How to take PCR to determine chlamydia, ureaplasma and mycoplasma. PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do
An external primary examination by a doctor does not allow accurate diagnoses. The patient is interviewed, and on the basis of his complaints, assumptions are made about a possible disease. Clarification of the controversial diagnosis is possible only on the basis of the results of laboratory tests and various tests. PCR is a polymerase chain reaction. A popular and effective method is to study the smallest particles of DNA in a sample taken from a patient. Artificial magnification of these particles with the help of enzymes makes it possible to see the causative agent of the infection - chlamydia. The accuracy of the PCR technique is significantly higher than that of similar assays. It is possible to determine chlamydia in the early stages only through PCR. Other diagnostic methods need to be confirmed.
The results of the tests depend on how the patient prepares, how much time has passed since the infection, and on the individual characteristics of the organism of the infected person. A smear on chlamydia by PCR is prescribed only by a doctor, and only an experienced specialist is engaged in deciphering the results. The determination of chlamydia using PCR will not take much time, and will allow you to start effective treatment of venereal disease as soon as possible.

be careful
Among women: pain and inflammation of the ovaries. Fibroma, myoma, fibrocystic mastopathy, inflammation of the adrenal glands, bladder and kidneys develop. As well as heart disease and cancer.
Preparation for analysis
PCR for chlamydia occurs only after careful preparation of the patient. Compliance with the recommendations of a specialist is a guarantee of accurate results. Rules for preparing for the delivery of biomaterial:
- Thirty days before the test, the patient should refuse to take any medication, including antibiotics and antifungal drugs. In exceptional cases, the doctor prescribes drugs that do not affect the future results of PCR (the patient suffers from chronic diseases or there was an urgent need for the diagnosis of chlamydia).
- It is possible to collect suitable material for further laboratory research only three or four hours after the last urination of the patient.
- Any sexual contacts stop a week before the test (PCR for chlamydia). Otherwise, the results will be inaccurate.
- For women, biomaterial sampling is prescribed only on the fourth day after the end of menstruation.
- A week before the analysis, the woman should refrain from douching or similar cleansing procedures that the gynecologist may prescribe.
Preparation of a sample taken from a patient for laboratory testing is a prerequisite for the correct diagnosis of infection. Neglect of the recommendation and appointments of a specialist can lead to complications due to incorrect treatment of chlamydia.

Blood sampling method


Purpose of the survey
An effective diagnostic method for detecting infection
The polymerase reaction method is used in modern medicine as one of the most effective methods for diagnosing chlamydia.

Conducting an analysis
The analysis, based on a chain reaction of small DNA particles under the influence of enzymes, occurs in several stages. The patient follows all the recommendations of the doctor and carefully prepares for the sample. The PCR study begins with the sampling of blood or biomaterial from the genitals of a patient with suspected chlamydia. If scrapings are taken for further laboratory tests, then the men undergo the procedure in the urologist's office, and the women turn to the gynecologist.
For a representative of the stronger sex, the process takes longer, since it is necessary to use special tools to take a sample: a spoon and a probe. Devices for sampling biomaterial are inserted directly into the urethra of a man, and then samples are carefully removed for analysis. The probe is placed in a prepared, cleaned tube (filled with transport medium). Similarly, biomaterial is collected from a woman's vagina. In special cases, when sampling from the urethra is not possible (for various reasons), saliva, urine after prostate massage, or ejaculate are taken from men. After taking a scraping, the obtained samples are sent to the laboratory for further research.
From whom:

For the last few years I have felt very bad. Constant fatigue, insomnia, some kind of apathy, laziness, frequent headaches. I also had problems with digestion, bad breath in the morning.
And here is my story
All this began to accumulate and I realized that I was moving in some wrong direction. I began to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, but this did not affect my well-being. The doctors couldn't say much either. It seems like everything is normal, but I feel that my body is not healthy.
A couple of weeks later, I came across an article on the Internet. literally changed my life. I did everything as it is written there and after a few days, I felt significant improvements in my body. I began to get enough sleep much faster, the energy that I had in my youth appeared. The head no longer hurts, there was clarity in the mind, the brain began to work much better. Digestion has improved, despite the fact that I now eat haphazardly. I passed the tests and made sure that no one else lives in me!
Deciphering the results
In fast and accurate diagnostics, it is not so much the methods of sampling the biomaterial that are important, but the results that should be correctly deciphered. For a person without a medical education, it is impossible to understand the conclusion of laboratory tests. The diagnosis is based on:
- questioning the patient (an anamnesis compiled at the initial examination);
- two or more laboratory test results;
- concomitant diseases that were detected during a comprehensive examination of the body.
Why is a PCR smear for the detection of chlamydia considered the most accurate? The delivery of biomaterial for further research by such methods allows you to get quick results, which is important in advanced disease. Different sampling methods help to avoid contraindications for pregnant women, women with hormonal disruptions, and men who fail to pass a scraping. PCR helps to identify many pathogens of dangerous diseases. A safe method is used at any stage of the disease, which is transmitted through sexual contact.
Everyone knows what the flu is. Everyone more or less knows how to behave if an infection has occurred, and what drugs can help. Only a few will be able to talk about what chlamydia is. And even less about what symptoms this disease has and how dangerous it is. Meanwhile, chlamydia is the second most common infectious disease after the flu. If you ignore its manifestations, you can cause serious and even irreparable harm to health.
What is chlamydia and when should you get tested?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease caused by Chlamydia Chlamydia trachomatis. The infection affects the urethra, rectum, vagina, cervix, and even the eyes (through orogenital contact or through household items). In most cases, infection occurs during sexual intercourse, less often through household contact. It is also likely that the infection is transmitted vertically (from mother to child), including transplacental.
The incubation period lasts about two weeks. At this time, infectious agents are embedded in healthy cells and begin to multiply actively. Symptoms of infection appear at 2–3 weeks, they are expressed in discharge from the urethra in men and from the vagina in women, pain during urination is noted. In addition, women feel pulling pain in the lower abdomen, may experience intermenstrual bleeding.
note
In 50-70% of cases, chlamydia is asymptomatic and is only diagnosed when a couple comes to the doctor complaining of an inability to conceive a child.
If the symptoms of the disease did not occur or if they were ignored, then the disease becomes chronic. In women, chlamydia causes inflammation in the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity, adhesions form in the fallopian tubes, which subsequently become the cause of female infertility. In men, chlamydia causes inflammation of the epididymis - epididymitis, which threatens infertility and impotence.
An analysis for chlamydia should be taken if the symptoms described above appear, as well as if there has been sexual contact unprotected by a barrier method of contraception with a person whose state of health is unknown.
What tests to take to determine chlamydia
For analysis, they take blood, urine or a smear - it depends on the type of study. What they are and what are the features of each - we will consider further.
-
Express test
Such a test can be bought at a pharmacy and carried out at home on your own. The material for the study is urine; in women, a smear is also acceptable. The biomaterial is placed on a cassette and observed - one red-purple stripe or two will appear. The test is based on the detection of lipopolysaccharide antigen (LPS). The accuracy of the express test does not exceed 20%, so it is recommended to contact the clinic to obtain a reliable result. -
cytoscopic method
For analysis, a urethral swab is taken from men and a cervical smear from women. The biomaterial is distributed on a glass slide, dried and immersed in methanol or acetone, after which it is examined under a microscope. Thus, in the smear, they try to identify cytoplasmic inclusion cells of Halberstedter-Provachek, indicating chlamydia. This method is reliable, but it is effective only for detecting infection in the acute stage. In the chronic form, the disease can occur without the presence of inclusion cells, which means it will not be recorded. -
ELISA
The enzyme immunoassay method involves the search for chlamydia antigens (IgG, IgA, IgM) in venous blood. With the help of ELISA, it is possible to diagnose a disease, identify its pathogen, and also determine at what stage the disease is. The accuracy of the method is 60%. A blood test for chlamydia may be prescribed not only for suspected disease, but also for infertility of unknown origin or during pregnancy, if there is a history of miscarriage. -
PCR
The essence of the method is to decipher a small section of DNA, the analysis of a fragment of which helps to identify chlamydia. The material for research by PCR is a urogenital smear. The advantages of the method are its high sensitivity and accuracy. Infection can be detected not only in the acute stage, but also in a latent or sluggish one. The analysis is prescribed for infertility of unknown origin and during pregnancy with complications. In addition, the study is prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of a course of antibiotic therapy. It should be borne in mind that after a course of chemotherapy, a false positive test result for chlamydia is possible. In this case, a re-examination in a different way is required. Also, the analysis is assigned to people with tuberculosis, viral hepatitis, HIV-infected.
by the way
In 1993, the American scientist Carrie Mullis was awarded the Nobel Prize for the discovery of the PCR method.
-
culture for chlamydia
This method is also called cultural, it is the "gold standard", as it is the most accurate (100% sensitivity) and allows not only to identify the pathogen, but its reaction to various antibiotics. This is necessary for the appointment of therapy for the disease. Also, bacterial culture is prescribed to patients after undergoing a course of antibiotic therapy - to evaluate its results. The essence of bakposev is that the biomaterial is "sown" in a favorable environment and grown. A few days later, by the nature and size of the colony, it is determined which infection is present in the material.
So, to date, PCR and bacterial culture are the most accurate. The remaining methods of diagnosing chlamydia are usually used as an additional method of research to confirm the diagnosis or question it.
How to prepare and how to donate biomaterial for the detection of chlamydia
In order to obtain a reliable result, biomaterial should be taken at a medical institution, and subsequent processing and analysis should be carried out in a specialized laboratory.
On the eve of biomaterial sampling, you should stop drinking alcohol, spicy and fatty foods. For 1-2 days before visiting a doctor, you should refrain from sexual intercourse. You should not be tested for chlamydia while taking antibiotics.
An hour before blood donation need to quit smoking. It is important not to be nervous, not to experience emotional overload before the study.
If you want to take a swab , then men are advised not to urinate for 1-2 hours before sampling. Women should take the material on the 5th-7th day of the menstrual cycle. In girls, biomaterial is taken from the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the vagina.
Urine for analysis collected in the morning, a medium portion of urine is required. That is, the first drops are flushed down the toilet, and the subsequent ones are collected in a sterile container. Approximately 50 ml of fluid is required for the study. Before collecting the material, it is worth rinsing the external genitalia with warm water; using soap, gels and other hygiene products is prohibited.
If the patient at the time of the test is undergoing a medical course of treatment of any disease, this must be reported to the specialist.
Deciphering the results of tests for chlamydia
The results of tests for chlamydia are usually prepared within 1-3 business days, some paid institutions provide an urgent analysis service, then the patient can receive a conclusion within a few hours after taking the material. An exception is bacteriological culture, this study takes several days, usually 5–7.
Linked immunosorbent assay
When analyzing biomaterial for chlamydia by ELISA, the concept of "titer" is used. The titers of antigens IgG, IgA, IgM are considered. The table below shows the meanings and interpretation.
|
Stage of the disease |
IgG titers |
Credits IgA |
Credits IgM |
|
Acute |
>100–6400 |
> 50–1600 |
> 50–3200 |
|
Chronic |
>100–1600 |
<50 |
>50–200 |
|
Exacerbation of a chronic disease or re-infection |
>100–51200 |
>50–400 |
<50 |
|
State of recovery |
> 100–400 |
<50 |
<50 |
In the body of a healthy person, antigens are not detected. Antigens of the IgM type appear 5 days after infection. IgG - after 10 days. IgA - after 2-3 weeks. Borderline values: IgM and IgA titers - up to 50, IgG - up to 100 - require a re-examination of the patient after 10-14 days.
PCR
It is a qualitative analysis, so the results form may say: “detected” or “not found”.
Sowing
In the laboratory conclusion, the first item will be the name of the infection found in the biomaterial. Further - its concentration, indicated in colony-forming units per milliliter (CFU / ml). One cell gives rise to an entire colony. A result of more than 103 CFU / ml indicates an inflammatory process occurring in the body caused by this pathogen. Also, the result will be a list of antibiotics that fight chlamydia. If the letter “R” is next to the antibiotic, it means that the bacterium is resistant (resistant) to it, the antibiotic will not work on it. And if there is a letter “S”, it means that chlamydia is sensitive to this antibiotic, it can be prescribed as a therapy for the disease.
The clinical picture of chlamydia is characterized by a latent course, absolutely asymptomatic or oligosymptomatic. The disease is dangerous with complications that lead to infertility, miscarriage, lesions of the genital organs. To date, there are several ways to diagnose chlamydia, but none of them gives a 100% answer. If one of the tests is positive, then additional studies are required. Only a specialist can interpret the results and prescribe treatment.
Wednesday, 03/28/2018
Editorial opinion
If you have found a bacterium, your sexual partner should also be examined. Even if it doesn't seem to bother him. It happens that the symptoms of the disease appear only in one partner, while the second continues to feel well. But the asymptomatic course of the disease does not reduce the risk of complications. It makes no sense for one partner to be treated - in this case, the disease will constantly “roam” from one to another and can lead to serious consequences.
Infection occurs during sexual intercourse, contact-household method. Chlamydia is an infection caused by bacteria of the Chlamydia trachomatis species.
In 90% of cases, the disease affects the genitourinary system. What tests are given for chlamydia in women and what is their reliability? Let's figure it out together.
What types of biomaterial studies for chlamydia are there?
When bacteria actively multiply, the woman's local immunity weakens. A decrease in protective reactions leads to concomitant diseases and complications.
Methods for diagnosing chlamydia in women:
- express test;
- smear on flora;
- polymer chain reaction;
- immunochromatographic analysis;
- enzyme immunoassay (immunomorphological);
- cytoscopic (RIF, PIF method);
- cultural method (bacteriological culture).
Each diagnostic method has its own characteristics in the collection of material and preparation for the study.
Watch a video about methods for diagnosing chlamydia:
Immunochromatographic analysis (ICA)
A rapid test is performed to detect infection. It is sold in a pharmacy. The manufacturer indicates that the reliability of the method is 75%. However, practice shows only 20-50% of coincidences with medical diagnostics. If the result is positive, the test does not exempt from additional tests in the clinic. According to the results of ICA, the doctor will not be able to prescribe treatment.
How to determine chlamydia in a woman by immunochromatographic method? For analysis, urine or mucus from the vagina is used. The prepared biomaterial is applied to the test indicator. Before sampling, manufacturers recommend:
- within 2 hours do not empty the bladder;
- on the eve of the test, you can not douching;
- do not use vaginal suppositories and creams a few days before the test.
Otherwise, the reliability of the result will remain in question. Everything you need to carry out the test is included in the kit, along with detailed instructions for use.
There are no contraindications to the rapid test.
This method is used after intercourse with a random partner. or with suspicious discharge from the genital tract.
The method is based on the principle of immunochromatography.
IHA Advantages:
- the ability to test at home;
- quick result;
- no special equipment is required to detect infection;
Most doctors consider this method a waste of money, because. treatment is prescribed according to the results of laboratory tests.
How is a swab taken for flora?
During a gynecological examination, a woman takes 3 smears for the flora:
- from the urethra;
- vagina;
- cervix.
How is an analysis for chlamydia taken in women in this way? Particles of secretions are collected with a special brush. The procedure is uncomfortable but painless. To detect chlamydia, a bacteriological culture of the material is carried out. A routine examination under a microscope will not determine the causative agent of the infection.
The study accurately determines the presence of an inflammatory process in the genitals. The probability of detecting chlamydia by this method is only 15%. A smear is taken along with other diagnostic methods.
If a woman has taken antibiotics, and a month has not passed since the last pill, the analysis is not performed. The drugs kill some of the bacteria. The rest of the chlamydia are temporarily inactive. The disease proceeds in a latent form.
Advantages of the method:
- the analysis is carried out free of charge in the state polyclinic;
- allows to identify associated pathologies.
We bring to your attention a video on how to take a smear on the flora for chlamydia:
Polymer chain reaction (PCR)
The most reliable of the methods. The accuracy of the study reaches 100%. A false result occurs only with improper collection and processing of the material. This method is preferred by most experts. If the result is positive, there should be no doubt about chlamydia.
Material for analysis:
- scraping of the upper cells of the mucous membranes;
- urine, with symptoms of infection of the urethra;
- blood - it may contain antibodies to chlamydia.
If the doctor gave a referral for a urinalysis, they give the first morning portion. The volume of material is 20-30 ml.
The study by PCR is carried out for 1-2 days. This method is preferred in the diagnosis of the disease.
Video about PCR analysis:
How to detect by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA)?
- allows you to detect microorganisms in the blood at 10-20 days of infection;
- determines the form of the disease - acute or chronic;
- indicates activation of poorly treated chlamydia;
- detects antibodies to other types of chlamydia, not only to the genital ones.
ELISA complements PCR. These two analyzes are carried out together. ELISA is also taken to check the treatment. According to the test results, it is not always clear whether a person is sick at the moment or the infection was transferred earlier.
How to prepare for an antibody test:
Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF)
In some clinics, such an analysis is called the cytoscopic PIF method.
The study of the material is carried out under a fluorescent microscope. If there are chlamydia in the cells, a glow is observed. Microorganisms resemble an asterisk in shape. Error probability is 50%.
The method is rarely used, because. it is easy to confuse chlamydia with other groups of bacteria. Most often they are confused with staphylococci. The human factor also plays a role. If the analysis is carried out by an experienced doctor, the reliability of the result increases significantly.
How to diagnose with bacterial culture?
And how is the analysis for chlamydia in women with the help of bacterial culture? For research, a smear is taken from a woman. The collected material is placed in a nutrient medium. The result is evaluated after 6-8 days. If there is chlamydia in the smear, during this period of time they will multiply and will be visible to the laboratory assistant. The reliability of the result is 100%.
After identifying the bacteria, they conduct a study of their properties and the period of life in the patient's body.
Sowing is rarely carried out due to labor intensity and high cost. Bacterial culture is recommended:
- in the event of medical and legal conflicts;
- for the diagnosis of chlamydia in virgins;
- if you suspect an infection in your mouth or rectum.
How to prepare for surrender?
For the reliability of the result, a woman must follow the rules of preparation:

The rules of preparation apply to all diagnostic methods. If the woman has recently been treated with antibiotics or topical antibacterial agents, the analysis is carried out later.
Pregnant women are subject to all rules except for recommendations on the days of the menstrual cycle.
Attempts to self-medicate lead to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage. The treatment is complex, based on the intake of several active agents that require the right combination. Otherwise, therapy will not work or lead to complications.
More details about how to properly prepare for the analysis, the doctor will tell you:
Decryption
Normally, a woman should not have chlamydia in a smear. The table below shows the possible results of the analyzes and their interpretation:
| Name | Result interpretation | After how many days is the analysis ready | Price in rubles |
| PCR | - no chlamydia Chlamydia found | 1-2 | 250-300 |
| ELISA | - no antibodies detected +/- doubtful, there is a small amount of antibodies Antibodies detected | 2-3 | 450-500 |
| mutual fund | – bacterial antigens were not detected (negative result) Antigens detected (chlamydia present) | 2-3 | 350-400 |
| Sowing | - growth is not observed, there is no chlamydia, There is growth, chlamydia are found | 6-8 | 1000 |
| Express test | 2 strips - chlamydia is present, 1 strip - no chlamydia | 10 minutes | 300 |
| cytological method | - no chlamydia were found in the cells, Chlamydia found | 2-3 | 450 |
Which diagnostic method to choose?
How to take an analysis for chlamydia in women and which diagnostic method to choose? This is decided by your doctor.
But the most accurate studies:
- bacterial culture.
The same methods are suitable to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. An important nuance - It makes no sense to take PCR if a month has not passed since taking the last pill of antibiotics. After conducting primary studies, the doctor will compare the results. If necessary, he will prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
When the main tests show the presence of chlamydia in the cells, other types of studies are not prescribed. But if the data contradict each other, it is advisable to undergo additional analyzes.
Specialists do not adhere to one scheme for diagnosing chlamydia. The analysis is usually done in 3-5 ways. This diversity allows you to prescribe the right treatment, to exclude false conclusions.
OCR for chlamydia, ureaplasma and mycoplasma will identify the primary source of illness or ailment in men and women. It will also make it possible to make a correct diagnosis in case of unclear or not completely correct clinical picture of diseases, such as AIDS or hepatitis. Diseases can be hereditary, acquired or infectious.
This type of analysis of samples to determine the presence of XUM genes (chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma) is one of the most accurate and fastest.
Its merits include:
- The test procedure allows achieving high sensitivity of the analysis (at least 95%).
- It can be used at all stages and forms of the disease: latent (hidden, asymptomatic), chronic, acute period of the disease.
- Allows you to determine whether the patient is a carrier of the disease.
- A huge range of possibilities for taking material for research.
- High speed of obtaining data and results after analysis. Usually, the result is issued within one to two days, but if there is an urgent need, then the test result can be obtained on the day the sample is taken.
- This type of analysis is "direct". It detects exactly the factor of the disease, which is the cause.
- Availability of analysis. If the patient has suspicions or symptoms, it can be done on their own initiative, without waiting for a doctor's referral.
- Allows you to detect and identify not only the disease itself, but also concomitant diseases or diseases with similar symptoms. Almost all urogenital infections and HUM diseases have such properties.
Despite many positive aspects, this test has several disadvantages:
- Must be carried out in laboratories with a high degree of sanitary standards. They are strictly required to avoid false positive results due to sample contamination. The chance of getting an erroneous result is about 5%.
- The result is difficult to interpret. For accurate diagnosis and data processing, it is necessary to have a medical education. The study should be evaluated by a qualified specialist in immunology and the field of infectious diseases.
- The high cost of the test. It is caused by the need to install expensive equipment and hire highly qualified specialists to study, conduct and verify the result.
Indications for the appointment of ORC for chlamydia
This procedure is prescribed to determine the following diseases:
- human papillomaviruses of all types, including oncogenic strains;
- AIDS;
- herpes caused by cytomegalovirus;
- tuberculosis;
- hepatitis;
- diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Symptoms with which you can get a referral for analysis:
- planning a future pregnancy or a complex course of an existing one;
- the need to find out the likelihood of violations in the child and the chance of hereditary pathologies;
- determination of the causes of infertility in both men and women (difficulties in fertilizing an egg);
- the appearance in the body of inflammatory processes of unclear etiology;
- the presence of the fact of unprotected sexual intercourse recently;
- the need to determine sensitivity to antibiotics;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- signs of the transition of the disease into a chronic form;
- the absence of such an examination before.
If a patient has a positive result for the bacterium chlamydia trachomatis, then the analysis is mandatory assigned to his sexual partner. Even in the absence of any manifestations, symptoms or ailments.
The presence or absence of contaminated trace elements is indicated by a qualitative PCR analysis. However, if general testing is carried out and it is necessary to know the stage of development of the infection, the foci of infection and the rate of reproduction, a quantitative analysis is also carried out.
How to prepare for analysis
To diagnose, you should carefully prepare and follow a few simple rules:
- Exclude the possibility of urination 3 hours before the smear.
- A few days (2-3 days) before the study, exclude the use of local contraceptives or vaginal preparations.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse for two days before the test.
- 3 hours before the delivery of PCR for chlamydia, avoid treatment with genital hygiene products. Do not douche or similar procedures on women.
- The best time to take PCR for chlamydia in girls is the middle of the menstrual cycle.
- The cycle of taking antibiotics and antibacterial agents should not coincide with or overlap with the cycle of preparation for DNA analysis for chlamydia.
- Refrain from smoking or using tobacco, electronic cigarettes, a few hours before the test.
- Absolutely exclude any use of alcohol-containing drinks, fried foods, fatty foods.
After completing all these procedures, you can proceed to the delivery of the analysis. The sampling process for men and women is somewhat different.
More information about preparing for analysis is presented in the video from the Medical Journal channel. The author is Candidate of Medical Sciences S. G. Lenkin, a venereologist and urologist of the highest category.
How to take
Before taking a PCR smear for chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, you need to check with your doctor what kind of material will be taken in your case.
Depending on the diagnosis and the causative agent determined by the test, the samples of the taken material may be:
- sperm;
- blood;
- saliva;
- other liquids;
- sometimes PCR is performed in the urine.
Blood in both sexes for analysis is carried out by taking 10-15 ml of material from the ulnar section of the circulatory system.
Women
In women, collection of fluids, samples of membranes for PCR analysis can be done at the following places:
- The inner lining of the urethra.
- The inner lining of the vagina. For girls, a scraping is done from the vestibule of the vagina to avoid tearing the hymen.
- synovial fluid.
- cervical canal. A smear or scraping is performed. The smear is preferable because it does not cause painful effects, but the accuracy of the polymerase chain reaction analysis in this case may be slightly reduced.
- conjunctival mucosa. The outer shell of the eyeball or smear under the eyelid.
The analysis itself is given in a short period of time. It all depends on the area where the material will be taken from. For example, the sampling of synovial fluid, in other words, the puncture of the articular apparatus, occurs by introducing a large diameter needle - 0.8 mm. This causes acute pain and may require local anesthesia and therefore take longer.
For the study and analysis of PCR in urine, a woman must be provided with material collected in the morning in the middle of the jet. At the same time, the first and last two drops are discarded, in an amount of 50 ml. This achieves high reliability of the analysis, excluding possible errors.
During pregnancy
For all cases of admission of pregnant women to the antenatal clinic, it is mandatory to prescribe a polymerase chain reaction test for the presence of chlamydia and mycoplasma in the body.
The analysis itself is given in one of the following ways:
- a smear is taken from the cervix;
- sample of amniotic fluid;
- study of placental tissues.
If an infection is detected in the fetal membranes, such as amniotic fluid, or in the tissue of the fetus itself, an analysis of the amniotic fluid should be done. If the period is already long, then placental tissues will be studied.
Men
In men, samples of the following mucous membranes can be taken for a PCR test for chlamydia:
- smear from the inner wall of the urethra;
- smear from the conjunctiva (the outer shell of the eyeball, under the eyelid);
- a sample of seminal fluid;
- fluid secreted by the prostate gland;
- synovial fluid.
The choice of the sampling site is carried out depending on the suspected or already diagnosed pathogen. For men and boys, before taking a sample of membranes or fluid, it is necessary to consult with a dermatovenereologist and urologist. This will contribute to a clearer definition of the alleged disease and, as a result, a more accurate analysis result.
How research is done
Features of PCR and ELISA tests for chlamydia:
- Special reagents are added to the sample of tissues or mucous membrane collected as a result of sampling.
- Enzymatic substances recreate a copy of the studied material or microorganism by binding these substances to a DNA fragment. The number of copies and clones of the material is formed enough to accurately study, diagnose the disease by examining and identifying the microorganism in the mass.
- Cells affected by the infector differ sharply from healthy biological material. This allows the microbe to be isolated and examined under a microscope.
- To identify the disease, ELISA (enzymatic immunoassay) is performed. It is used to qualitatively and quantitatively determine the presence of infections, viruses, microorganisms, bacteria and other pathogens. These tests complement each other if a single test does not give an accurate result.
- Based on the received data, an analysis protocol is formed.
With the help of this test, specialists are able to identify the following types of bacteria and viruses:
- immunodeficiency;
- Chlamydia Trachomatis;
- mycoplasma;
- ureaplasmia;
- tuberculosis;
- hepatitis;
- Epstein-Barr;
- papillomas.
It is possible to analyze these infectious agents only in a special laboratory, or in a modern clinic with the proper equipment for PCR.
Deciphering the results of the analysis
The column with the name of the test may contain the wording:
- study type: polymer;
- type of study: enzyme immunoassay.
This means performing quantitative and qualitative PCR tests.
If the study is carried out to detect pathogenic bacteria, then:
- in the column with the name of the bacterium, the name of the pathology will appear (for example, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis);
- diseases will be marked with "+" or "-" symbols depending on the result.
The result might be:
- Positive (bacteria detected), sometimes indicated in the field next to the name by the “+” symbol. This indicates the presence of an acute process in the body and treatment is necessary or the patient is a carrier of the disease.
- Negative (bacteria not detected), also denoted in some cases by the symbol "-".
- The wording is "negative PCR culture". This means that the patient has not been diagnosed with the infection under study, that is, the person is healthy.
How much does a PCR test for chlamydia cost?
Prices for polymerase chain reaction analysis vary by region:
According to patients, the price of a PCR test varies depending on the number of studies required. If a comprehensive examination is prescribed, then the total cost of the tests can be much higher.
Photo gallery
Example of an examination protocol Negative PCR result
Video
You can learn more about how a PCR test is taken for chlamydia in women in a video from the author of "SiberianMedicalLaboratory"
 Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?
Does ureaplasma pass by itself (can it pass on its own)?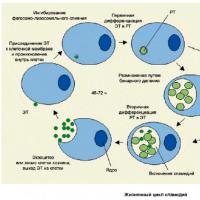 PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do
PCR analysis to detect chlamydia Chlamydia PCR how to do COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs
COCs with different daily dosages: how to choose, an overview of the best drugs Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat
Ureaplasma parvum: characteristics, tests, symptoms in women and men, what is dangerous, whether it is necessary to treat Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials
Basic technologies for obtaining nanomaterials How to tell the time in English?
How to tell the time in English? Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis