Technology for producing plaster figures at home. How to make money on gypsum products. Description of the industry and company
Gypsum is a natural, natural, durable, environmentally friendly material. Is it possible to build a profitable business in the manufacture of gypsum products? When opening your own business, you need to decide for what purposes the products will be produced and whether their sale will be profitable.

The business of creating large products from gypsum is more profitable, as it gives greater profit than the sale of small piece products: a variety of garden figures ok, souvenirs, figurines, which are not in great demand.
Business idea for manufacturing and selling gypsum products, can bring its owner a pretty good stable income.
Beginning entrepreneurs need to consider the following points::
- what production processes are planned;
- what is the volume of capital investment;
- expected profitability.
Gypsum stucco molding is used for external and internal decoration of buildings. Used for interiors decorative items, which decorate ceilings, walls, niches. Most often, stucco is used to create classic style. Lighting fixtures are decorated with small decorative elements.
Gypsum is considered the most popular and cheapest finishing material. It is durable, aesthetic, non-flammable, fire-resistant, and increases heat and sound insulation. When hardening, the gypsum heats up, expands and is able to penetrate into the most inaccessible places of the prepared form. The shelf life of the material is no more than three months. It must be kept in a dry, ventilated area. Plaster products can be restored and any part can be repaired.
For creative people gypsum is the embodiment various ideas and fantasies. Modern technologies make it possible to produce molded elements that imitate natural stone. This finish gives both interior and exterior cladding a graceful, elegant, luxurious and cozy look.
The technology for making gypsum stucco molding is easy to use and affordable. The mold blank is made of silicone, wood or cardboard. Plaster is poured inside. You can make the mold yourself or order it from craftsmen who do this kind of work. It must be of high quality, since this determines how the finished product will turn out.

It is best to use a silicone mold. Otherwise you will have to use liquid oil for lubricating the surface of the table and the internal parts of the mold in order to remove finished products.
For organization of production of gypsum products you will need to carefully select the premises. A large building with several rooms, equipped with good ventilation, is suitable. It should not be located within the city, but in the suburbs.
For the production of different products, the required strength of gypsum is selected. There are several brands of this material, designated by the letter “G” and numbered from 2 to 7 and from 10 to 25.
Gypsum is divided into three types:
- building;
- sculptural;
- molding
Coarse raw materials are used in construction; fine gypsum is used for sculptures. To make disposable molds, the most fragile type of grinding is used - molding. This material has a reddish tint.
To produce gypsum products you will need plumbing and power tools.:
- drill with a nozzle for mixing the solution;
- jigsaw to remove excess;
- grinding machine;
- screwdriver;
- drill;
- Bulgarian.
For smaller workpieces, molding and plastering blades, chisels, cycles, knives, and wooden stacks are used. Tools for working with solid or liquid plaster should be made of stainless steel or brass. You will also need sandpaper from the coarsest to the finest grit; floor and table scales.

You don’t have to purchase expensive equipment for your business; you can get by with simple means at hand. Employees involved in production require personal protective equipment.
How to organize sales of finished products for a beginning businessman?
There are many ways to sell your plaster products using:
- post photos of products and advertisements on stands or on social networks;
- enter into an agreement with a network of construction stores;
- take individual orders.
If the business is only initial stage, it is recommended to make gypsum products small sizes in the form of various garden figurines, busts, figurines. When you have already gained some experience in this craft, then you can set your sights on larger-scale works in the form of columns, statues, and so on.
In our age of all kinds of innovative technologies, gypsum products remain as popular as in past centuries. Working with this material guarantees the realization original ideas, development of creative abilities, getting pleasure from what was conceived and implemented.
If it's a hobby, you can always turn it into a business and earn extra income.
That’s probably all, for those who are also interested in business ideas, we have made a selection of the best ones, and of course, don’t forget to subscribe to

*Calculations use average data for Russia
1. PROJECT SUMMARY
This business plan discusses the opening of an enterprise specialized in the production and sale of plaster garden figures in a city with a population of more than 1 million people. The goal of the project is to meet the demand of the local population for quality products landscape design and making a profit.
Among the advantages of the project are a low barrier to entry into business and low cost of raw materials. To organize production, you will need to master the technology of creating molds (matrices), casting, painting and working out figures, and equip a production and storage facility total area 70 sq. meters, purchase necessary equipment and material.
The starting investment will be 228.5 thousand rubles. Financial calculations of this business plan are made for a three-year period of activity. According to them, the payback period of the project will be 5 months. Integral indicators of project effectiveness are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Integral performance indicators
2. DESCRIPTION OF THE INDUSTRY AND COMPANY
Tradition to decorate personal plots garden figures appeared in Germany in the 19th century. The experience of the Germans was adopted by gardeners from other countries of the world, including from Russia. The growth in demand for such goods in our country is caused by the fact that dachas and suburban areas have become increasingly perceived by Russians as a place to relax rather than to work in the garden. Today, according to VTsIOM, country houses and about 50% of Russians own dachas. At the same time, one can note a tendency to increase the number of cottages, the number of which is constantly growing. To decorate the areas, a variety of sculptural forms are used, which are made from gypsum, ceramics, concrete, artificial stone and wood. They are installed in the garden near decorative slides and ponds, in flower beds, near gazebos and garden paths. Despite the fact that the market for garden figures offers a wide variety of products that vary in quality, the products remain in high demand.
Our project involves the creation of a production facility for plaster garden figures. The production will be located on rented space in a city with a population of more than 1 million people. To organize a business, several steps will be implemented. Firstly, an individual entrepreneur will be opened, registration and tax registration procedures will be carried out. Secondly, the technology for producing molds for the production of products and the products themselves will be mastered. Thirdly, the necessary equipment and materials will be purchased, and employees will be hired and trained.
Finished products will be sold at retail through our own online store, as well as wholesale and small wholesale to organizations engaged in the sale of garden goods, household goods, decorative items and other related products. Investments in the project will amount to 228.5 thousand rubles. Starting cost items are detailed in Table. 2 real business plans.
Table 2. Investment costs of the project
3. DESCRIPTION OF GOODS
Our company will produce and sell garden figures and sculptures intended for decorating gardens and personal plots. The range will be expanded to include the production of souvenirs and piggy banks. Unlike most competitors, the company's products will be distinguished by originality and high quality workmanship. In particular, for the production of figures we will use our own, rather than purchased ready-made molds. Due to the low cost of raw materials, finished products high markups will be set (234%). The list of main groups of goods sold and final prices are presented in Table. 3.
Table 3. Nomenclature and variable costs
Sculptural gypsum will be used as the production material. The advantages of working with gypsum include: its low cost, lightness technological process during operation (does not require the purchase of expensive equipment), work safety for employees (non-toxic, no protective equipment, exhaust hoods, etc. are required). At the same time, the material is quite fragile, and therefore attention will be paid special attention proper warehousing, reliable packaging and transportation of finished products.
4.SALES AND MARKETING
The scope of application of garden figures is quite wide. Products can be used not only to decorate a garden or cottage, but also to decorate baths and saunas, improve parks, playgrounds, gardens and schools. Often, figures serve not only for aesthetic, but also for purely practical purposes. For example, they can be used to cover hatches or disguise other objects that spoil the view. Accordingly, the target audience is quite varied. It includes owners of private houses located both in the city and outside the city, summer residents and amateur gardeners, owners of baths and saunas, management of parks and children's institutions, and so on.
Finished products will be sold at retail through our own online store, as well as wholesale and small wholesale to organizations engaged in the sale of garden goods, household goods, decorative items and other related products. Thus, the sales channels for our products will be:
Wholesale companies;
Specialized garden stores or departments in stores;
Stores of fresh and indoor flowers;
Hardware stores;
Souvenir shops;
Interior shops;
Entrepreneurs-hawkers (trade along the highways);
Construction companies;
Parks, cafes, baths;
Children's institutions.
An online store will be created for retail sales and presentation of product samples. IN electronic catalog the client will be able to see prices, select the product he is interested in, place and pay for the order. To promote services and stimulate sales, online advertising methods will also be used on partner websites, links from specialized resources dedicated to landscape design and so on. The company is also expected to participate in agricultural fairs.
Since this line of business is subject to seasonality, during the winter period production will be transferred to the New Year's range (souvenir products).
5. PRODUCTION PLAN
The process of making garden figures involves the implementation of several main stages. This:
Preparing the mixture;
filling the mold (matrix) with the mixture;
hardening of the product (drying);
product processing (impregnation);
painting;
varnish treatment.
If the time for manufacturing and processing of products does not take much time and takes from 5 to 20 minutes, then the drying process will require up to 3 days. Thus, the entire production cycle will be 3 days. To produce the figures, we will prepare our own set of original molds not available on the market.
Earn up to
200,000 rub. per month while having fun!
Trend 2020. Intellectual business in the field of entertainment. Minimum investment. No additional deductions or payments. Turnkey training.
To organize the work, you will need to rent a premises for production and warehouse with a total area of 70 square meters. meters. You will also need to purchase the equipment necessary for production, the list and cost of which is given in Table. 4.
Table 4. List of equipment
In addition to what is given in the table, you will need to purchase the raw materials necessary for the work (gypsum, paints, varnish, additives for gypsum). For these purposes, 40 thousand rubles will be required.
The planned sales volume in the first year of operation will be 600 thousand rubles, which is planned to be achieved during the period of growing seasonal demand (May-June); in the second year, seasonal turnover can be increased to 1 million rubles. The sales plan for the off-season (September-February) in the first year of operation is set at 100-300 thousand rubles. in the first year, 200-400 thousand in the second year.
6. ORGANIZATIONAL PLAN
The organizational and legal form for running this business will be an individual entrepreneur. The taxation system is simplified (6% of income received). The project will be managed by the project initiator, whose responsibilities will include organizing the production process, setting shifts, monitoring the work of employees, searching and expanding markets for products. The company will need to hire three foundry workers and three painters, whose work will be organized in shifts. Payment for their labor will be piecework and depend on the volume of work performed. Maintaining financial statements will be provided to a third party.
Table 5. Staffing and wage fund
7. FINANCIAL PLAN
Investments in the project will amount to 228.5 thousand rubles. Starting cost items are shown in Table. 2 real business plans. Fixed production costs will include rent, accounting, and advertising (for more details, see Table 6). The variable part will include remuneration of personnel, purchase of raw materials and tools, delivery, and tax deductions. A detailed financial plan with indicators of revenue, net profit and operating expenses is given in Appendix 1. Calculations are made taking into account indicators of seasonality of demand, with the highest rates from March to August and low season in September - February.
Table 6. Fixed costs of the enterprise
8. EVALUATION OF EFFECTIVENESS
The project for the production and sale of garden figures from gypsum can be called investment attractive, which is confirmed by the integral performance indicators presented in Table. 1. It is expected that the project will reach payback and begin to make a profit by the 5th month of operation. The effectiveness of the chosen direction is evidenced by the net present value (NPV), which in our case is positive (260,758), the profitability index (PI), exceeding 1 (1.14), as well as the internal rate of return (IRR), which is greater discount rates (25.83>15).
9. RISKS AND GUARANTEES
The main risks of the business of producing and selling garden figures are analyzed in Table. 7
Table 7. Possible risks and ways to prevent them or their consequences
|
Risk factor |
Probability of occurrence |
Severity of consequences |
Events |
|
Receiving low-quality products |
Preliminary mastery of production technology and compliance with all necessary technological processes, purchase of high-quality raw materials |
||
|
Low production profitability |
Competent pricing, maintaining a competent marketing policy, working to expand the sales market |
||
|
Emergence of new competitors 3466 people are studying this business today. In 30 days, this business was viewed 331,979 times. Calculator for calculating the profitability of this business |
For casting miniatures from metal, the classic one is a collapsible two-part mold - plaster or silicone. Experience with this type of form allows us to list its disadvantages: relatively large number silicone is required for the manufacture of each of the two halves, the time for silicone vulcanization is 8-12 hours for each layer of silicone at room temperature, and when there are three such layers, then the manufacture of two halves silicone mold takes two days. And the main drawback is flash - metal that gets into the gap between the two halves of the mold. Anyone who cast knows how difficult it can sometimes be to get a casting on which the flash line is invisible and exactly matches. The method of making the mold that I want to demonstrate successfully overcomes all three difficulties and allows you to obtain high-quality molds and, therefore, high-quality figurines at home.
Photo 1. As an example, we take a 28 mm master model of an elf for the Blood Bowl game, made from Quick-Wood epoxy patty.
Before starting to make the mold, you need to prepare the model itself. First, place the model on the sprue and the fence. The models that I sculpt myself have a wire frame of legs, and I use the ends of the wire to make a sprue (a piece of such wire is clearly visible in the first photo). So, the sprue has a conical shape, there is only one protrusion, not too thick, to the other leg. If it is difficult to install the sprue and the support separately, then sometimes you can do without the support at all. Next, the entire structure is installed and glued to a cardboard base. Secondly, in order to easily separate the model from the silicone later, I paint the model with a thin layer of metallic acrylic or some kind of nitro aerosol. If your master model is metal, then I recommend tinting it with nitro, and if it is plastic, epoxy or green stuff, then acrylic metallic is quite suitable.
Why metallic? From experience, it comes off most easily and can be applied in a fairly thin layer. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that all undercuts are covered with paint (in other literature the names “undercuts” or “negative angles” are found). The third step - optional, but highly recommended - is to draw an imaginary line dividing the halves of the form with a felt-tip pen - this will greatly help to subsequently make an accurate cut of the silicone shell.
In the photo, the model is prepared for the start of manufacturing the mold itself. The sprue and the projection are visible, and the cut line is visible, at least on the legs. Don't look for it on your head - it's not there. The cut will only reach the fingertips of the left hand and the top pole of the ball. The entire model is mounted on a base.
Second part. Silicone cocoon and stone coffin.
We begin to apply silicone layer by layer. The first layer requires a lot of attention and patience. The task is to introduce silicone into all the cracks, crevices and depressions. Silicone is a rather capricious material and will not fit in there of its own accord, so I take a small drop of silicone and put it in there, indentation by indentation, checking again and again to see if I have forgotten any other crack.
The already applied silicone can be pressed down with a damp finger. Another reason I prefer to work with clear silicone is that you can see if any air bubbles are forming under the silicone layer. At the end of this stage of work, our model should be completely covered with a thin, preferably less than a millimeter, layer of silicone.
In the picture: like this, drop by drop, silicone is applied to all “problem” areas.
Next we need to let the silicone dry. Drying time may vary depending on different types silicones, but in most cases the next layer of silicone can be applied after eight hours. And never apply the next layer until the previous one has dried! After the first layer of silicone has dried, carefully inspect the “cocoon” again; if there are no bald spots in the silicone layer, then move on! If there is, then fill the gaps with silicone and move on anyway! And then - the second, third and further, as needed. These layers should tightly wrap the model in a single cocoon without any undercuts. How thick should it be? Let's just say that an extra layer of silicone will not harm it, but too thin a layer can lead to deformations during casting, especially in the area where the mold is cut. On the model shown here, silicone was applied in four layers and in some places I added an additional fifth layer. When the application of silicone is completed, the excess cardboard of the stand is cut off.
Now we have a silicone mummy from which our model is barely visible. It's time to build a "stone coffin". I make formwork from Lego parts, spread plaster and pour the first half of the coffin, half-burse the cocoon in the plaster, and wait.
Pay attention to the rubber cup for diluting the plaster. An extremely easy-to-use item, a veteran of production. Initially, it is a dental instrument, but can also be made from half a rubber ball. Working with the same container for diluting plaster, over time you learn to dose water and plaster “by eye” so that there is not too much waste, and after work, clean off the hardened plaster - simply by turning it inside out.
When the plaster hardens, which is determined by its heating, I move the formwork higher, but under no circumstances remove the cocoon from the plaster! Then you must remember to lubricate the surface of the plaster with some cham, so that you can then separate the halves of the plaster. No special mixtures! Dishwashing liquid or liquid soap will do. We dilute the second portion of gypsum and pour it into the formwork. Again, wait until the plaster heats up. When the plaster has hardened, remove the formwork, separate the halves of the “coffin” and take out the mummy.
Part three. Surgical.
At this point we already have a fully manufactured injection mold. Now all that’s left to do is take the model out of the mold and graphite the casting surface. In fact, opening the silicone and removing the model is the most important operation, so it must be taken very seriously. Swinging a knife is not like smearing silicone. First, I highly recommend getting a brand new scalpel blade. Secondly, take your time, examine the mummy and remember or try to carefully find the cut line that we drew when preparing the model. And only after thinking about how the cut should go, start. You need to cut slowly, little by little, but with a “steady hand.” Start making cuts, your guideline is the line, it’s not for nothing that we drew it, meanwhile, gradually and very carefully separate the silicone from the model. Although silicone is very elastic, tearing off a piece from it or cutting off anything extra with a scalpel is not so difficult, so no use of force or haste. The final task of this operation is to twist the silicone shell so that the model can be pulled out, but at the same time leave the shell intact, so that when it is released it will again take its original shape.
When removing the mold from complex-shaped models, you can make additional cuts to remove individual parts from the silicone, but do not cut off anything completely. As if we wanted to peel the whole orange. This is the meaning of the method. We succeeded! Now the surgeon can take off his mask and gloves, brew coffee and light a tired cigarette.
Before casting internal surfaces The molds must be properly treated with graphite powder (I use the insides of batteries as a source of graphite, although it can be the graphite lead of a pencil), the excess graphite must be blown off and the entire mold must be reassembled. The mold is completely ready for casting. The clamp is simple and incredibly convenient - two sticks and two elastic bands.
Of course, it would be good to give the plaster time to dry, at least a couple of days, but who can resist the pleasure of making a couple of test castings when I already have a completely finished mold? I can’t resist either...
Time consumption.
Preparing the model: making sprues - half an hour, painting and applying a dividing line - let it be another half an hour (of course, this is the maximum time spent, all this can be done even faster). Applying the first layer of silicone takes about twenty minutes. Subsequent layers are operations that do not require super precision, so they take 5-15 minutes of time. Drying each layer of silicone, as I already said, takes about eight hours, but there is a little trick here. If you put the model in a warm place, probably 60-80 degrees, it’s hard for me to say for sure without a thermometer, the silicone will vulcanize in an hour. I put it in the electric oven. Flaws: bad smell in the oven and throughout the kitchen. If the smell is very unpleasant, try lowering the temperature. You can, of course, turn on the hood, if anyone has one. A total of five layers will harden in six hours. I prefer to take my time and leave the outermost layer (it's the thickest anyway) overnight at room temperature. The next day: to make a plaster coffin - about 20 minutes for each half. Trick: dilute gypsum in salted water. Salt is a catalyst for the crystallization of gypsum. In total, it took an hour to do everything, including cleaning. Without cleaning - 40 minutes and my wife would be very angry. The operation of opening the “cocoon” took me 15 minutes, timed by the clock. It took another fifteen minutes to graphite the surfaces of the mold and assemble everything in full combat readiness.
So: yesterday at 11 am I started making the mold, today at 1 pm I was already holding the cast figures in my hands.
Method capabilities.
I have been making molds this way for two years now, and I have seen from experience that there is a significant saving of silicone and time compared to other methods of making molds. I now make molds from two silicone parts only for completely flat parts, and everything else - arms, bodies, heads - just like that. Quality has improved, especially in terms of flash and accuracy of alignment of the mold halves. This method can be successfully used to make molds for figures of any shape and complexity. I used it equally successfully for casting 28 mm 54 and even 75 mm figures.
In conclusion, I want to say a few words about silicones.
Making molds for stucco with your own hands
Finding the right material for the job is not easy. We have to try many varieties. To save money, do not look for dental silicones and jewelry (they are proudly called “liquid rubber”) for casting metals - they are not heat-resistant. There are probably exceptions, but as a rule they are also expensive.
I use the most common construction silicone, Silirub, from the Belgian company Soudal. Syringe 330 g. You can hardly smell the vinegar from it. It comes in three types: black, white and transparent. The first and last temperature of tin casting, i.e. Holds 300-400 degrees well. After several pours, white becomes covered with cracks and a “burning” crust. After repeated pouring, it practically does not deform. All that remains is to wish good luck to all those who like to smear themselves in silicone.














How to cast plaster molds
This business plan is designed to invest in production of gypsum tiles.
Purpose of developing a business plan: to receive a grant;
Volume of work: 42 pages;
Business planning horizon: 3 years.
Last year, the volume of gypsum tiles sold in the Russian Federation amounted to more than 7 million square meters, while maintaining a steady growth trend. The bulk of products are produced for the domestic market, export volumes are small. Tiles from Russian manufacturers are mainly exported to the countries of the former CIS, since transporting these products over long distances is unprofitable. The same applies to imports; the list of importing countries is limited to Germany, Finland and Ukraine.
The development of the production of the project initiator in this type of activity has a large social and economic role, therefore, carrying out activities in the production and sale of tiles is advisable, this is due to the fact that similar products from local suppliers are practically not represented in the region and nearby areas.
The area of the rented production premises is 90 sq.m. The project initiator will produce gypsum tiles, and subsequently paving tiles, at a professional level using modern equipment.
When starting the project, it is planned to purchase the following equipment and inventory:
- airbrush;
- compressor;
- spray gun;
- concrete mixer;
- vibration forming table;
- polyurethane molds;
- silicone molds 20 units;
- heat gun 2 units;
- table for unpacking products (metal);
- office furniture.
In a year, it is planned to reach tile production volumes equal to the output of the mini-factory. The number of workers involved in the production process at the time of opening will be 3 people. Over the next three years, with the expansion of production, increasing the range and volume of products, the staff number will be increased to 15 people. The staff will include specialists in the following specialties: loaders, product casters, general workers and others.
The advantages of gypsum tiles over other materials are:
- cost-effective finishing material existing on the market;
- biostability - gypsum tiles eliminate the appearance of fungi and mold;
- environmental friendliness - all components of gypsum tiles are natural;
- lightness there is no need to strengthen the walls, the tiles can be mounted on drywall;
- the ability to regulate indoor humidity;
- ease of application in hard-to-reach places;
- effective use in building renovation.
New business ideas
A practical guide on how to open a workshop for the production of gypsum products. The material addresses the following issues: workshop arrangement, necessary raw materials, required equipment and personnel, manufacturing technology and advice on organizing the sale of finished products.
Types of products that can be cast from gypsum
- It is profitable to produce large objects: ceiling and wall rosettes, wide cornices and moldings, capitals ( upper part columns) and decorative columns.
- Large size wall panels.
- Pilasters, ceiling borders and domes.
- Everything that cannot be produced using the old technology of casting from plastic molds.

Organization of a production workshop
The workshop premises should be located in an industrial area, away from residential buildings.
Casting from gypsum is an environmentally friendly production, but the heart of this production is the production of fiberglass molds from which this casting will be made. This is associated with some inconveniences: it is necessary to have a molding chamber with local (above the table) exhaust and protective equipment for the respiratory system. We will be dealing with a polyester resin, which emits styrene during polymerization.
The production workshop should have six rooms isolated from each other:
- A service area where personnel change clothes, eat, wash and rest.
- The room where models are assembled for the production of injection molds. This room is equipped with tables welded from iron corner, shelves with plumbing and electrical tools.
- A small isolated room where the molding and subsequent polymerization of injection molds takes place. Also, their trimming and subsequent sanding. All these operations involve the release of chemical fumes and very unpleasant dust. Here you need a reliable table, welded from a 50 mm corner, a local hood above the table itself, and lighting located low and not casting shadows.
- The room where the decor casting process takes place. Tables welded from a corner, the height adapted to the height of the casters.
- Warehouse for raw materials, buckets and other utensils.
- Finished products warehouse. We need to dwell on it in more detail. The fact is that casting a product is not everything; it is equally important to preserve it so that it does not twist when drying, and the geometry of the casting remains correct. To do this, you need to build drying racks in the warehouse, which are made from a metal corner, and between the corners there is a metal square for support. The entire structure is checked with a level and then carefully painted. The warehouse must be equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation.

Necessary raw materials and supplies
To produce gypsum products you will need
- Main production material gypsum grade G-5. When purchasing in hardware stores and wholesale warehouses, you must require a certificate with the date of issue. Gypsum stored for a long time is unsuitable for production.
- Ordinary water. You need to make sure that there is no rust in the water; the water should be clean and transparent. Otherwise, all inclusions that may be in the water will appear on the surface of the casting.
- Another expense item is polymer materials for the production of fiberglass injection molds: gelcoat, molding polyester resin, curing catalyst, three types of glass mat, release pastes. Suppliers can be found through advertisements and on the Internet using the keywords Neste Chemicals and Reichhold. Typically, these supply companies offer courses that will train your staff in the molding technology required to produce injection molded fiberglass molds.
Required Equipment
The beauty of making stucco from gypsum is that you do not need bulky and expensive equipment. Everything you need can be made with your own hands, and hand tool buy:
To organize production you will need:
- Tables welded from angle iron.
- The exhaust installation in the molding room consists of: a box above the table, an electric motor, which with a volute is mounted behind the wall on the street. Supply and exhaust ventilation consists of two fans at different ends of the finished product warehouse. They are mounted in holes made in the wall.
- Power tools: small drill, medium drill, it will be used to prepare gypsum mortar by inserting a special mixer into it. A jigsaw, an orbital sander, a mini-drill for working with forms, a screwdriver for self-tapping screws, a medium-power grinder with a speed control function.
- Scales: floor and table scales.
- Locksmith tools and consumables: sandpaper of different grain sizes, polishing pastes for finishing injection molds.
Staff
- Head of workshop(business owner): organizes all the work, monitors the uninterrupted supply of materials, searches for and places orders.
- Foundry workers- two people. Recruitment is not critical. Both a woman and a teenager do an excellent job as a foundry worker. The work is not harmful or difficult, the result is visible right away. With little skill, mistakes are rare. Payment is piecework.
- Molders- two people. These are the ones on whom the success of the whole business depends. Their responsibilities include: preparing the polyurethane model (training with release agents), assembling the structure on which the model is attached, molding and subsequent processing (polishing and grinding).
- Installers- at least two people. They are engaged in the installation of finished products for the customer. This operation is very responsible and thorough, and also not cheap. Candidates are selected from experienced installers. As a last resort, such a tandem should consist of an experienced person and a diligent student.
 Plaster ceiling rosettes
Plaster ceiling rosettes
Technology for the production of gypsum products
The process of casting from plaster is simple: open the bag of plaster. The material must be fresh, without lumps or foreign inclusions. If you come across lumps, you must sift it through a sieve. You can use a sieve through which the flour is sifted.
- After this, the required amount of gypsum is weighed. You definitely won’t be able to find out how much solution is needed to fill a mold for, say, a ceiling rosette from the first pour. You need to take more volume than needed, and with each new fill, bring the volume to the optimal amount. It is helpful to keep detailed notes for each type of form.
- The ratio of gypsum to water is one to one.
Copying figurines. Making molds for casting.
The mixture turns out to be somewhat liquid, but this prevents the appearance of holes (where air bubbles escape) on the surface of the casting. From experience: this ratio of components does not affect either the rate of hardening of the mass or the final strength of the product. But, in addition to the absence of unpleasant holes on the surface, we save on a vibrating table - an expensive, bulky and very unpleasant thing to hear.
- We insert the mixer into the drill, pour the required amount of water into a plastic bucket, and pour the plaster into it. In a few moments he will disappear under water. We begin to carefully stir it with a mixer at low speeds, trying not to air the mixture.
- So, let's start filling. Using a flat brush, apply refined sunflower oil, the cheapest one possible, to the front surface of the mold. We do not apply generously, but rather rub it in.
- Pour the mixture into the mold in a thin stream, taking your time, but not hesitating either. The solution should spread smoothly throughout the entire mold, gradually squeezing out the air.
- Leave the mold filled to the brim alone for a few minutes. After the plaster has thickened, but not completely, you need to use an absolutely flat bar (wood, aluminum, plastic), while leaning on the opposite ends of the mold, to “cut off” the excess so that the pouring surface is even. As the plaster hardens, it warms up, but when it then begins to cool, this is a sign that the casting is ready and it’s time to remove it from the mold.
- Carefully clean the edges and very carefully bend the edge of the mold around the perimeter. After this, holding it by the middle, we turn the mold with the frozen plaster over and place it on the table. Holding the top of the mold, we begin to bend the edges in a circle, at the same time lightly and often tapping the entire structure on the table surface. At some point the product will fall out of the mold. Carefully lift up the now empty form.
That's it, you did it! And if the surface of the matrix was well ground and polished, then the surface of the product will reflect the glare of the sun.
Principles for selling finished products
The business owner is responsible for the sale of finished products. The methods for achieving results are different - from giving advertisements describing the properties of products in the media, to installing advertising stands in places with high human traffic.
One of the main sales channels is sales through construction stores: samples of finished products are displayed in the store and anyone can make individual order by contacting the sellers.
 Decorating a fireplace and chimney with plaster structures
Decorating a fireplace and chimney with plaster structures
In conclusion, a few words about production profitability.
I will give just one example, from which everything will be clear.
A bag of plaster (40 kg) costs 200 rubles, from it you can cast up to ten ceiling rosettes with a diameter of 70 cm, costing at least 200 rubles, the gross profitability is more than 10,000%!
Questions and answers on the topic
No questions have been asked about the material yet, you have the opportunity to be the first to do so
Several types of this powdery substance are produced. There are medical, high-strength autoclave and construction (called alabaster in the old days) gypsum. The produced material is marked with the letter G with digital indexing indicating the compression force withstood by the brand. The higher the index, the better the score.
Indexes from five to twenty-five are classified as building alabaster. The most best brand(autoclave) can easily withstand two hundred and fifty kilograms of compression and is marked G-250. The last type of material is considered to be the least suitable for products. But it is widely used in construction as a component that ensures rapid setting of putty solutions (lime-gypsum).
In view of high speed After setting, only a small portion is prepared per operation. However, with compositions that retard setting, the working time can be increased. One of them is animal bone glue. For example, a good solution for lubricating cracks can be prepared from one part of such building plaster, two parts of chalk and five percent bone glue, with which the sifted mixture is diluted to a working thickness.
It is better to manufacture products from gypsum using an autoclave high-strength type (it is preferred by dental prosthetists), but also medical type will do too. In general, both of them are often used for molding and casting all kinds of panels, architectural parts, cladding slabs and other products in both medicine and construction, and other industries.
Proper use must take into account the property of the material to increase its volume by up to one percent when hardening. The powder has a certain shelf life and gradually loses its ability to harden over time.
Technology for manufacturing gypsum products - basic rules
When gypsum products are created, the technology must be strictly followed, from mixing to casting. If production rules are not followed, products may have various voids, cavities, or even fall apart. The quantity of ingredients is taken by volume.
So, one part of water no warmer than twenty-five degrees Celsius is poured into the container for preparing the solution. According to the rules, you cannot pour water into the powder. On the contrary, the material is poured into it in a volume of two to two and a half parts with constant vigorous stirring. You should get a solution with the thickness of homemade sour cream.
During the preparation process, the composition is constantly tapped to remove air bubbles from it. It should be noted that it is unlikely that anything can be sculpted from diluted dough. It hardens too quickly and is therefore used for casting. So the mixed mixture needs to be poured into a pre-prepared mold with walls coated with a release agent.
This composition is prepared from a saturated soap solution or heated Vaseline or other oil. Usually the solution begins to harden at the fourth minute, and after that it becomes completely solid. The process continues for about another day, it is by this time that the product will acquire the required strength.
Decorative plaster products - little secrets for good quality
Technology for manufacturing gypsum products provides the ability to accelerate or slow down the hardening of the composition. At the same time, acceleration is considered as a factor deteriorating the properties of the product and is rarely used. Slowing down, on the contrary, has a positive effect on the quality of the resulting casting and is quite widely practiced.
Hardening proceeds more slowly, and the final strength of the product increases if the mixing is carried out with solutions of borax, sugar, ethyl alcohol or, as mentioned above, bone glue. These sealers are prepared using water with a concentration of three to six percent, depending on the selected substance. The volumetric parts of the powder are the same.
By the way, if a completely hardened product (in water without a moderator) is boiled for twenty minutes in the already indicated borax solution, its strength increases. You can prepare a good mold from talc mixed with PVA or silicate glue. Instead, red brick ground into dust or fine porcelain chips are also suitable.
The post has been changed:
Making gypsum products as a profitable business idea
Often, when searching and analyzing ideas for your own business, a significant obstacle arises: initial investments require more financial resources than an entrepreneur can afford. The project may be successful by default, but without the availability of start-up capital sufficient to cover the needs, the venture will not take place. Any beginning businessman faces this fact. A business option that does not require large investments is the production of gypsum products - a pleasant, resource-intensive activity that can develop over time into a hobby.
Brief business analysis:
Costs of setting up a business:3.5 thousand dollars
Relevant for cities with the population:from 100 thousand people
Industry situation:average competition
Difficulty of organizing a business: 2/5
Payback: 3-6 months
Business relevance
Gypsum is a mineral sedimentary material mined in the form of stone. The mineral acquires a powder state after heat treatment at a temperature of 100-150˚C to remove moisture and subsequent grinding. The first traces of the use of gypsum were found in Turkey and date back to 9000. BC How building material in the form of additives in plaster mixtures When finishing walls and floors, gypsum was used in Ancient Egypt, starting in 5000. BC When creating decor, the material began to be used in Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome from the 3rd century BC

The mineral is distributed throughout the planet in places where ancient oceans existed. Depending on the size of the deposits and the density of the layers, gypsum is mined by open-pit mining. The largest producers are China, Iran, Spain. 1894 marked the emergence of a new area of application for gypsum - as a raw material in the manufacture plasterboard sheets, used for internal construction work currently. The mineral has become widespread as a binding material in construction, but differences in chemical and physical properties distinguish several types of gypsum:
- building– a binder material used in plastering work, the production of drywall, gypsum concrete, as an additive to other binder components.
- High strength- obtained from the usual one by adding anhydrite, which is why the resulting products have a reduced water requirement. Used in the manufacture of cast forms in construction, dentistry, and drilling.
- Polymeric– isoprene plastic material, used since the 1970s as an alternative to traditional plaster casting in traumatology, the composition does not contain traces of natural material.
- Cellacast– a synthetic substance, an improved polymer gypsum with the addition of polyurethane resin, which has high elasticity. Used for immobilization in traumatology.
- Molding(structural, sculptural, architectural) - natural gypsum obtained from building gypsum by sifting or grinding. The material of the smallest fraction is characterized by high strength and an almost perfect white color. It is used in the manufacture of molds in the porcelain, ceramic, and automotive industries.
- Acrylic(plasticcrete, organic glass) - a waterproof material, an artificial analogue of molding plaster. Convenient for making forms, decorations, sculptures, but the price of plasticcrete is high.
- Polyurethane– another alternative to natural substances when used in traumatology.
- White– building gypsum used in relief stucco molding, as well as eliminating unevenness during finishing.
- Fine grain(alabaster) is a natural material, crushed to a powder state, fired at a temperature of 180˚C. An environmentally friendly substance used for plastering and surface finishing.

The production of cast models involves the use of molding, acrylic plaster, alabaster (building plaster G-5). Sculptural and building materials are used more often due to their availability, prevalence, and low price. Acrylic material is more expensive than natural material and is used to create small-sized forms that are distinguished by detail.
Business organization
The commercial direction of manufacturing figured products is easy to organize and does not impose special requirements on skills, qualifications, or education. Such a business is available to a student, a pensioner or a group of people of different ages who are passionate about common interests and goals. At the initial stage of business planning, orientation is thought through. Without understanding the sales market, you can produce high-quality products, but difficulties arise during sales. The following are made from gypsum mixtures:
- elements of the internal and external design of buildings and premises - cornices, column capitals, ceiling rosettes;
- ceiling, wall panels, bas-reliefs;
- decorative sculptures, busts, statues;
- stucco decor - elements imitating natural stone, tile, brick;
- niche, fireplace stucco structures;
- other interior details - flowerpots, sconces, balusters;
- small designer products – refrigerator magnets, tabletop figurines.

Such a business does not require large investments; the amount of starting capital is limited to $2-3 thousand, although it can be tens of thousands of dollars. Production is organized both in an apartment, a garage, and in a large workshop. Due to the accessibility of the business, the stage of distribution of finished products is difficult.
The product is not a consumer product; the consumer audience is limited in size: most people have not bought and will not buy gypsum products. For these reasons, understanding product distribution channels comes first and is regulated by the business plan.
Workshop room
Despite the fact that it is possible to organize the production of gypsum products in a residential area, it is highly undesirable to do this. Gypsum, the raw material, does not pose a danger to workers or others, but casting molds are made of fiberglass, silicone, and polyurethane. Working with such materials is subject to safety requirements for the disposal of toxic emissions. For this reason, the mold making workshop is located at a distance from the residential area and is equipped with exhaust ventilation.

Requirements are also put forward for the drying room: the air temperature in the drying compartment is 25-32˚C. At the same time, overheating of the product, which can lead to cracking of the gypsum, is unacceptable. The room is equipped with a thermostatic fan heater and an air dehumidifier for recirculation and lowering the humidity inside the workshop.
This is where the requirements for the equipment of production areas end: warehouses in which raw materials and finished products are stored are located both in the production workshop and separately. At the same time, the requirements for temperature and moisture content for raw materials and resulting products are met.
Household, sanitary and hygienic compartments are an integral part of the areas involving production activities.
Raw material supply channels
The choice of base material depends on the focus of the business and the finished product. Due to the high cost of plasticcrete, it will not be possible to initially plan the production process for the use available materials, among which:
- building gypsum G-5 is produced in accordance with GOST 125-79, used for molding when creating decor and sculptures of increased dimensions. Raw materials are supplied in bags weighing 35 kg or big bags of 0.75-1.2 tons for large-scale production, and are sold in construction stores. One kilogram of the substance costs $0.07 or less.
- Molding raw materials used when casting sculptural elements in production with repeated use of molds. It differs from construction materials in the increased strength of finished products and smooth surface. High-strength molding gypsum of the GVVS-16, GVVS-19, GVVS-22 and GVVS-25 grades is supplied in 30 kg bags or big bags. The cost of a kilogram of sculpture plaster is in the range of $0.15-0.18 depending on the brand. This type of raw material is used in the manufacture of small, high-precision sculptures and decorations. The material is less often presented on the shelves of construction stores and is purchased at building materials stores or directly from the manufacturer.
- Plasticcrete– the most expensive type of raw material, therefore small-sized figures are made from acrylic. The raw materials are produced by chemical plants; plasticcrete is supplied in containers weighing 3-60 kg, while a kilogram of acrylic substance costs $5.0 and more. This is convenient for the manufacturer, but also the most expensive material, which, due to the cost factor, is not widely used. A life-size figurine 20cm high weighs about 400 grams. Accordingly, the cost of plasticcrete for the production of a unit of production, excluding other production items, is $2.0. In other words, the total cost of producing one figurine, including painting and packaging, is close to $2.8-3.0. It is useful to take such figures into account when planning a business and searching for distribution channels for finished products.

Taking into account these features, on initial stage It is advisable to abandon the use of acrylic. Construction and molding gypsum have almost no differences in organoleptic, physical properties, therefore the technology does not depend on the feedstock. The use of a particular substance is determined by the size of the finished product and the requirements for surface quality. The quality of the raw materials is confirmed by the manufacturer’s quality certificate.
Production technology
From a technological point of view, making gypsum castings is not difficult and is identical to children's stucco molding in a sandbox:
- A mold is made from a silicone or polyurethane mixture to cast the final product. A designer is hired to create an artistic layout of the form. In addition, ready-made forms are sold by specialized stores, but this method is unacceptable for medium or large businesses whose products differ from the options available on the market.
- A liquid mixture is pre-prepared: the powder is mixed with water in a 1:1 ratio or according to the instructions of the raw material manufacturer. The mixture is then thoroughly mixed, eliminating inhomogeneous formations, and filtered through a fine-mesh sieve. The stage is characterized by the speed of execution of the processes: the mixture hardening time is 8-15 minutes.
- The inner surface of the mold is lubricated with release paste or oil over the entire area. Such mixtures make it easy to separate the finished product from the walls of the mold and help avoid damage and defects on the surface. In handicraft production, special pastes are often replaced with vegetable oil.
- The gypsum mixture is fed into the prepared mold so that the internal space of the mold is completely filled. The mixture is poured in a thin stream to avoid the formation of air bubbles. The mold is maintained until the contained mixture has completely hardened.
- During hardening, excess is removed from the outside of the mold. Extraction of foreign elements is carried out using wooden or plastic tools with a smooth surface.
- Upon completion of hardening, the mold is turned over and the finished product is removed. The ease and speed of removing the product from the mold depends on the quality of the release mixture.
- Finally, the shaped product goes through the sanding stage using sandpaper of the desired grit or automatic sanding tools.

Molding sands initially come in white, pink, blue and other colors. Adding dyes at the stage of preparing gypsum mortar allows you to produce products of various shades. In addition, the finished shaped product is additionally painted and packaged if such stages are provided for by the requirements for the finished product.
Required Equipment
It is usual that the list of equipment for organizing a technological process is the main cost component. The production of gypsum products, contrary to this, does not require a long, costly stage for equipment of areas. The complex for equipping a business with mechanical or manual means includes the manufacture or acquisition of:
- metal and plastic tanks for preparing gypsum mixtures;
- work tables on which the solution is poured into prepared forms;
- a small number of power tools - drills or mixers for mixing gypsum mass, electric jigsaw, removing excess entries from the surface, a grinding machine to give the final product a smooth finish.
- floor scales, if the sale of goods involves selling by weight of finished products.

The production is additionally equipped with packaging machines, unloading and weighing equipment for deliveries in big bags, and multi-color printers for the production of refrigerator magnets. The final configuration of production areas with equipment depends on the nature of the products being manufactured and is regulated by the business plan.
Business registration
It is not required to register a small or medium business legal entity: it is enough to register a private enterprise with a fixed tax rate. The production of gypsum products is regulated by OKVED code 23.6 according to the classifier of types of economic activities. Before launching, permits from Rospotrebnadzor and fire inspection authorities are issued; licenses are not required for this type of activity.
In cooperation, collaboration with municipal enterprises, construction networks An additional motivating factor will be a quality certificate for finished products. Drawing up such a document takes a minimum of money and time - about $300 and ten days - but a certificate of quality for manufactured products will open additional doors for a businessman.
Marketing and sales channels
The owner has a lot of options for business orientation. The production of gypsum products is focused on retail trade in specialized stores, production of custom design elements, contractual activities for decorating parks, gardens, and private estates with sculptural compositions.
A good starting point would be the conclusion of contracts with municipal contractors for the production of life-size plaster figures placed in public recreation areas and the design of reconstructed buildings. Relations with municipal partners will provide the business with large orders, the acquisition of business reputation, while low profitability is sufficient for the existence and development of the business.

An effective means of distributing products is thematic racks placed by large hardware stores. Properly designed points of sale simultaneously advertise the company and its products. Such points are equipped with free samples of printed advertising, managers produce competent free consultations. A beautiful presentation website serves as an additional tool to attract the target audience.
Costs and return on business
To understand the financial indicators of product production, let’s consider the production of the simplest product - gypsum tiles. This product is used for interior decoration premises, tiles imitate all kinds of surfaces made of other materials - natural marble, granite, building bricks. The set of cost items consists of the following stages:
- rent, retrofitting of space: $500;
- purchase of equipment: $1200;
- design development, mold production: $300;
- purchase of raw materials: $500;
- organizational expenses: $300;
- salary: $700.
The starting capital to start tile production is $3,500. A block of 0.52 square meters of tiles or 18 pieces weighs 6.2 kg, with one unit weighing 0.344 kg. Physical dimensions of the tile: 31.5 x 9.0 x 1.8 cm. To cover a square meter of area, 35 tiles weighing 11.92 kg are needed. The retail price per square meter of gypsum tiles is $12 with wholesale prices of $8-9 per square meter. m.
The cost per unit of production from molding gypsum of the GVVS-25 brand of increased strength consists of the cost of raw materials, painting of the finished product - $2.15 + $1.85, respectively. Additional manufacturing costs include packaging of the finished product, which is $0.70 per square meter of material. The profitability of production without taking into account the tax base is thus:
$8.00 / (2.15+1.85+0.70) = 70%.
With a monthly volume of 800 square meters of tiles, the payback period for the business is: $3,500 / (800x$3.3 – $700 – $500) = about 2.5 months.
Simple, undemanding in terms of professional skills and initial funding, the business is suitable for those who have neither significant capital nor special education. The risks are also negligible: failure to manufacture a product for one niche entails a quick repurposing of production to a product of another segment. A business with high profitability, no risks - what is better for a beginner or an established entrepreneur.

 What documents are evidence that the apartment is a service apartment?
What documents are evidence that the apartment is a service apartment? Space donut hole
Space donut hole Types of discounts on Russian Railways tickets and rules for obtaining them Train tickets for students
Types of discounts on Russian Railways tickets and rules for obtaining them Train tickets for students Lecture on syndromic pathology
Lecture on syndromic pathology Organizational aspects of the activities of pharmacy organizations
Organizational aspects of the activities of pharmacy organizations Water pressure in the depths of the ocean Practice reports
Water pressure in the depths of the ocean Practice reports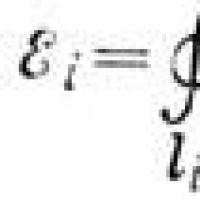 What is inductance, its definition and unit of measurement
What is inductance, its definition and unit of measurement