 51 in women appear already in the incubation period, which can last several years. In this period, single genital warts, genital or flat condylomas are poured out in women. The classical localization of these neoplasms is the genital organs (vaginal walls, cervix, small and large labia), but the process can also spread to the eyelids, inguinal and axillary region.
What type 51 papillomavirus infection looks like can be seen in the presented photos.
Human papillomavirus type 52
A feature of the human papillomavirus type 52 in women is that it is activated mainly during the period when the aging of the body begins (after 35 years).
For this type of papillomavirus infection, the same symptoms are characteristic as for other types, namely: warts and condylomas on the genitals, as well as cervical dysplasia.
Human papillomavirus type 56 is characterized by a short incubation period (up to three months).
Symptoms of type 56 papillomavirus in women appear at the end of the incubation period and are characterized by the formation of genital warts and genital warts on a thin stalk, which are localized on the walls of the vagina and cervix. In advanced cases, cervical dysplasia occurs, which is a precancerous condition.
Human papillomavirus type 59
A distinctive feature of the human papillomavirus type 59 in women can be called the fact that warts and condylomas affect not only the genitals, but also the anus and rectum, which increases the risk of anorectal cancer.
Warts reach a fairly large size (up to 10 mm) and have a rough surface and uneven edges, which can be seen in the photo.
Genital warts have a thin stalk and a pointed apex (see photo). The color of warts may differ from skin color.
Papillomas are characterized by rapid growth and spread.
Skin rashes (warts, warts and papillomas) can be easily seen during external and internal gynecological examination (see photo).

Also, in the process of diagnosing HPV, colposcopy can be used - examination of the cervix with a special device - a colposcope, which allows you to enlarge the image several times and even display the image on a computer monitor.
But the most accurate diagnostic method is an analysis for the human papillomavirus, which is carried out using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
PCR is used both to confirm the presence of the human papillomavirus in the female body, and to identify its type.
The "gold standard" for diagnosing HPV is the Digene-Test, which determines the number of viral bodies in the body. Knowing the number of viruses in the body, you can estimate the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Also, all patients with suspected HPV are assigned a cytological examination.
How to treat human papillomavirus in women?
Treatment of human papillomavirus in women can be conservative and surgical.
Tablets from the human papillomavirus should have both antiviral and immunomodulatory effects. The following medications are considered the most effective today:

Monotherapy with these drugs is rarely used. Basically, one drug is combined with another, for example, Allokin-alpha is prescribed systemically, and Epigen-Intim cream is locally prescribed. Also, therapy is supplemented with immunomodulators, such as Likopid, Immunomax and others.
Since genital warts, papillomas, genital warts and cervical dysplasia increase the risk of cancer, they are removed using minimally invasive surgical techniques, which include the following:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- chemodestruction;
- removal by radio waves and others.
In severe cases, amputation of the cervix may be used.
Is there a specific prevention of human papillomavirus?
Today, two vaccinations against the human papillomavirus in women are certified in our country, namely: Gardasil and Cervarix.
These vaccines protect the body against HPV types 16 and 18, which most commonly cause cervical cancer. In the developed countries of America and Europe, these vaccines are included in the vaccination schedule for girls. For example, in Germany, the HPV vaccine is shown to all girls who have reached the age of 12. Vaccination is carried out in three stages.
In Russia, the vaccine can be purchased at the pharmacy chain. The average cost of the drug is 7200 rubles.
Any neoplasm on the body is a signal of the body about the presence of a particular problem. Modern man is irresponsible about his health, so dangerous ailments often occur. Can papilloma virus be cured? In a brief review, we will talk about the nature of the infection, effective methods of getting rid of it, and what will happen if the process is left to chance.
Many people face the problem of papillomavirus
reference Information
HPV is one of the most common diseases on the planet. Doctors note that at least 60% of people are infected or are carriers of the virus. The disease is dangerous because patients do not even know about the presence of a problem, because all processes are asymptomatic.
Papilloma exists and divides at the cellular level of the basement membrane, so it is easily transmitted from one person to another. In essence, it refers to benign tumors. Experts distinguish three types of infection.
- Safe. It does not threaten to degenerate into oncology and does not show any symptoms.
- Dangerous. There is a risk of mutation into cancer.
- Most threatening. The neoplasm is more likely to become malignant.
Now there are more than a hundred viruses, but not all of them are dangerous to health. Depending on the pathogen, the infection has different manifestations.
- Nodules. Almost colorless formations on the leg occur on the neck, armpits and genitals.
- Corns. Solid tumors appear on the feet, characterized by itching and peeling of the surface.
- Warts. Round seals up to 20 mm are on the knees, elbows and hands. The color changes from flesh to brown.
- Condylomas. Soft tubercles on the leg grow rapidly on the affected surface. They often mutate into cancer.
There are three ways to get infected with human papillomavirus.
- Domestic. Non-compliance with the rules of hygiene or the usual handshake with the carrier opens the gate for infection. Often the disease is transmitted through other people's things or household items. Moisture in a bath, pool or gym is an excellent environment for the spread of ailments.
- From mother to child. At the time of passage through the infected channels of a woman, the baby becomes infected with a probability of 100%. Tumors appear in the larynx and mouth of the newborn.
- Sexual. One of the most common ways the virus enters the body. Condoms are not reliable protection, as the disease can enter the body even through a kiss.
It is very difficult to recover from HPV, so it is easier to prevent the onset of the disease than to fight it for a long time. It is enough just to follow the rules of hygiene and not to use other people's things. Conventional barrier contraceptives must be combined with special medications that block the spread of infection.
While in public places, do not forget about disinfection. You can fly on a plane or touch the handle of an office, but don't be too lazy to wipe your hands with antibacterial wipes. Treatment cost will be much more expensive than a bottle of disinfectant liquid.

HPV is manifested by warts, papillomas and condylomas on different parts of the body
Causes of the disease
The infection does not manifest itself in the human body for many years. The patient even forgets that he was once infected. However, there are catalysts that activate the disease.
- Violation of the protective functions of the body. Immunity is reduced due to severe illness, diabetes or pregnancy. The use of antibiotics and hormonal agents in therapy suppresses the natural barrier of the body. The risk group includes HIV carriers, since the disease tends to degenerate into oncology.
- Wrong way of life. Bad habits are one of the culprits for the manifestation of HPV. Irrational nutrition, the use of newfangled diets or banal gluttony also provoke an infection.
- Nervous tension. The human papillomavirus in women and men is activated during a period of depression or stress. The body is exhausted by regular experiences, which becomes a catalyst for illness.
Determining the causes of the awakening of the disease is one of the main tasks that will help the doctor stop the spread. It is possible to cure effectively only if the culprit is eliminated. Otherwise, the disease will begin to manifest itself after the completion of the full course or at the first symptoms of a weakened immune system.

Nervous tension stimulates the development of the virus
Therapy
Can HPV be cured permanently? If a person becomes infected after 30 years, then until the end of his life he will remain a carrier of the disease. The disease will then "wake up", then fade. Depending on the quality of the protective functions of the body, rashes are characterized by minimal manifestation or active spread through tissues and mucous membranes.
In childhood, the immune system more vigorously destroys foreign bacteria, so it is possible to cure human papillomavirus infection. The body does not allow pathogenic cells to degenerate into oncology, and also banishes the disease forever. Most often, HPV is suppressed or destroyed by the natural forces of the body.
Depending on the location of the nodules, therapy should begin with a visit to a specialized doctor. If they are on the skin, then it is better to see a dermatologist, in the mouth - to the dentist, on the genitals - to the gynecologist or urologist.
The specialist will determine the strain of the disease, and after that he will develop an individual program. A complex alternation of methods will activate protective functions and suppress bacteria.
- Medicines. The basis is antiviral drugs that kill the pathogen. Injections, tablets and ointments destroy the infection.
- Immunomodulation. Preparations and procedures aimed at strengthening the protective functions of the body are used. Modern pharmaceuticals offer a huge selection of chemical and herbal substances that promote health.
- Lifestyle correction. Normalized physical activity, getting rid of bad habits and regular worries improve the quality of existence.
- Vitamin therapy. The lack of useful trace elements negatively affects the general condition of the body. Doctors often observe that it is easy to cure papillomavirus if you drink a course of multivitamins. Tumors stop growing, and rashes decrease and disappear.

A healthy lifestyle will help the body fight the virus
Many compatriots are embarrassed to visit a specialist, so they prefer to carry out the procedures on their own. Remember: before therapy, it is imperative to check the neoplasm for a predisposition to oncology. Dangerous melanoma is often hidden under inconspicuous nodules and seals. You can not pull or destroy the structure of growths, because these actions will provoke the active spread of the disease.
There are several proven methods that will allow you to clear the integument from formations.
- A liquid nitrogen. As a result of treatment, the nodules disappear a couple of days after the procedure.
- Electrocoagulation. Due to the directed action of the current, the tumor gradually disappears.
- Laser. The feeding blood vessels are sealed, which leads to the complete destruction of the growths.
- Radio wave knife. With the help of a special device, papillomas are removed.
- Surgical. If the tumor is neglected, then the method of excision with a scalpel is used. In this case, it all depends on the experience of the surgeon, because you can get ugly scars.
Before choosing one or another method, remember: all actions must be carried out by a professional. The lack of qualifications of the doctor activates the virus to further spread through the integument. A visit to a beauty salon to remove formations should be done after consulting a doctor.

Electrocoagulation of papillomas on the face
Things to remember
Should the infection be treated or not? Many do not even realize that inconspicuous-looking nodules can cause disease. If you leave everything as it is, then at the first stress or a cold, your skin will begin to become covered with ugly formations. Often defects "jump up" in the most unexpected places (on the eyelids, lips, nose), which makes a person complex.
HPV in women is a dangerous disease that provokes the occurrence of cervical cancer. The virus mutates, as a result of which a harmless papilloma becomes a source of cancer cells. Gynecological observation by a doctor at least once every 6 months will protect against the appearance of a dangerous disease. Visiting a specialist should become a habit of modern ladies.
If the condyloma is allowed to grow, it can even cause problems with childbearing by blocking the future person from leaving the uterus.
Doctors note that approximately 500 thousand patients are annually diagnosed with a malignant tumor caused by the virus. Most often, the victims are young ladies aged 16 to 24 years. This is due to an increased level of the hormone estrogen in the blood, which provokes the degeneration of HPV in women into oncology.
Over 240,000 women die from cervical cancer every year.
If HPV is not treated, then the expectant mother will pass on the disease to the child. A small organism does not yet have innate protection, therefore, in the first two years, they are the most dangerous for the baby. Most often, neoplasms appear on the mucous membranes.
More serious trouble can be caused by warts growing inside the body: in the urethra or in the vagina. They cause problems with urination or complicate sexual intercourse.
In men, the human papillomavirus causes warts and genital warts on the genitals. In more severe cases, the larynx is affected. The growths gradually grow, which makes them look like a comb. Nodules are easily damaged, so they often bleed and are a source of bacterial contamination.
Solarium is a very dangerous procedure for the body. The aggressive effect on the skin of artificial irradiation provokes a virus. Regular visits to the salon destroy the body's natural defenses, which activates the degeneration of a small seal into melanoma.
Is it possible to cure the human papillomavirus completely? Doctors say that if the disease has not disappeared within 48 months, then the infection becomes chronic. The older the patient, the less likely he is to finally get rid of an unpleasant ailment. But properly prescribed therapy will nullify all manifestations of the disease.
Most people are infected with the human papillomavirus, but with a normal state of health and the functioning of the immune system, it does not manifest itself in any way.
Under the influence of third-party factors, HPV provokes the appearance of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes - formations resulting from the growth of epidermal tissues.
Such symptoms can provoke severe complications or transform into malignant tumors, so the decision of a specialist in their treatment is required.
Papillomas are often localized in the genital area, so their treatment in men and women has its own individual characteristics. This article discusses the nuances of the course of the disease in women and ways to get rid of such formations.
What is HPV in women?
HPV is present in the body of 70% of women, but asymptomatic course is observed only in 20% of all cases.
One way of getting infected is through sexual contact, during which women are at higher risk of transmitting the virus because their genital mucosa is less protected than men's.
Papillomas can have different localizations, usually problems with them in women occur in the following cases:
- The appearance of formations on the face, neck and other visible areas of the body; papillomas are an aesthetic defect;
- The appearance of formations on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, larynx, respiratory tract, in the rectum or near the anal area, which at certain times causes physical discomfort.
In cases where the papillomas that have appeared do not cause pain or other types of discomfort, an appeal to a specialist is still required, since it is impossible to independently assess the stage and degree of danger of internal changes.
Causes of the disease
The reason for the appearance of papillomas is infection with HPV.
The following provoking factors lead to the activation of the virus and the appearance of noticeable manifestations:
The first signs in women and additional symptoms
The main sign of HPV activity, which can be detected independently during a visual examination, is the appearance of papillomas in various parts of the body. Most often they affect the mucous membranes of the genital organs or the area around them.
In some cases, a number of additional symptoms may be observed, including:

Features of the course of the disease
Signs of HPV activity usually appear at the age of 25: experts believe that in most cases by this time there is an independent cure for the virus or the beginning of its pathological activity.
The main features of the course of the disease are described below:
- The process of virus reproduction occurs in the epidermis with localization in the cells, penetration into internal organs and blood is absent;
- The causative agent of the disease, which has reached a certain level of development, under the influence of factors favorable for growth, is located on the epithelium, the first papillomas appear on the surface of the skin;
- After the appearance of external signs of the disease, a person becomes not only a carrier, but also a distributor of HPV. While the virus is in sleep mode, it does not pose a threat to others;
- Further progression and development of complications occurs when papillomas are injured., as well as their initial tendency to transform into malignant tumors or unfavorable localization.
How does infection occur?
HPV infection can occur in one of the following ways:

HPV types in women
To date, more than a hundred types of HPV are known that can be found in a woman's body.
Below are the most common types of viruses and formations, the growth of which they provoke:
- Common warts flat- their appearance can be caused by more than 10 types of the virus;
- Virus 30, 11 and 6 types- can provoke the appearance of warts in the genital area or papillomas on the mucous membranes of the larynx and respiratory tract;
- Virus 40, 43, 44, 45, 51 and 54 types- provokes the appearance of genital warts;
- Virus type 41- causes the appearance of ordinary and genital papillomas.
Why is HPV dangerous in women?
Papillomas, which appeared due to the activation of HPV, in themselves do not pose any threat to health.
Dangerous complications that they can provoke:
- The appearance of malignant neoplasms such as cancer of the vulva or cervix;
- Infertility;
- Deterioration in the quality of life due to physical discomfort during bowel movements, urination, or sexual intercourse.

What type of HPV is considered the most dangerous in women?
The most dangerous types of HPV in women are the following viruses that can lead to the development of severe complications:
- Virus 34, 42 and 55 types- already at the initial stage it is considered a precancerous condition, therefore it requires treatment under the supervision of a specialist;
- Virus 45 and 51 types- provokes the appearance of genital warts, in which there is a tendency to pathologies in the development of uterine tissues and the development of malignant neoplasms;
- Virus types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 52, 56 and 58- often causes cancer and provokes cervical cancer.
65% of infections with the most dangerous type of HPV end up with cancer for a woman. Each strain carries a risk of becoming cancer to some extent.
Diagnosis of the disease in women
When infected with HPV, a woman will need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis to confirm the diagnosis, determine the type of virus and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic measures are as follows:

How to treat HPV in women?
Depending on the type of virus and the characteristics of the course of the disease, women may be prescribed the following treatment methods to get rid of HPV:
- Reception and local application of pharmacological preparations;
- Undergoing hardware treatment to eliminate existing papillomas.
Various methods of traditional medicine are also popular, which should first be agreed with the attending physician.
The procedure is determined after the diagnosis and the receipt of research results:
- In the absence of the risk of developing malignant neoplasms and physical discomfort treatment is not required, it is recommended to visit a specialist for preventive purposes once a year;
- If there is a risk of developing malignant neoplasms due to oncogenic HPV infection, but in the absence of clinical manifestations, specific treatment is not required - it is necessary to undergo an examination by a specialist every 3 months. Symptomatic and antiviral therapy, as well as a set of measures to maintain immunity, may be prescribed;
- In the presence of malignant neoplasms, an oncologist's consultation is prescribed who will conduct additional diagnostics and, based on it, determine the subsequent course of action.
Medical therapy
When starting HPV treatment in the early stages, immunostimulants are often prescribed if the diagnosis confirmed the deterioration in the functioning of the immune system.
This group of drugs stimulates the activity of the immune system and helps the body to resist the virus on its own, accelerating the overall healing process.
In the treatment of HPV, the following immunostimulating agents are usually prescribed:
- Immunomax- corrects the state of weakened immunity and allows you to eliminate pathological phenomena caused by HPV activity. Before use, the contents of the ampoules are dissolved in 1 ml of injection solution, in total, from 3 to 6 intramuscular injections are prescribed for 10 days, depending on the degree of damage and the severity of symptoms. The cost of the drug is from 750 rubles ;
- Gepon- is an immunostimulant with increased antiviral activity, is available in the form of a solution for external treatments 1 time per day. The solution can be taken orally, the daily dosage should not exceed 10 mg. The duration of the course can be from 1 to 3 months. The cost of the drug in pharmacies from 720 rubles ;
- Galavit- in tablet form contains 25 mg of aminodihydrophthalazinedione sodium. With an increase in HPV activity and the occurrence of complications caused by this virus, 3-4 tablets per day are prescribed; the duration of the course is determined individually. A specialist can prescribe intramuscular injections of Galavit with a treatment regimen of 100 mg of the drug per day for 5 days, then another 15 injections are given every other day. The cost of the tablets is from 320 rubles, cost of injection solution from 560 rubles .
To date, there are no specific antiviral drugs aimed at completely getting rid of HPV. However, complex therapy involves the use of broad-spectrum antiviral drugs - they reduce the activity of HPV and inhibit the process of its reproduction.
Some of the drug options are discussed below:
- Viferon- available in the form of ointment, gel and suppositories; only ointment is suitable for the treatment of papillomas. The tool locally affects the lesions and stops the process of HPV reproduction. Processing is carried out 3-4 times a day immediately after the appearance of the first formations, the duration of the course is no more than a week. The cost of a tube of Viferon ointment varies from 100 to 180 rubles ;
- Altevir- has a combined effect, eliminating viral activity and stimulating the immune system. The solution is used for subcutaneous injection in the localization of papillomas in the larynx; the procedure is carried out 3 times a week after removal of the formation to prevent recurrence. The dosage is determined individually. With a tendency to the appearance of new papillomas, treatment can be long and up to six months. The cost of the injection solution from 1000 rubles ;
- Allokin Alpha- is considered one of the most powerful antiviral drugs, is available in the form of an injection solution. Its use is prescribed to women in case of problems with the cervix against the background of HPV activity. A single dosage is 1 mg, the introduction is carried out subcutaneously every other day, the course includes 6 injections. The average cost of an HPV treatment package is 7500 rubles .
Drugs with a destructive effect are prescribed to destroy existing papillomas.
A few modern effective tools are discussed below:
- Solcoderm- is a solution for external use, which contains oxalic, lactic, acetic and nitric acid. The application of the agent to the papilloma is carried out using a capillary, then it is distributed over the surface of the formation with a special capillary. After 5 minutes, the papilloma can be easily removed, but this process is best left to a qualified specialist. The cost of a vial with a solution is from 620 rubles ;
- Kondilin- like other drugs based on podophyllotoxin, it is indispensable in the treatment of papillomas. Process 2 times a day - 3 days. Break 4 days. Again processing 3 days. Another 4 day break. The course of treatment is no more than 5 weeks. You can buy a solution at a price from 500 rubles .
Hardware methods of combating HPV in women
If it is impossible to eliminate papillomas through the use of pharmacological preparations, hardware removal techniques are practiced.
Modern methods are as follows:
- Cryodestruction- consists in freezing and subsequent removal of papilloma;
- Electrocoagulation- destruction of papilloma with the help of electric current discharges. After the procedure, it is possible to transfer the formation for histological examination;
- laser removal- this is the most common and modern way to remove papillomas, is carried out in most clinics. The procedure is carried out quickly and painlessly, the wound is immediately cauterized, which speeds up the healing process and eliminates the risk of secondary infections. The only drawback is the complete destruction of the material, which makes it impossible to conduct additional histological studies;
- Surgical removal- excision of papilloma with a scalpel, today such an operation is almost never practiced, since it is inferior to laser removal in all respects.
Treatment of HPV in women with alternative methods
The use of any methods of traditional medicine should be previously agreed with the attending physician, otherwise you can cause serious harm to your own health.
One way to get rid of papillomas is to prepare and drink a coniferous vitamin drink.
It has antiviral and immunostimulating effects, suitable for the treatment of HPV, regardless of the location of the formations.
The recipe and instructions for use are as follows:

Another folk remedy is made on the basis of potato juice, it is also aimed at stimulating the immune system and is suitable for the treatment of HPV with any localization of formations.
Preparation and use are described below:

No methods of traditional medicine are practiced for self-removal, cauterization or other means of eliminating papillomas that have arisen on the genitals. This procedure is carried out only by a qualified specialist.

HPV during pregnancy
HPV does not affect the health and development of the fetus; infection during childbirth can occur only if papillomas are localized in the vagina or near the anal area.
In most cases, the body of a newborn child is able to independently resist the virus. The threat to the life of the fetus occurs in rare cases.
This occurs when the following types of HPV are present in the body of a pregnant woman:

During pregnancy, the activation of the virus often occurs, which was previously present in the woman's body and was in a dormant state, and existing papillomas can also change their color, shape and size.
During pregnancy, HPV treatment by taking pharmacological preparations and burning papillomas with liquid nitrogen is contraindicated.
The following options for getting rid of formations are possible:
- Electrocoagulation;
- Surgical excision;
- laser removal.
Prevention
It is impossible to rid yourself of the risk of getting into the body of HPV.
Compliance with the following preventive measures will reduce the likelihood of activation and reproduction of the virus:
- Normalization of sexual life- close relationships and sexual contacts only with proven and regular partners;
- Providing protection against disease sexually transmitted, with the help of barrier means of protection;
- Active sports and the rejection of bad habits- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Visiting a gynecologist at least once a year and preventive testing;
- Compliance with the norms and rules of personal hygiene, as well as providing a balanced and complete diet;
- Providing enough rest avoidance of stressful situations and emotional overwork;
- Proper upbringing of girls from an early age.
 Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?
Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?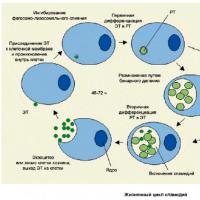 PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do
PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs
COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat
Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials
Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials How to tell the time in English?
How to tell the time in English? Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis